Neer 3 Part Proximal Humerus Fracture

Neer Proximal Humerus Fracture Classification Rayorthos These fractures account for approximately 5% of proximal humeral fractures 6. four part fracture. fracture lines involves all 4 parts. three parts are displaced (i.e. >1 cm or >45°) with respect to the 4 th. these fractures are uncommon (<1% of proximal humeral fractures) 6. Proximal humerus fractures. proximal humerus fractures are common fractures often seen in older patients with osteoporotic bone following a ground level fall on an outstretched arm. diagnosis is made with orthogonal radiographs of the shoulder.
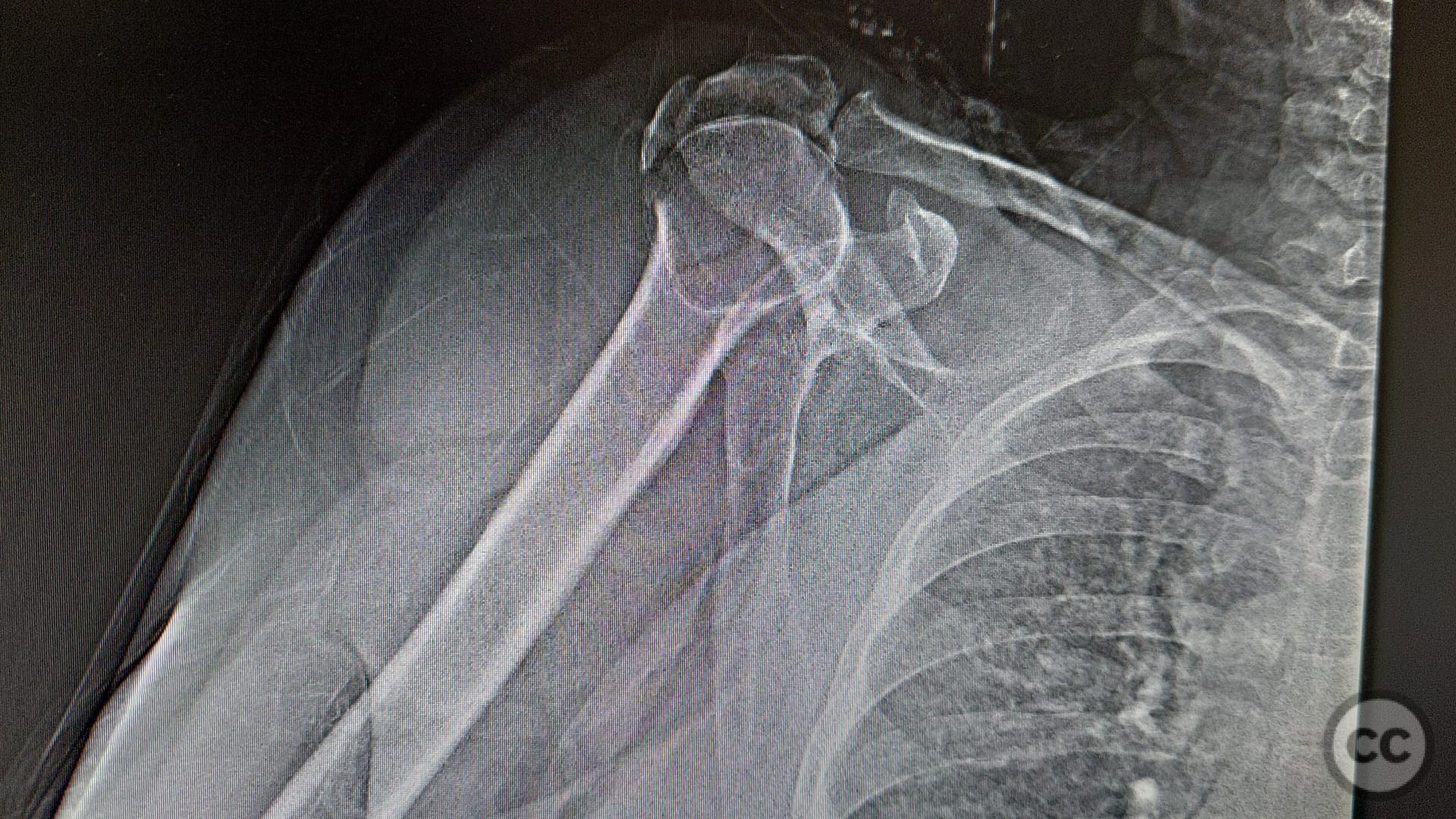
Neer 3 Part Proximal Humerus Fracture The neer system divides the proximal humerus into four parts and considers not the fracture line, but the displacement as being significant in terms of classification. the four parts are: humeral head. greater tubercle. lesser tubercle. Neer classification of humeral head fractures. 09. upper extremity. reference: kilcoyne, r. f., et al. (1990). “the neer classification of displaced proximal humeral fractures: spectrum of findings on plain radiographs and ct scans.”. ajr am j roentgenol 154 (5): 1029 1033. The neer fracture classification system provides a useful framework for clinical assessment of and research for proximal humerus fractures. this classification system has moderate interobserver reliability, and correlates to a large degree (albeit not perfectly) with complications and functional results. The neer four segment classification system for proximal humerus fractures is shown. this diagram includes the valgus impacted four part fracture (a) and the classic displaced four part fracture (b). (reprinted with permission from neer cs 2nd. displaced proximal humeral fractures. i. classification and evaluation.
