Muscles Of The Hand Anatomy
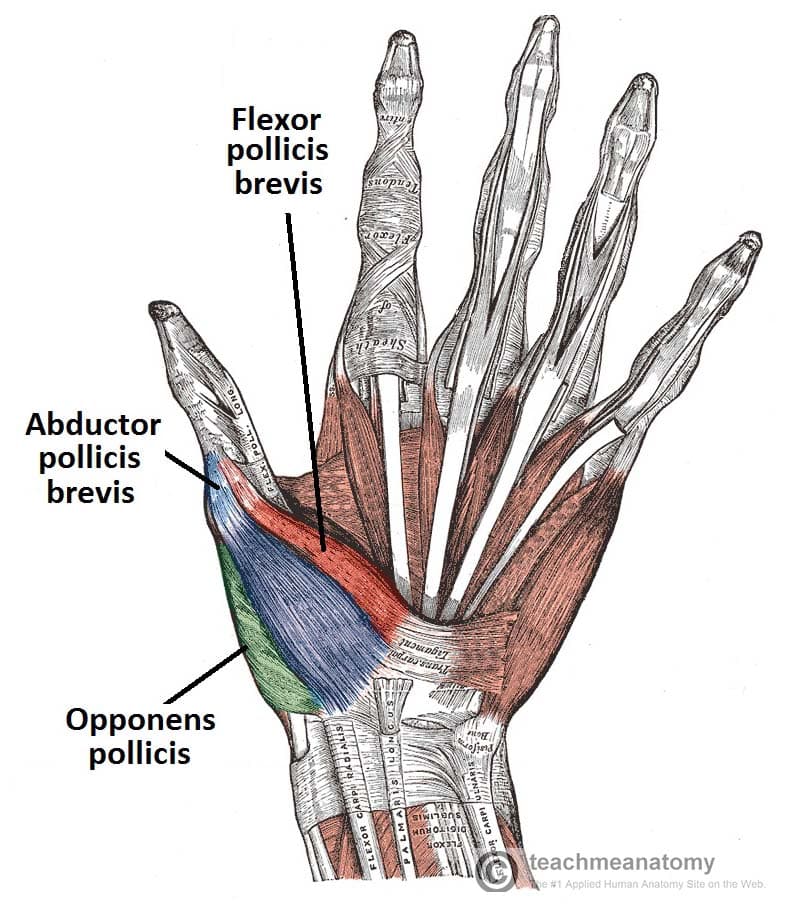
The Muscles Of The Hand Thenar Hypothenar Teachmeanatomy The thenar muscles are three short muscles located at the base of the thumb. the muscle bellies produce a bulge, known as the thenar eminence. they are responsible for the fine movements of the thumb. the median nerve innervates all the thenar muscles. opponens pollicis. the opponens pollicis is the largest of the thenar muscles, and lies. The interossei are small, worm like muscles located between the metacarpal bones. they are divided into two groups based on their location – dorsal and palmar interossei. each hand has 4 dorsal and 3 (sometimes 4) palmar interossei. they help with abduction, adduction, flexion, and extension of the fingers. muscle.
