Musculoskeletal System Study Guide Musculoskeletal System Skeletal
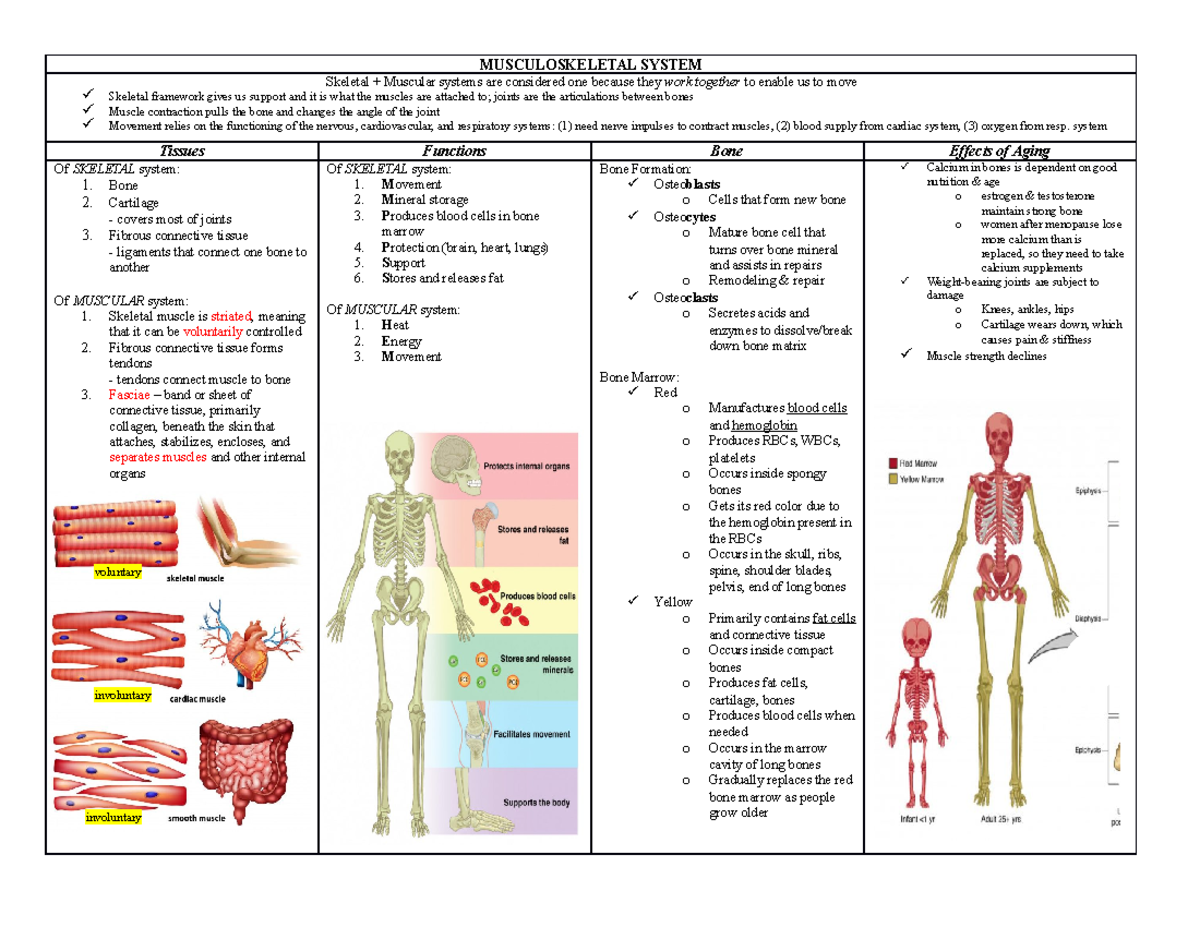
Musculoskeletal System Study Guide Musculoskeletal System Skeletal The musculoskeletal system (locomotor system) is a human body system that provides our body with movement, stability, shape, and support. it is subdivided into two broad systems: muscular system, which includes all types of muscles in the body. skeletal muscles, in particular, are the ones that act on the body joints to produce movements. Science understanding – musculoskeletal system. structure and function of bones and joints. bones and joints in the skeletal system facilitate the support and movement of the body. location and structure of joints in the skeleton allow for a range of movement. structure and development of long bones provide for strength, growth, and repair.