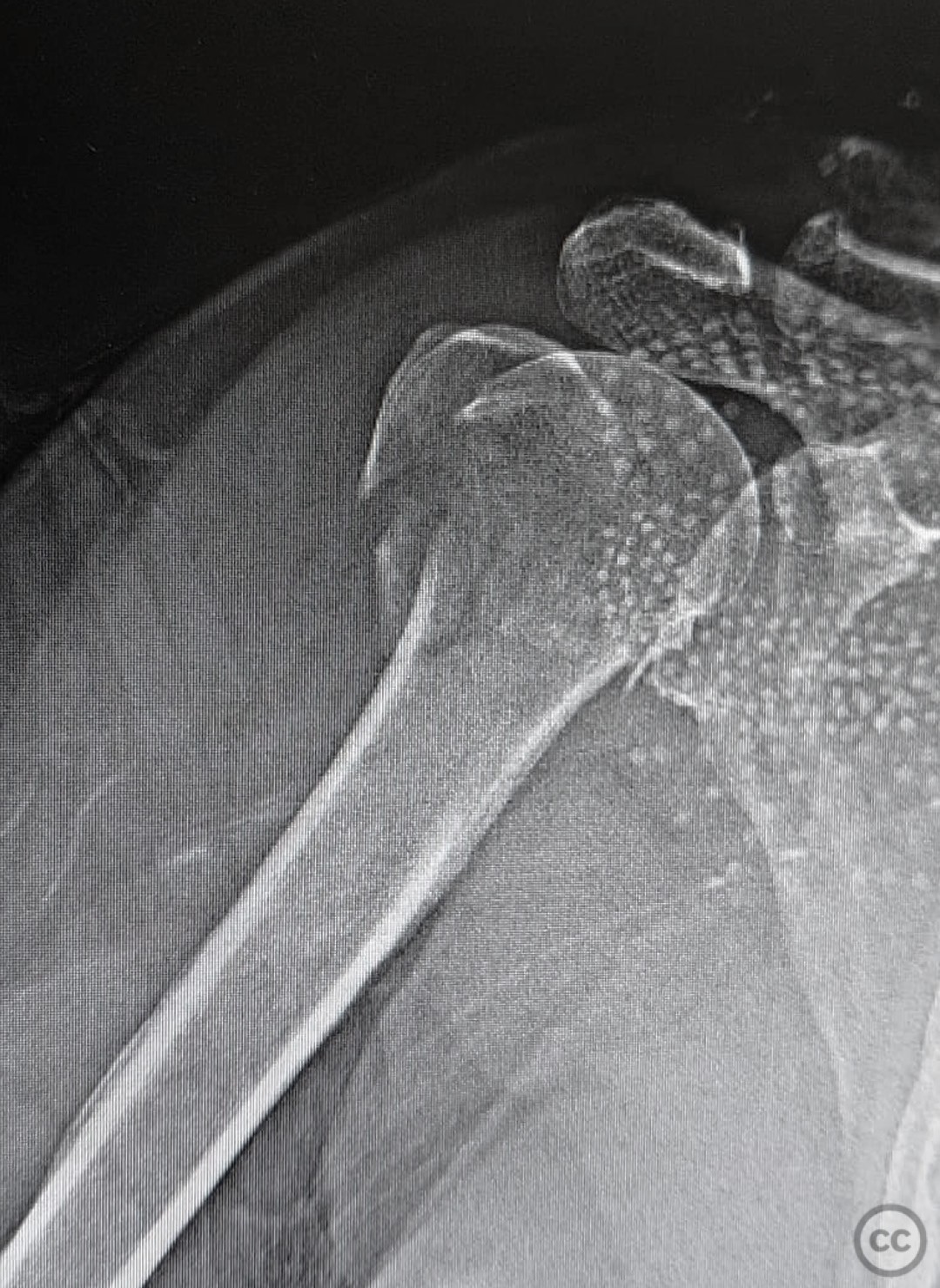
Neer 3 Part Proximal Humerus Fracture The neer fracture classification system provides a useful framework for clinical assessment of and research for proximal humerus fractures. this classification system has moderate interobserver reliability, and correlates to a large degree (albeit not perfectly) with complications and functional results. The neer four segment classification system for proximal humerus fractures is shown. this diagram includes the valgus impacted four part fracture (a) and the classic displaced four part fracture (b). (reprinted with permission from neer cs 2nd. displaced proximal humeral fractures. i. classification and evaluation. Vast majority. high energy trauma in younger population. 3 main loading modes: compressive – humeral head impacts at glenoid. bending – angular forces at surgical neck. tension – rotator cuff pulling on greater and less tuberosities. fall on outstretched hand. valgus impacted proximal humerus