Muscles Of The Back Teachmeanatomy
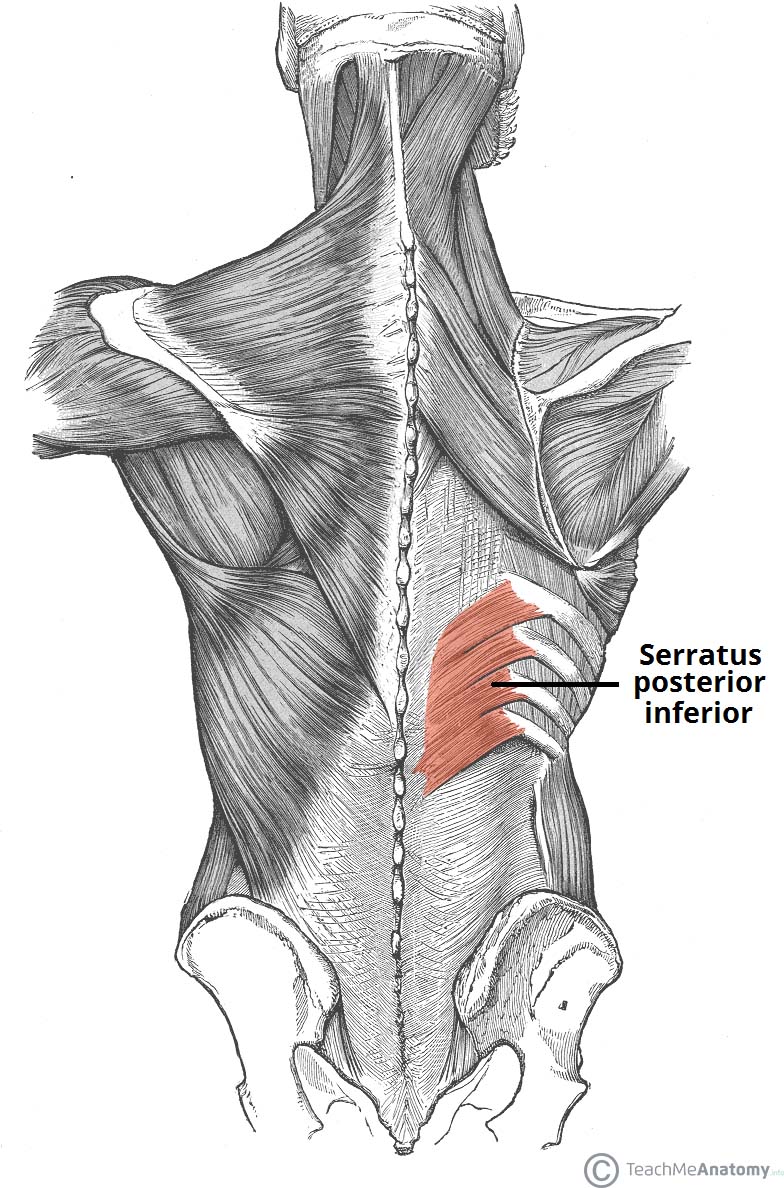
The Superficial Back Muscles Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy The muscles of the back can be arranged into 3 categories based on their location: superficial back muscles, intermediate back muscles and intrinsic back muscles.the intrinsic muscles are named as such because their embryological development begins in the back, oppose to the superficial and intermediate back muscles which develop elsewhere and are therefore classed as extrinsic muscles. Attachments: arises from the common tendinous origin, and attaches to the spinous processes of c2, t1 t8 and the occipital bone of the skull. innervation: posterior rami of the spinal nerves. actions: acts unilaterally to laterally flex the vertebral column. acts bilaterally to extend the vertebral column and head.
