Nervous Tissue Labeled Diagram
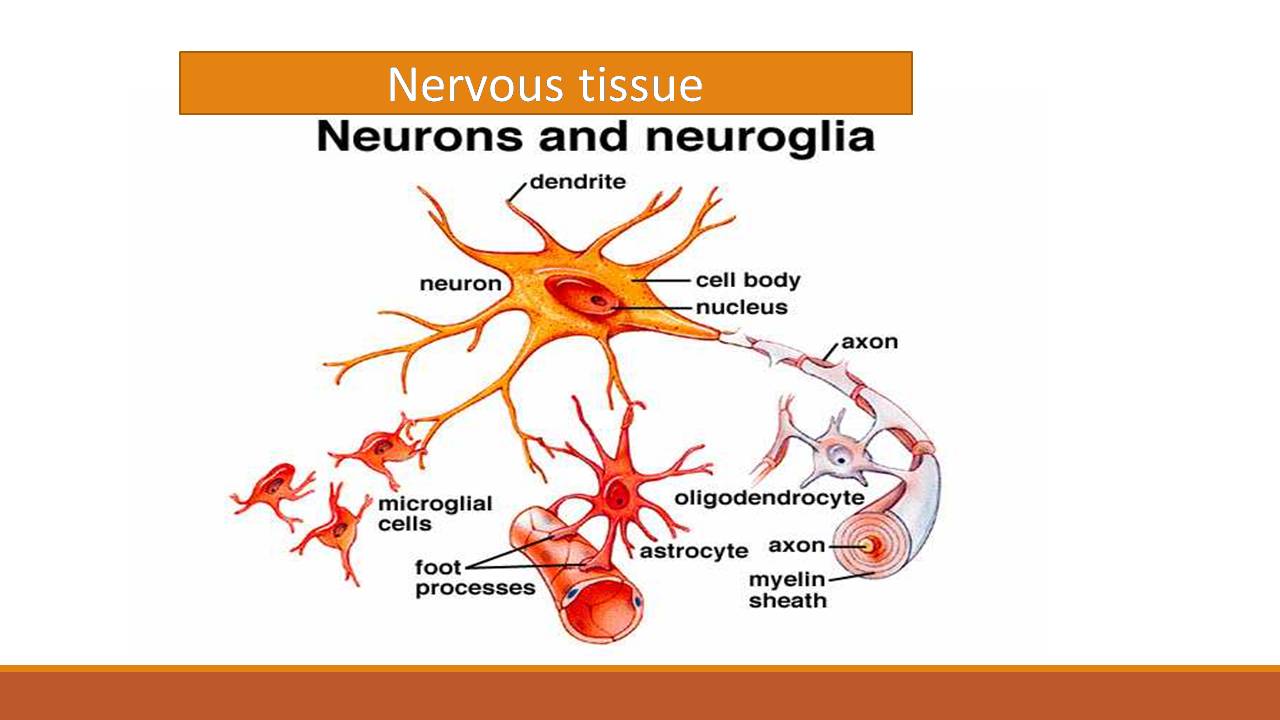
Nervous Tissue Characteristics Structure Function Nervous system breakdown (diagram) so nervous tissue, comprised of neurons and neuroglia, forms our nervous organs (e.g. the brain, nerves). these organs unite according to their common function, forming the evolutionary perfection that is our nervous system. the nervous system (ns) is structurally broken down into two divisions;. Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. neurons are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. they are electrically active and release chemical signals to communicate between each other and with target cells. glial cells, or glia or neuroglia, are much smaller than.
