Net Zero Now What Is Net Zero

What Is Net Zero Global momentum for setting net zero targets is growing quickly, with key economies like china, the united states, india and the european union articulating such commitments. bhutan was the first country to set a net zero target in 2015. now over 90 countries, representing nearly 80% of global emissions, are covered by a net zero target. The transformation of the global economy needed to achieve net zero emissions by 2050 would be universal and significant, requiring $9.2 trillion in annual average spending on physical assets, $3.5 trillion more than today. to put it in comparable terms, that increase is equivalent to half of global corporate profits and one quarter of total.
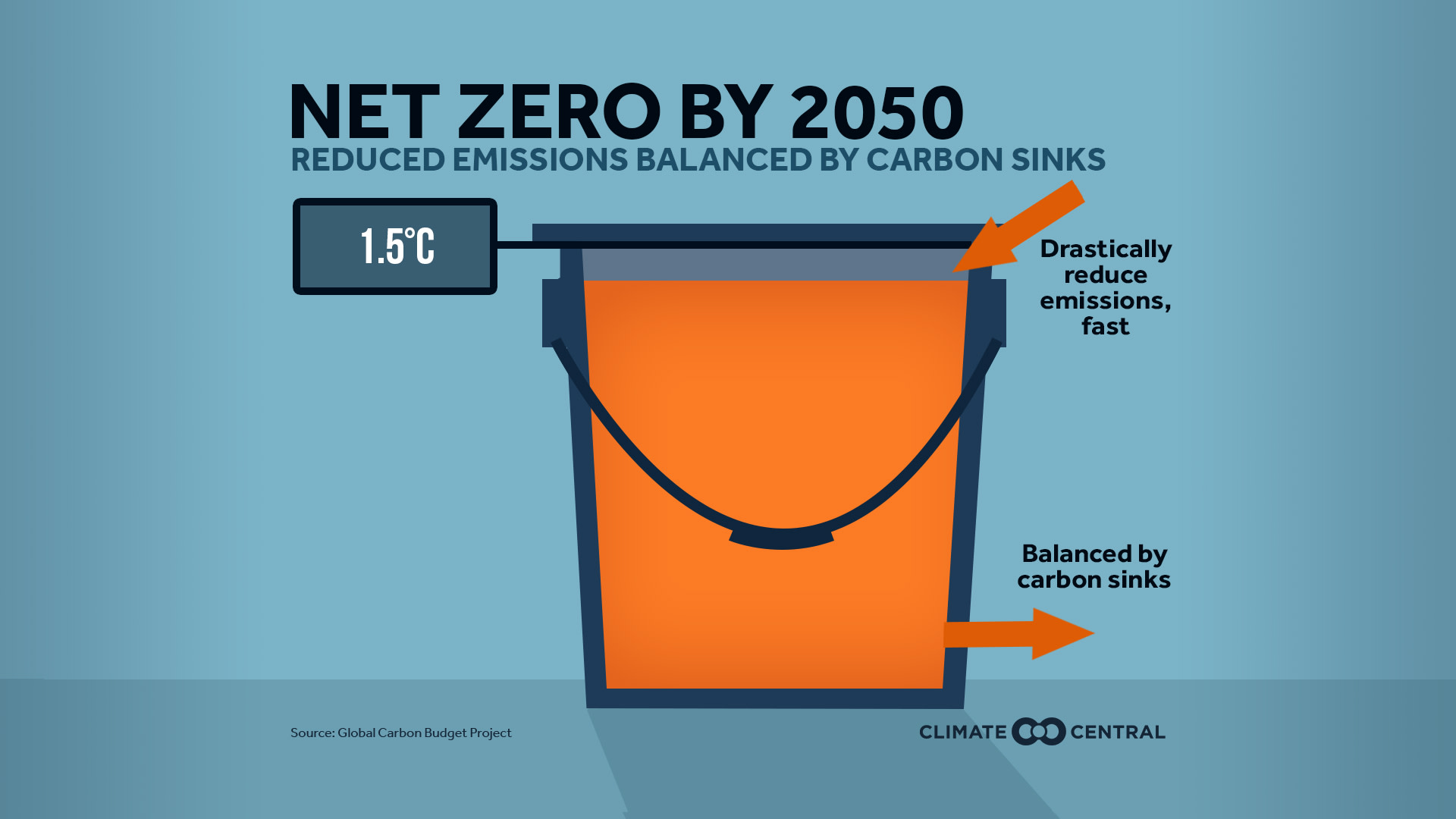
What Is Net Zero Climate Central Put simply, the term net zero applies to a situation where global greenhouse gas emissions from human activity are in balance with emissions reductions. at net zero, carbon dioxide emissions are still generated, but an equal amount of carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere as is released into it, resulting in zero increase in net. Today, the world is undertaking the net zero transition, an ambitious effort to reach net zero emissions of co 2 and reduce emissions of other ghgs. the goal of the transition is outlined in the paris agreement adopted at the united nations in 2015: to limit global warming above preindustrial levels to well below 2.0°c and ideally to 1.5°c. Solar becomes the largest source, accounting for one fifth of energy supplies. solar pv capacity increases 20 fold between now and 2050, and wind power 11 fold. net zero means a huge decline in the use of fossil fuels. they fall from almost four fifths of total energy supply today to slightly over one fifth by 2050. The concept of net zero has evolved over the past few decades, but gained significant momentum in recent years due to increasing concerns about climate change. 1970s early 2000s: early discussions. the idea of balancing emissions to achieve a net zero effect has its roots in the early discussions on climate change and sustainability. the term.

Net Zero Now Cambridge Carbon Footprint Solar becomes the largest source, accounting for one fifth of energy supplies. solar pv capacity increases 20 fold between now and 2050, and wind power 11 fold. net zero means a huge decline in the use of fossil fuels. they fall from almost four fifths of total energy supply today to slightly over one fifth by 2050. The concept of net zero has evolved over the past few decades, but gained significant momentum in recent years due to increasing concerns about climate change. 1970s early 2000s: early discussions. the idea of balancing emissions to achieve a net zero effect has its roots in the early discussions on climate change and sustainability. the term. Indeed, net zero demands greater focus on eliminating difficult emissions sources than has so far been the case. the ‘net’ in net zero is essential, but the need for social and environmental. What does 'net zero' mean? net zero means no longer adding to the total amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (co2) and methane. co2 is released.

Comments are closed.