fracture. Indications: neer 2 , 3 and 4 part fractures with rotation greater than 45 degrees or displacement greater than 5mm (or 1 cm, depending on source), head splitting fractures in younger patients (part of humeral head dislocates and the unfractured part remains attached to the shaft).
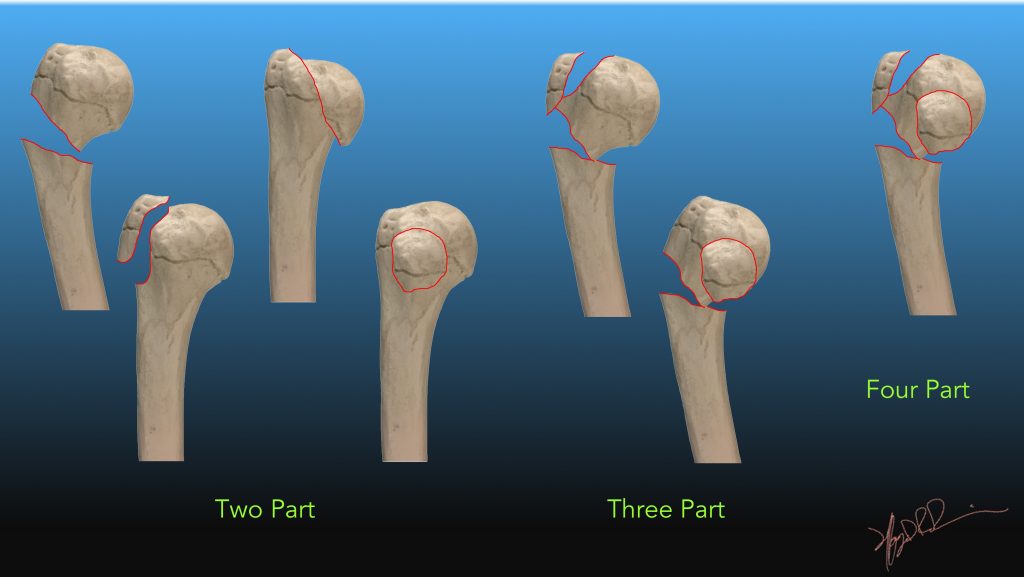
Neer Classification Of Humeral Head Fractures Uw Emergency Radiology Vast majority. high energy trauma in younger population. 3 main loading modes: compressive – humeral head impacts at glenoid. bending – angular forces at surgical neck. tension – rotator cuff pulling on greater and less tuberosities. fall on outstretched hand. valgus impacted proximal humerus fracture. Indications: neer 2 , 3 and 4 part fractures with rotation greater than 45 degrees or displacement greater than 5mm (or 1 cm, depending on source), head splitting fractures in younger patients (part of humeral head dislocates and the unfractured part remains attached to the shaft).

Comments are closed.