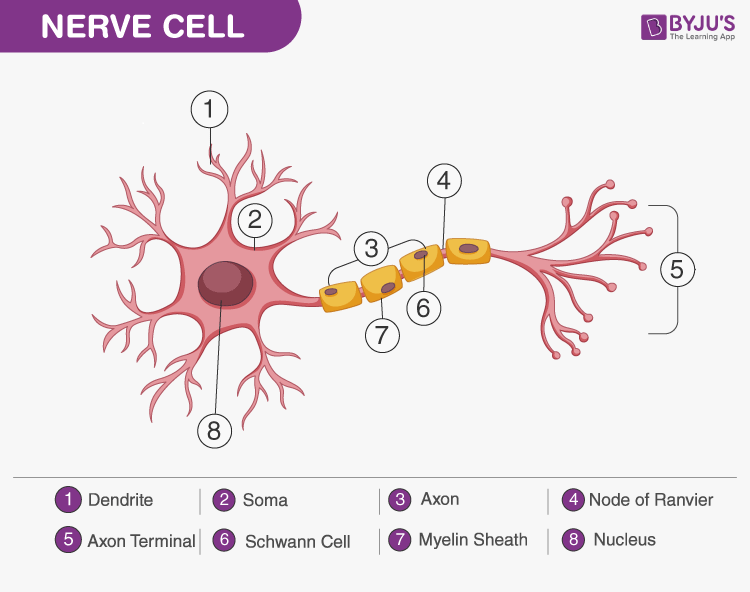
Labeled Neuron Nervous Tissue Cells The nervous system produces a response on the basis of the stimuli perceived by sensory structures. an obvious response would be the movement of muscles, such as withdrawing a hand from a hot stove, but there are broader uses of the term. the nervous system can cause the contraction of all three types of muscle tissue. Synonyms: nerve cells. nerve cells (neurons) form the structural and functional units of the central and peripheral nervous systems. their function is to receive stimuli and transmit nerve impulses to the target organ. nerve cells consist of a cell body (soma), dendrites, an axon and a specialized cytoskeleton. Click to view larger image. the nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, sensory organs, and all of the nerves that connect these organs with the rest of the body. together, these organs are responsible for the control of the body and communication among its parts. the brain and spinal cord form the control center known as the central. Nervous or the nerve tissue is the main tissue of our nervous system. it monitors and regulates the functions of the body. nervous tissue consists of two cells: nerve cells or neurons and glial cells, which helps transmit nerve impulses and also provides nutrients to neurons. brain, spinal cord, and nerves are composed of nervous tissue, they.
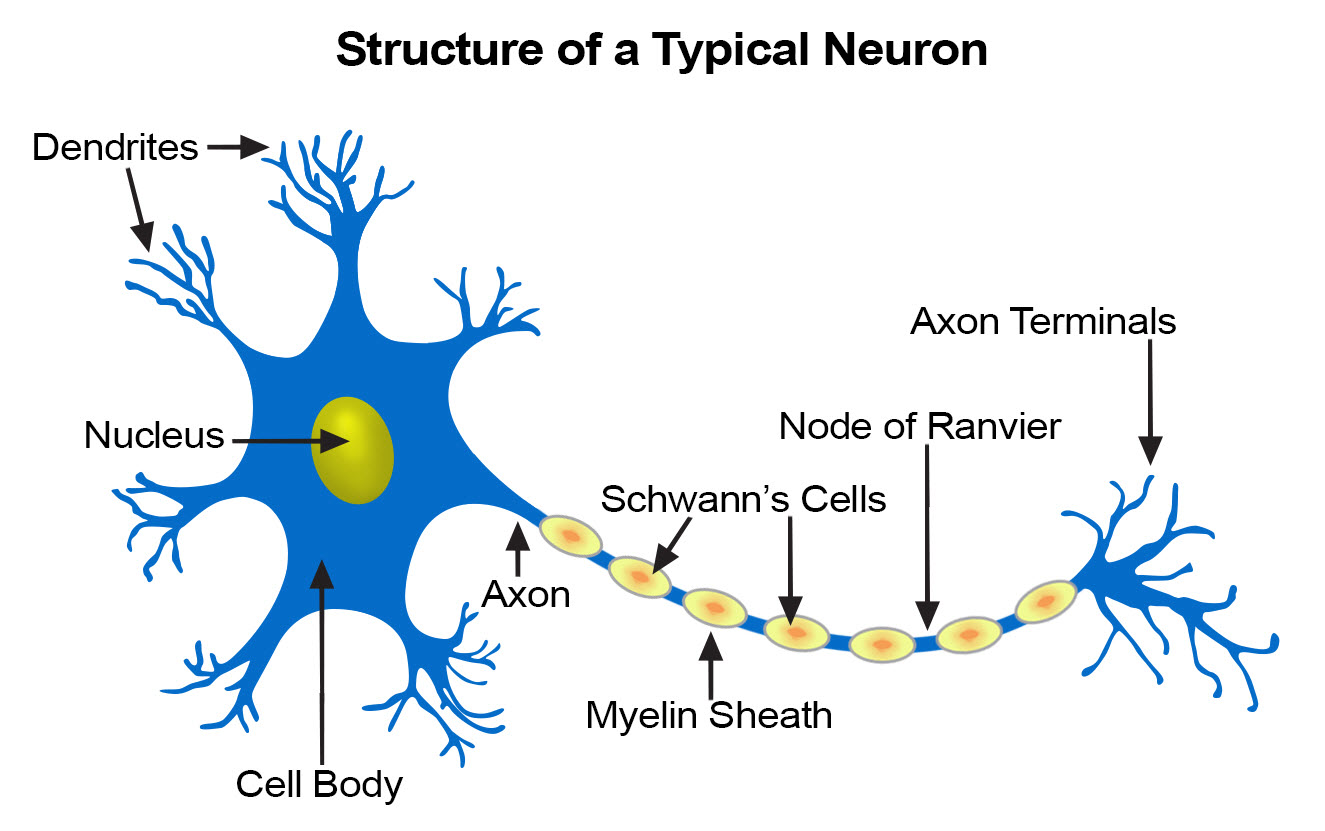
Nerve Tissue Seer Training Click to view larger image. the nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, sensory organs, and all of the nerves that connect these organs with the rest of the body. together, these organs are responsible for the control of the body and communication among its parts. the brain and