Nervous Tissue Neuron And Neuroglia
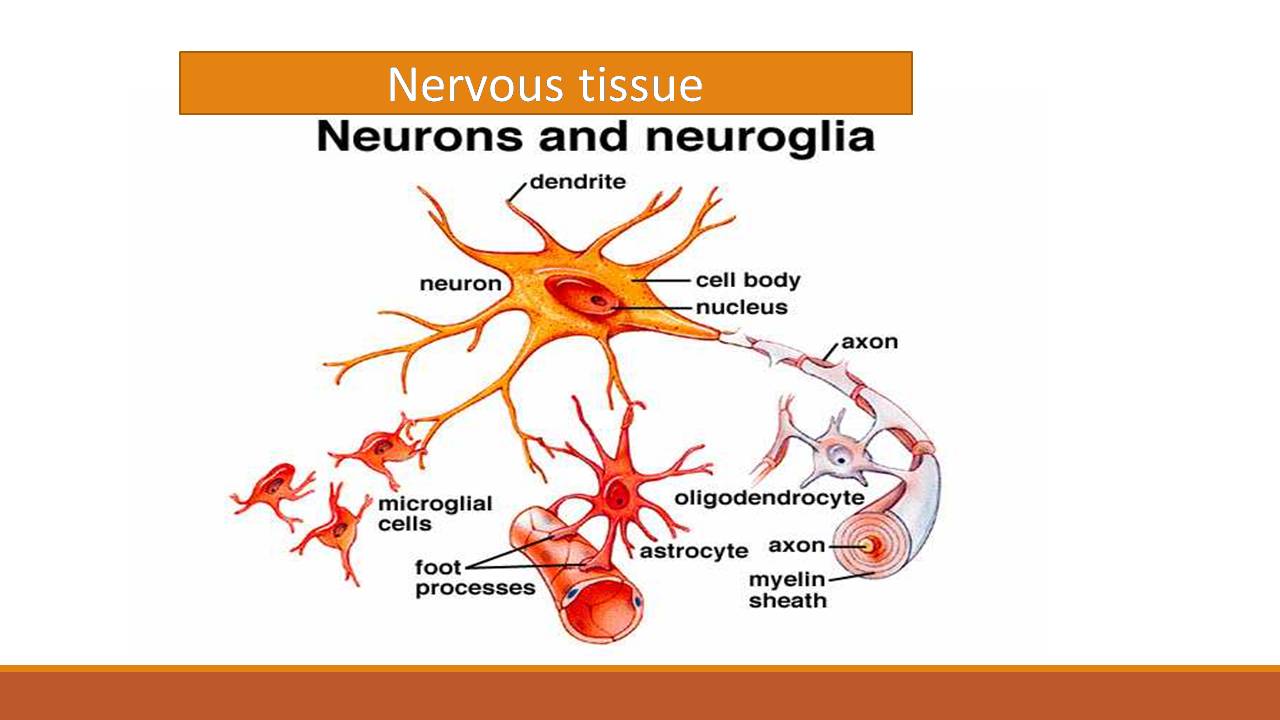
Nervous Tissue Neuron And Neuroglia Online Biology Notes Tissue – an organized group of cells that carries out a certain function. nervous system – the organ system responsible for controlling and coordinating body movements and functions. action potential – a sudden rise and fall in the electrical membrane potential of a neuron that leads to a signal being transmitted to other neurons or the. Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. neurons are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. they are electrically active and release chemical signals to communicate between each other and with target cells. glial cells, or glia or neuroglia, are much smaller than.