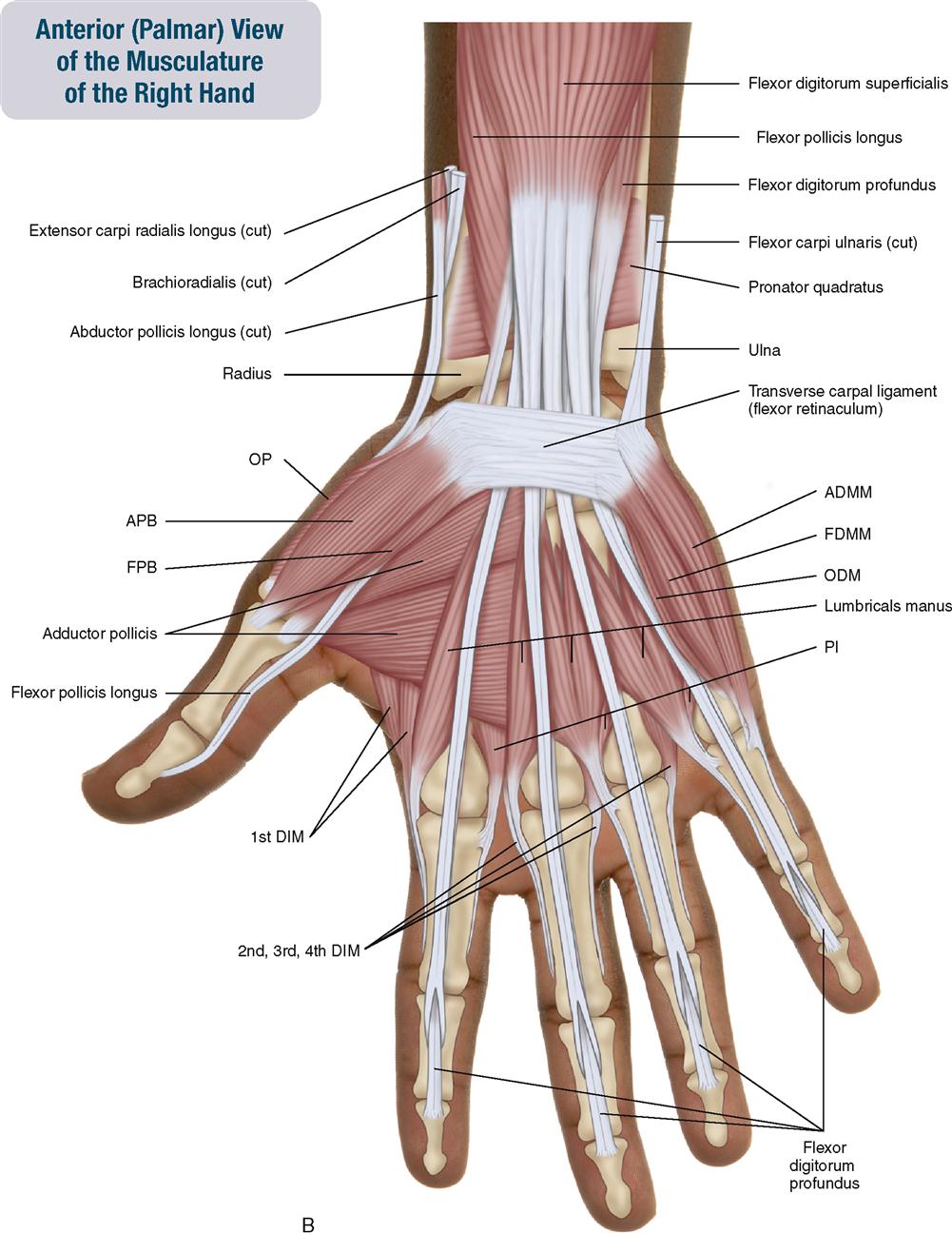
7 Muscles Of The Forearm And Hand Musculoskeletal Key Those are flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction of the hand. take this specially designed quiz to test your knowledge about the hand and wrist. it specifically focuses on bones, muscles (including attachments, innervation, functions), arteries, veins, and nerves. custom quiz: wrist anatomy start quiz. Learn about the muscles, tendons, and ligaments of the hand and forearm that enable various movements and functions. find out how carpal tunnel syndrome affects the hand and what treatments are available. To understand the anatomy of the hand we first must understand the anatomy of the forearm and wrist. the forearm consists of two bones, the radius and the ulna. both forearm bones articulate with the carpal bones of the wrist distally. the radius articulates with the cashew shaped scaphoid bone, and the croissant or moon shaped lunate bone. Learn about the structure and function of your hand and wrist, including the 19 bones, 34 muscles, nerves, tendons and ligaments that make them work. find out how to care for your hand and wrist health and what conditions can affect them.