spinal cord form the control center known as the central. Nervous or the nerve tissue is the main tissue of our nervous system. it monitors and regulates the functions of the body. nervous tissue consists of two cells: nerve cells or neurons and glial cells, which helps transmit nerve impulses and also provides nutrients to neurons. brain, spinal cord, and nerves are composed of nervous tissue, they. Figure 11.3.1 11.3. 1: nervous tissue. a small chunk of nervous tissue of spinal cord was spread on a microscope slide to show neurons and glial cells. glial cells are smaller and in larger quantities than neurons. the neuron shown is large and has multiple processes coming out of the soma. Nervous tissue is characterized as being excitable and capable of sending and receiving electrochemical signals that provide the body with information. two main classes of cells make up nervous tissue: the neuron and neuroglia (figure 4.5.1 the neuron). neurons propagate information via electrochemical impulses, called action potentials, which.
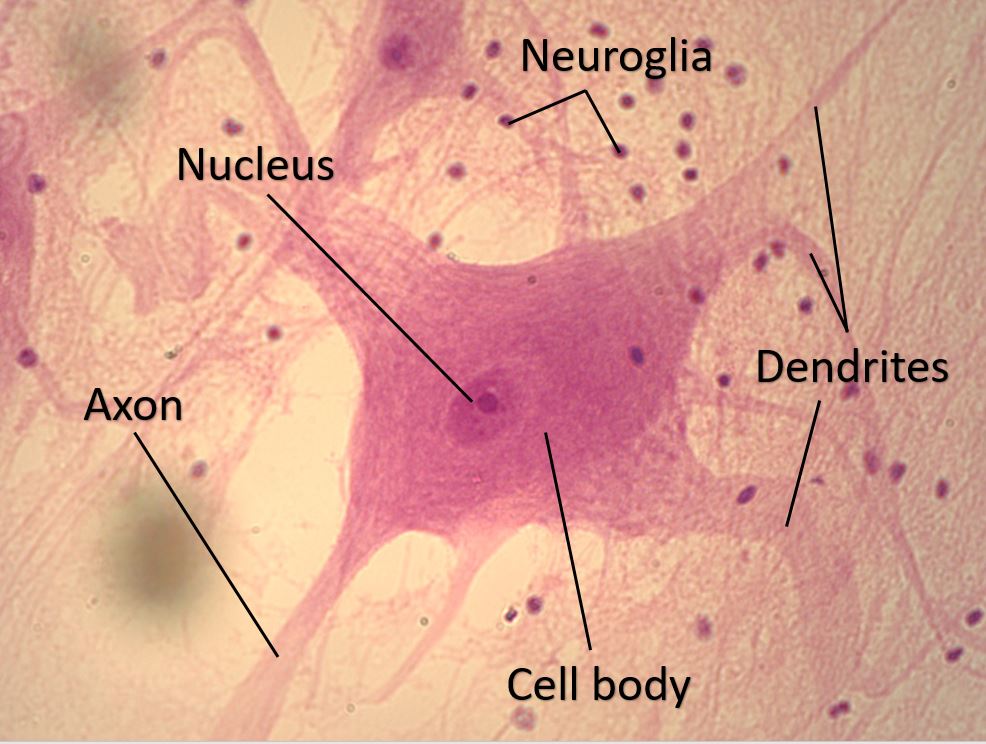
Nervous Tissue Scientist Cindy Figure 11.3.1 11.3. 1: nervous tissue. a small chunk of nervous tissue of spinal cord was spread on a microscope slide to show neurons and glial cells. glial cells are smaller and in larger quantities than neurons. the neuron shown is large and has multiple processes coming out of the soma. Nervous tissue is characterized as being excitable and capable of sending and receiving electrochemical signals that provide the body with information. two main classes of cells make up nervous tissue: the neuron and neuroglia (figure 4.5.1 the neuron). neurons propagate information via electrochemical impulses, called action potentials, which.

Comments are closed.