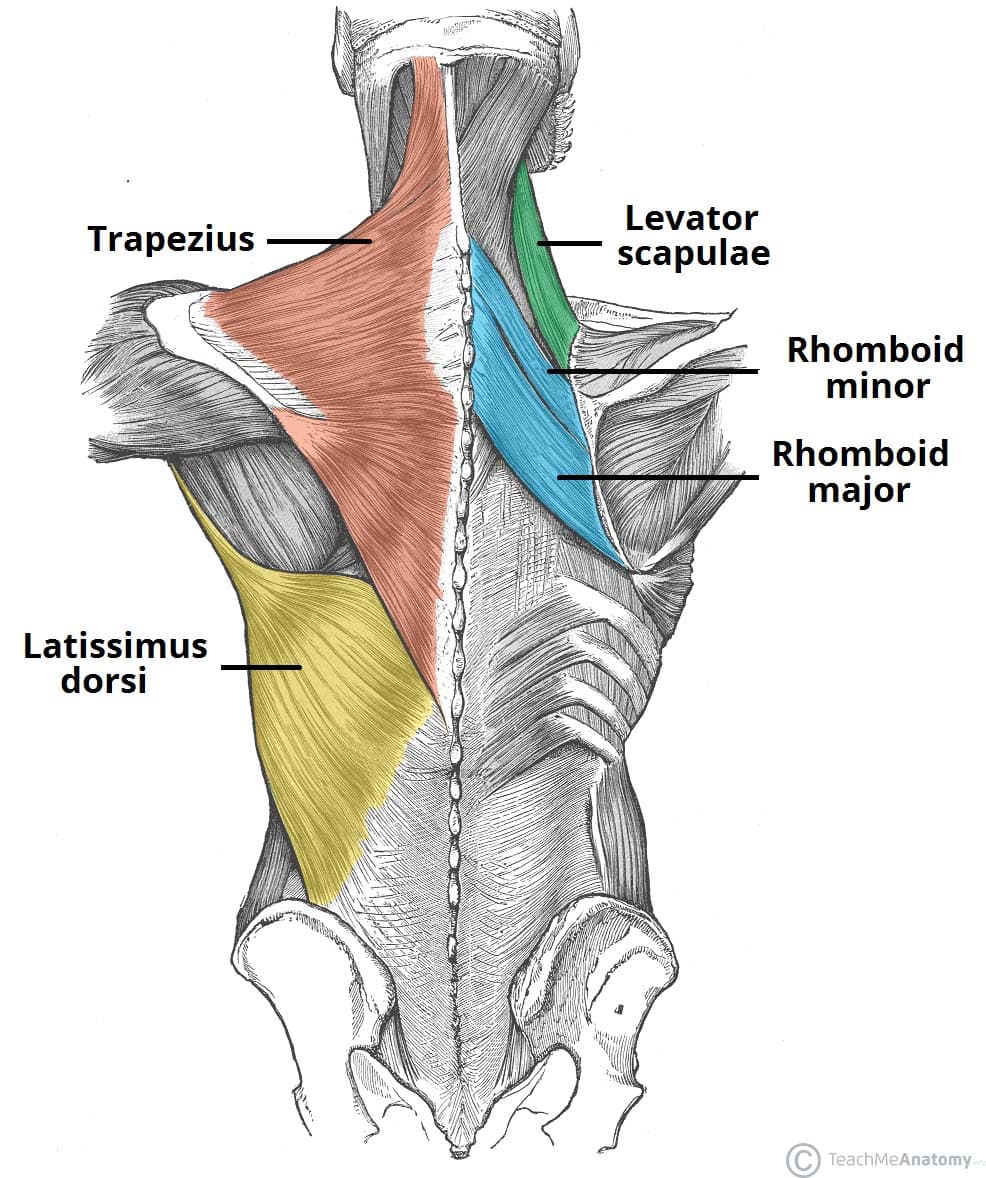
Muscles Of The Back Teachmeanatomy The superficial back muscles are situated underneath the skin and superficial fascia. they originate from the vertebral column and attach to the bones of the shoulder – the clavicle, scapula and humerus. all these muscles are therefore associated with movements of the upper limb. the muscles in this group are the trapezius, latissimus dorsi. 3d anatomy tutorials on the muscles of the back. systematically going through muscles of the back from superficial to deep. extrinsic, intermediate and deep. Action. innervation. 1. superficial or extrinsic muscles (5) have attachments on the shoulder and arm bones, which is why they are often considered to be upper limb muscles. trapezius. upper back and neck, spanning from the base of the skull to the middle back and out to the shoulders. The deep muscles of the back are well developed, and collectively extend from the sacrum to the base of the skull. they are associated with the movements of the vertebral column, and the control of posture. the muscles themselves are covered by deep fascia, which plays a key role in their organisation.