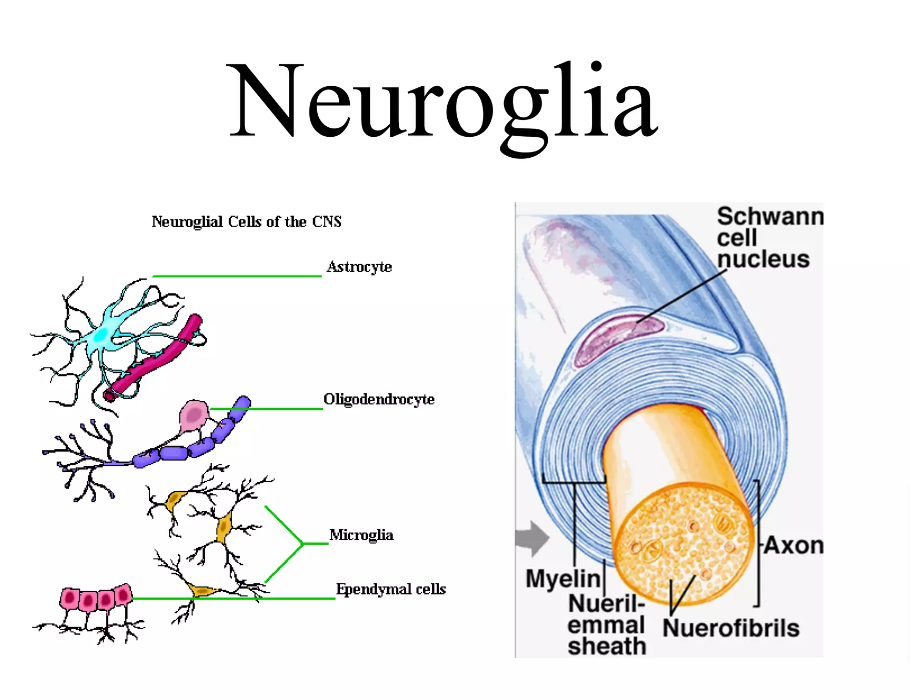
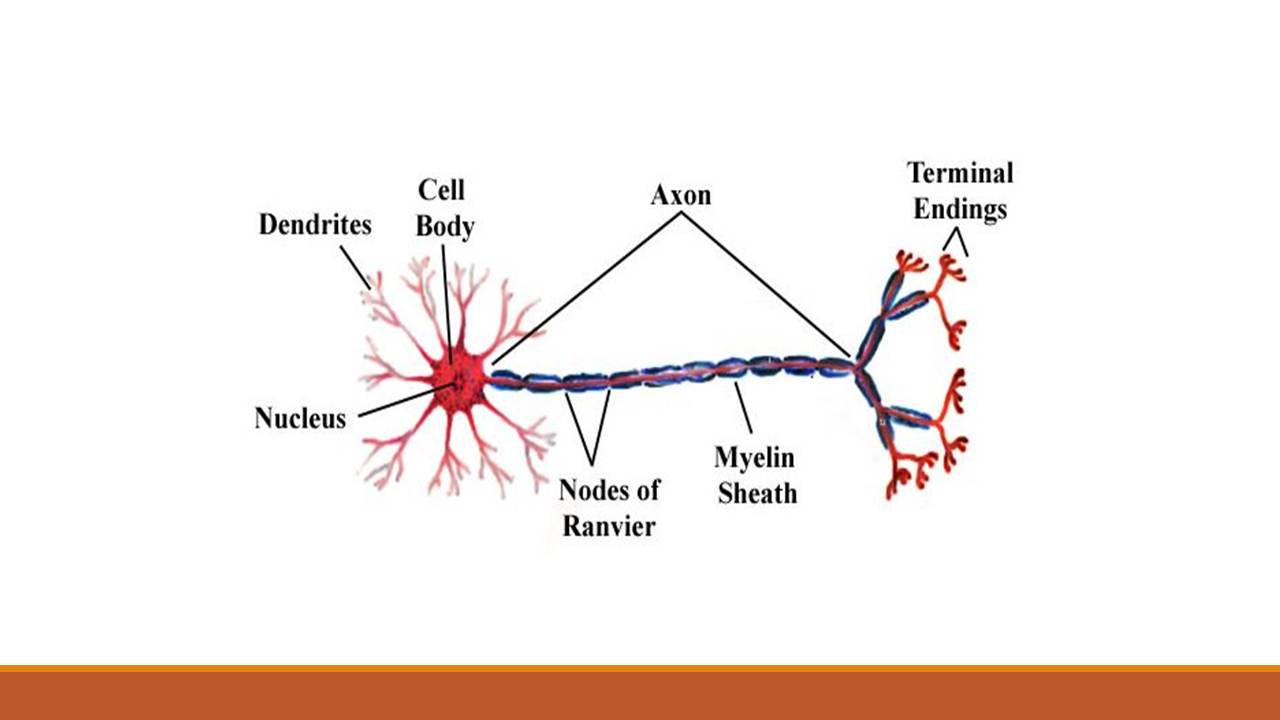
Vector Illustration Nervous Tissue Neuron Neuroglia Stock Vector Figure 8.3.4 the axon in this diagram is part of a motor neuron. it transmits nerve impulses from the central nervous system to a skeletal muscle, causing it to contract. neuroglia. in addition to neurons, nervous tissues also consist of neuroglia, also called glial cells. the root of the word glial comes from a greek word meaning “glue. Nervous tissue is characterized as being excitable and capable of sending and receiving electrochemical signals that provide the body with information. two main classes of cells make up nervous tissue: the neuron and neuroglia (figure 4.5.1 the neuron). neurons propagate information via electrochemical impulses, called action potentials, which. Synonyms: nerve cells. nerve cells (neurons) form the structural and functional units of the central and peripheral nervous systems. their function is to receive stimuli and transmit nerve impulses to the target organ. nerve cells consist of a cell body (soma), dendrites, an axon and a specialized cytoskeleton. However, recent investigations suggest that in some regions of the brains of humans and other primates, that ratio is closer to 1:1. however, the ratio of glia to neuron from region to region varies considerably. the central nervous system contains four main types of glial cells: astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, and oligodendrocytes.

Neuron And Neuroglia Structure Of A Neuron And Glial Cells Stock Synonyms: nerve cells. nerve cells (neurons) form the structural and functional units of the central and peripheral nervous systems. their function is to receive stimuli and transmit nerve impulses to the target organ. nerve cells consist of a cell body (soma), dendrites, an axon and a specialized cytoskeleton. However, recent investigations suggest that in some regions of the brains of humans and other primates, that ratio is closer to 1:1. however, the ratio of glia to neuron from region to region varies considerably. the central nervous system contains four main types of glial cells: astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, and oligodendrocytes. Neurons, or nerve cell, are the main structural and functional units of the nervous system. every neuron consists of a body (soma) and a number of processes (neurites). the nerve cell body contains the cellular organelles and is where neural impulses (action potentials) are generated. the processes stem from the body, they connect neurons with. Astrocyte: a neuroglial cell, in the shape of a star, in the brain. neurogila or glial cells, are non neuronal cells that maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons in the central (cns) and peripheral nervous systems (pns). it was long believed that neuroglia did not play any role in neuro transmission.