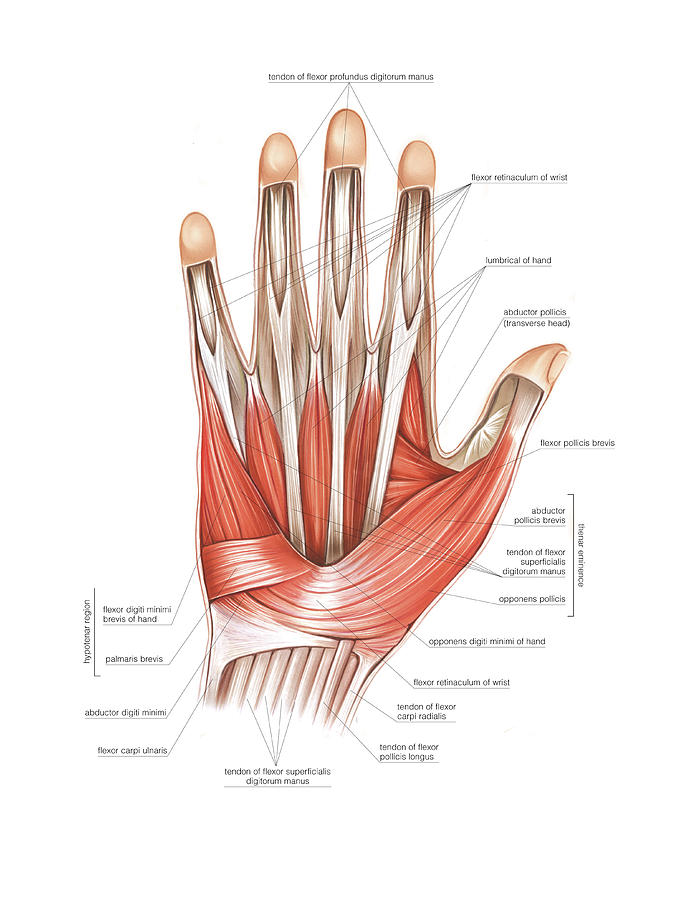
Muscles Of The Hand 5 By Science Photo Library To understand the anatomy of the hand we first must understand the anatomy of the forearm and wrist. the forearm consists of two bones, the radius and the ulna. both forearm bones articulate with the carpal bones of the wrist distally. the radius articulates with the cashew shaped scaphoid bone, and the croissant or moon shaped lunate bone. Learn about the structure and function of your hand and wrist, including the 19 bones, 34 muscles, nerves, tendons and ligaments that make them work. find out how to care for your hand and wrist health and what conditions can affect them. The muscles of the hand are the skeletal muscles responsible for the movement of the hand and fingers. the muscles of the hand can be subdivided into two groups: the extrinsic and intrinsic muscle groups. the extrinsic muscle groups are the long flexors and extensors. they are called extrinsic because the muscle belly is located on the forearm. The muscles of the thenar and the hypothenar eminence along with the adductor compartment make up the intrinsic muscles of the hand. their origin and insertion is within the carpal and metacarpal bones and are surrounded by ligaments, and fascia of the hand. they help with fine motor movements of the hands. [3].

Muscles Of The Hand Wikipedia The muscles of the hand are the skeletal muscles responsible for the movement of the hand and fingers. the muscles of the hand can be subdivided into two groups: the extrinsic and intrinsic muscle groups. the extrinsic muscle groups are the long flexors and extensors. they are called extrinsic because the muscle belly is located on the forearm. The muscles of the thenar and the hypothenar eminence along with the adductor compartment make up the intrinsic muscles of the hand. their origin and insertion is within the carpal and metacarpal bones and are surrounded by ligaments, and fascia of the hand. they help with fine motor movements of the hands. [3].

Intrinsic Hand Muscles Msk Medbullets Step 1

Comments are closed.