Musculoskeletal System Study Guide Anatomy Practice Guide Etsy Skeletal muscle is mainly involved in moving bones and the type of muscle typically referred to in anatomy when referring to the musculoskeletal system. muscles are attached to bones via tendons or aponeuroses and receive a rich nerve supply to allow precise movement control. Movement relies on the functioning of the nervous, cardiovascular, and respiratory systems: (1) need nerve impulses to contract muscles, (2) blood supply from cardiac system, (3) oxygen from resp. system tissues functions bone effects of aging of skeletal system: 1. bone 2. cartilage covers most of joints 3. fibrous connective tissue. The adult skeleton is composed of 206 bones and there are two basic types of osseous, or bone, tissue: compact bone and spongy bone, and are classified into four groups according to shape: long, short, flat, and irregular. compact bone. compact bone is dense and looks smooth and homogeneous. spongy bone. Explore. our mission is to provide a free, world class education to anyone, anywhere. khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization. donate or volunteer today! about. news. impact. our team. our interns.
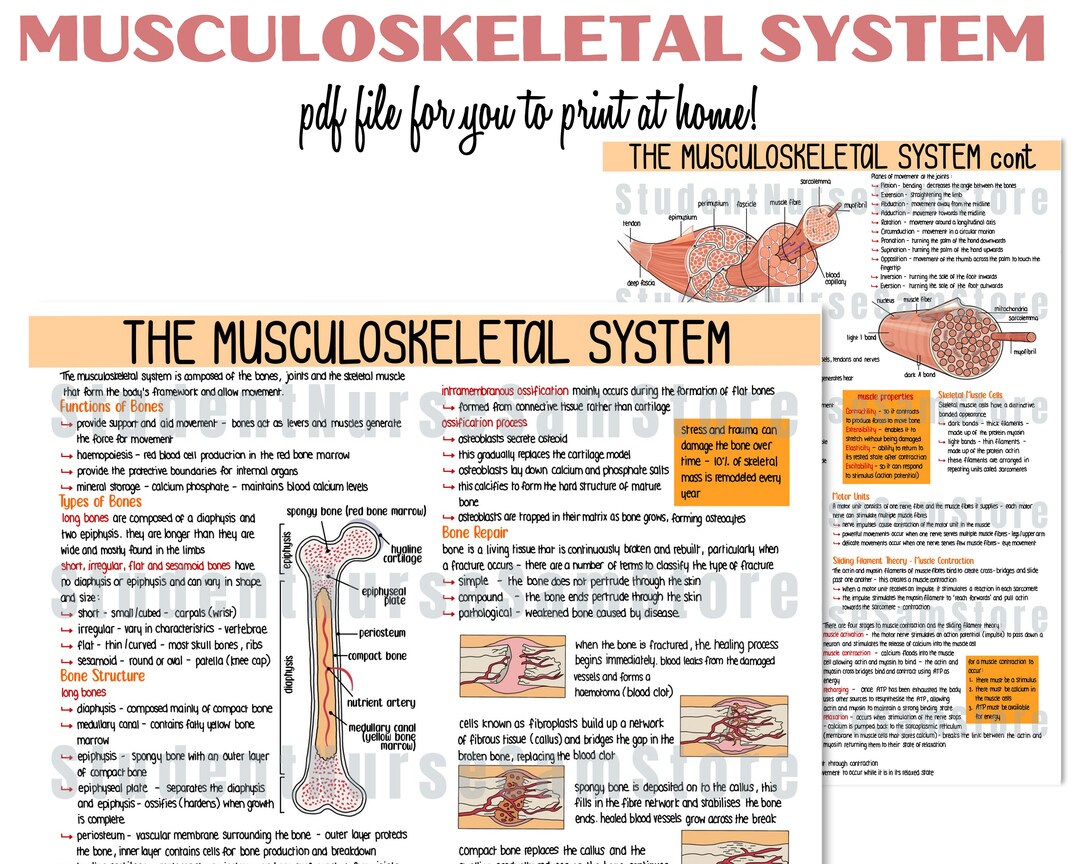
Digital File The Musculoskeletal System Revision Notes Anatomy The adult skeleton is composed of 206 bones and there are two basic types of osseous, or bone, tissue: compact bone and spongy bone, and are classified into four groups according to shape: long, short, flat, and irregular. compact bone. compact bone is dense and looks smooth and homogeneous. spongy bone. Explore. our mission is to provide a free, world class education to anyone, anywhere. khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization. donate or volunteer today! about. news. impact. our team. our interns. Learn anatomy faster andremember everything you learn. a free website study guide review that uses interactive animations to help you learn online about anatomy and physiology, human anatomy, and the human body systems. start learning now!. The musculoskeletal system consists of the body's bones, joints, and muscles. humans need this system (1) for support to stand erect, and (2) for movement. the musculoskeletal system also functions (3) to encase and protect the inner vital organs (e.g., brain, spinal cord, heart); (4) to produce the red blood cells, white blood cells, and.

Skeletal System Medical Anatomy Poster 24 X 36 Laminated Quick Learn anatomy faster andremember everything you learn. a free website study guide review that uses interactive animations to help you learn online about anatomy and physiology, human anatomy, and the human body systems. start learning now!. The musculoskeletal system consists of the body's bones, joints, and muscles. humans need this system (1) for support to stand erect, and (2) for movement. the musculoskeletal system also functions (3) to encase and protect the inner vital organs (e.g., brain, spinal cord, heart); (4) to produce the red blood cells, white blood cells, and.

Musculoskeletal System Structure Medicinebtg

The Musculoskeletal System Anatomy Physiology Notes Study Guide I

Comments are closed.