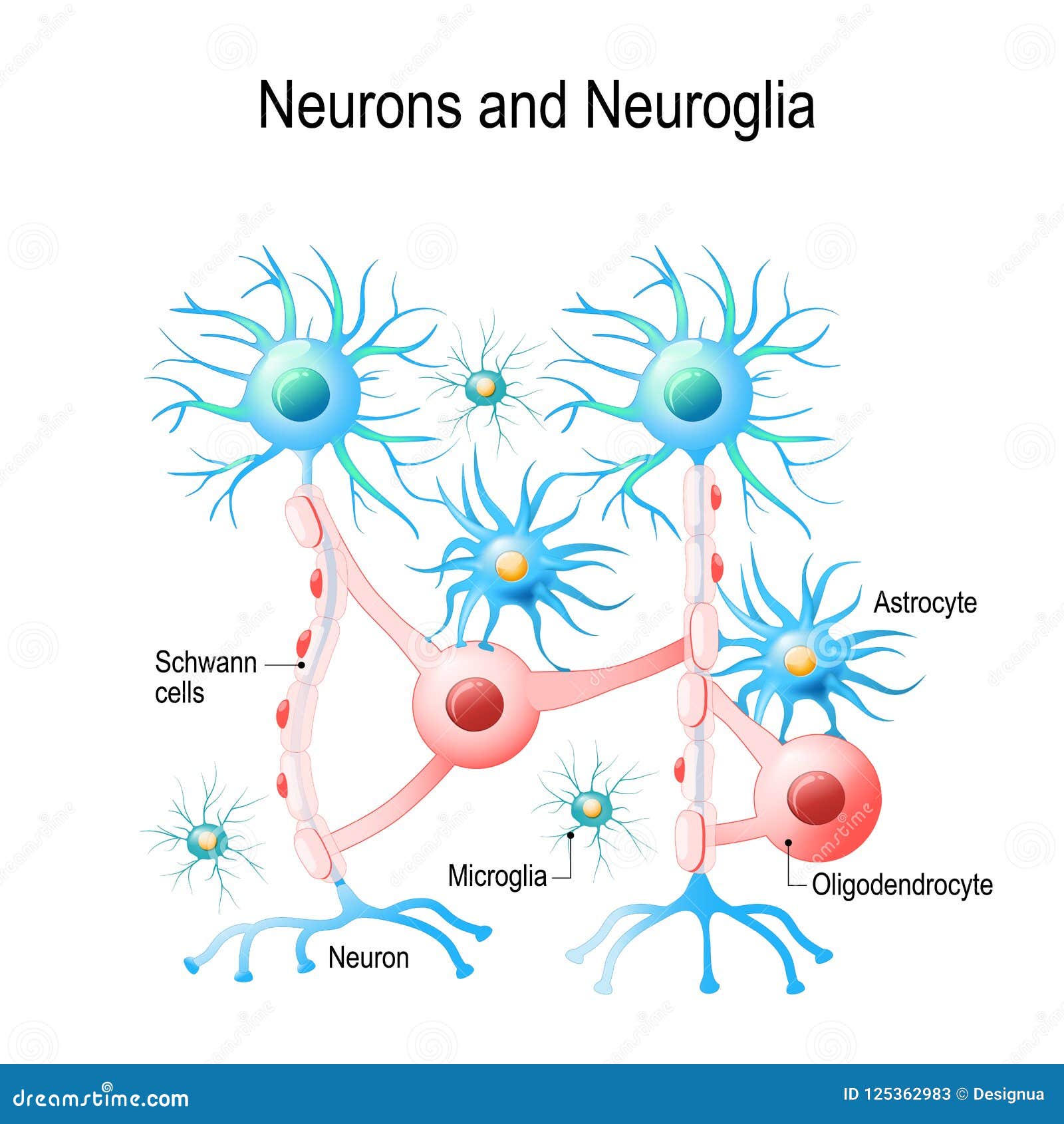
Neurons And Neuroglial Cells Stock Vector Illustration Of Glia Neurons, or nerve cell, are the main structural and functional units of the nervous system. every neuron consists of a body (soma) and a number of processes (neurites). the nerve cell body contains the cellular organelles and is where neural impulses (action potentials) are generated. the processes stem from the body, they connect neurons with. Astrocyte: a neuroglial cell, in the shape of a star, in the brain. neurogila or glial cells, are non neuronal cells that maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons in the central (cns) and peripheral nervous systems (pns). it was long believed that neuroglia did not play any role in neuro transmission.
Nervous Tissue Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
Nervous Tissue Neuron And Neuroglia Online Biology Notes

Comments are closed.