Museum Of Science And History Subscribe Discovery Of The Dna Of The

Discovery Of Dna Double Helix 65th Anniversary Of Crick And Watson S The 1953 discovery of the double helix molecular structure of dna, the long chain like molecule deoxyribonucleic acid, is a key moment in modern history. dna, the molecule in our cells that carries information in the form of genes, was revealed to be a twisting pair of strands that has been unravelling to replicate itself since the dawn of life. April 26, 2023 at 12:59 pm. rosalind franklin’s role in the discovery of the structure of dna may have been different than previously believed. franklin wasn’t the victim of data theft at the.
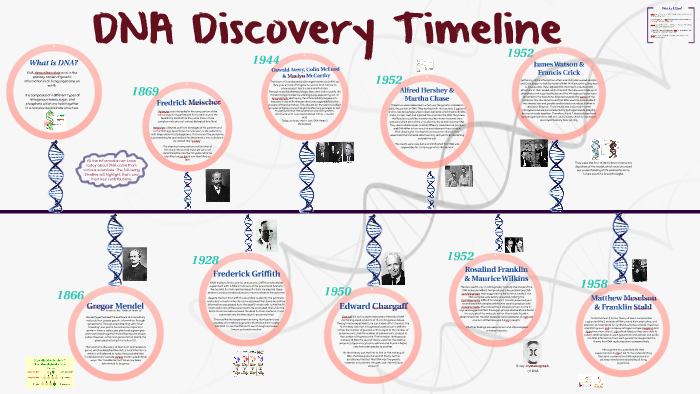
Timeline Of The Discovery Of Dna By Archana Rajah On Prezi This day in history: 02 28 1953 dna structure discovered an unflattering portrayal in watson's account franklin, who died of ovarian cancer in 1958 at the age of 37, was ineligible to receive. Rosalind franklin (born july 25, 1920, london, england—died april 16, 1958, london) was a british scientist best known for her contributions to the discovery of the molecular structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna), a constituent of chromosomes that serves to encode genetic information. franklin also contributed new insight on the structure. The new tree of life. for a century after charles darwin published the origin of species in 1859, scientists could compare only physical features to describe evolutionary lineages. the picture that resulted was often illustrated as a tree of life. in 1953 james watson and francis crick discovered the structure of dna – the molecular basis of. These four scientists—crick, franklin, watson, and wilkins—codiscovered the double helix structure of dna, which formed the basis for modern biotechnology. at king’s college london, rosalind franklin obtained images of dna using x ray crystallography, an idea first broached by maurice wilkins. franklin’s images allowed james watson and.

Share The new tree of life. for a century after charles darwin published the origin of species in 1859, scientists could compare only physical features to describe evolutionary lineages. the picture that resulted was often illustrated as a tree of life. in 1953 james watson and francis crick discovered the structure of dna – the molecular basis of. These four scientists—crick, franklin, watson, and wilkins—codiscovered the double helix structure of dna, which formed the basis for modern biotechnology. at king’s college london, rosalind franklin obtained images of dna using x ray crystallography, an idea first broached by maurice wilkins. franklin’s images allowed james watson and. The discovery in 1953 of the double helix, the twisted ladder structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna), by james watson and francis crick marked a milestone in the history of science and gave rise to modern molecular biology, which is largely concerned with understanding how genes control the chemical processes within cells. 70th anniversary of dna double helix breakthrough. francis crick’s announcement to patrons of the eagle pub that he and james watson had "discovered the secret of life", the evening after their determination of the structure of the dna molecule, has become a part of cambridge folklore. their breakthrough – pinpointing how our genetic code.
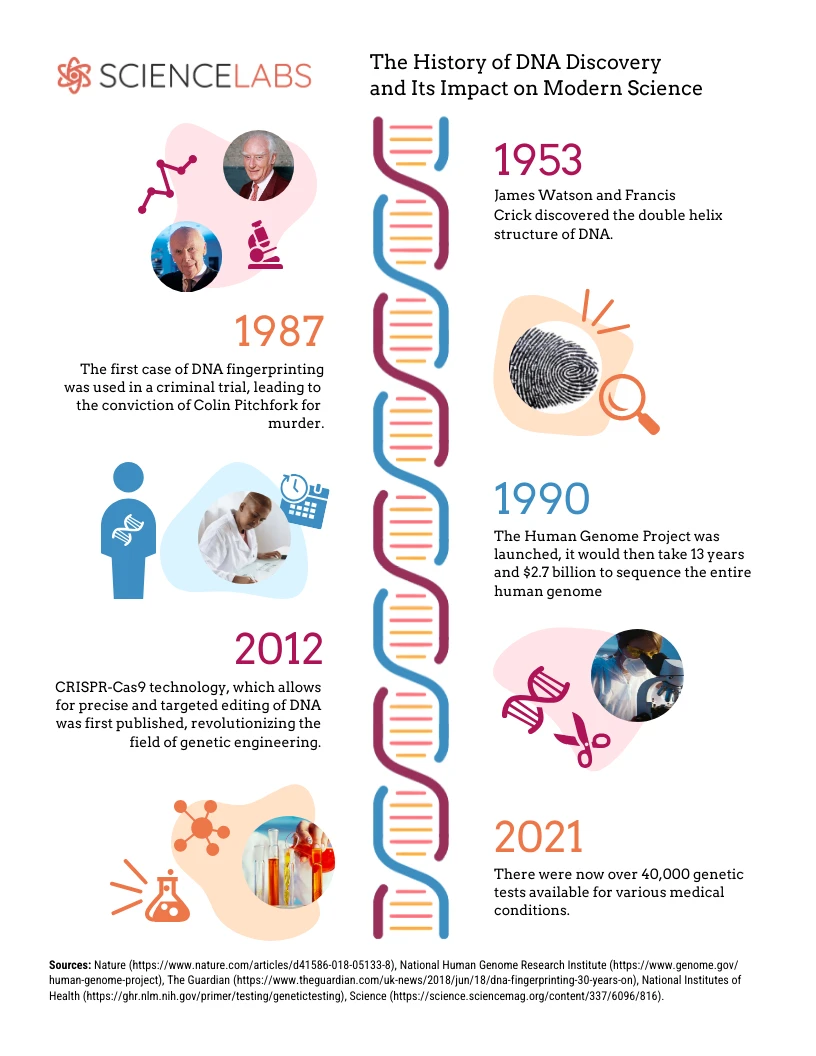
History Of Dna Discovery Timeline Infographic Template Venngage The discovery in 1953 of the double helix, the twisted ladder structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (dna), by james watson and francis crick marked a milestone in the history of science and gave rise to modern molecular biology, which is largely concerned with understanding how genes control the chemical processes within cells. 70th anniversary of dna double helix breakthrough. francis crick’s announcement to patrons of the eagle pub that he and james watson had "discovered the secret of life", the evening after their determination of the structure of the dna molecule, has become a part of cambridge folklore. their breakthrough – pinpointing how our genetic code.

Discovery Of Dna Structure

Comments are closed.