The Intrinsic Back Muscles Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy Action. innervation. 1. superficial or extrinsic muscles (5) have attachments on the shoulder and arm bones, which is why they are often considered to be upper limb muscles. trapezius. upper back and neck, spanning from the base of the skull to the middle back and out to the shoulders. The deep muscles of the back are well developed, and collectively extend from the sacrum to the base of the skull. they are associated with the movements of the vertebral column, and the control of posture. the muscles themselves are covered by deep fascia, which plays a key role in their organisation. The first subgroup consists of two superficial muscles: the trapezius and latissimus dorsi. the trapezius is a large triangular muscle that covers the posterior aspect of the neck and the superior half of the back. there are two trapezius muscles in the back, which when seen together, look like a trapezium. proximally, the trapezius originates. Your lat muscles are the largest muscles in the upper half of your body. they start below your shoulder blades and extend to your spine in your lower back. levator scapulae: these are smaller muscles that start at the side of your neck and extend to your shoulder blades. rhomboids: the rhomboid muscles connect your shoulder blades to your spine.
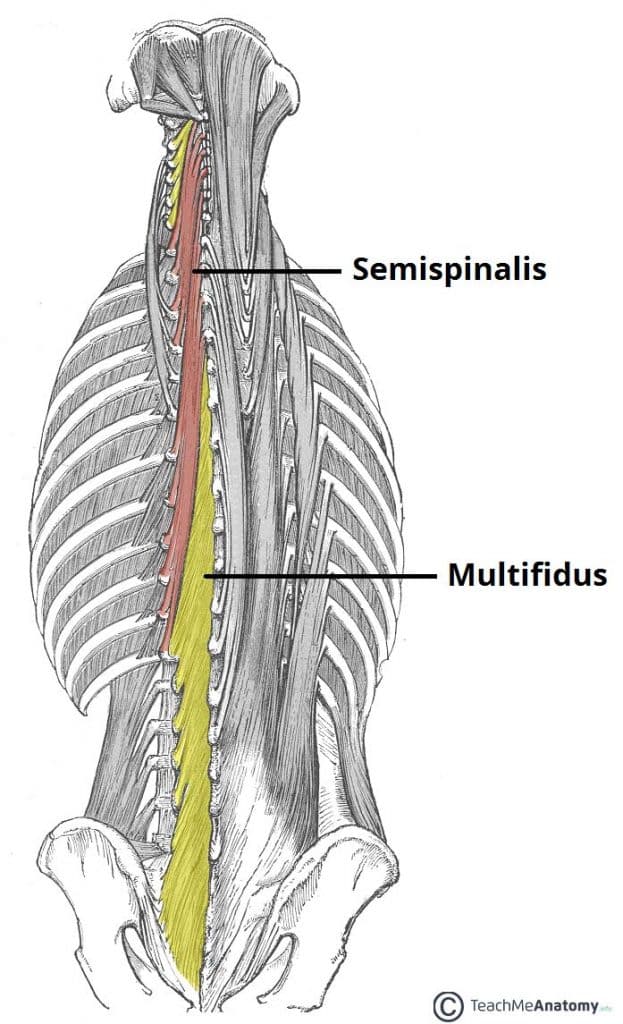
The Intrinsic Back Muscles Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy The first subgroup consists of two superficial muscles: the trapezius and latissimus dorsi. the trapezius is a large triangular muscle that covers the posterior aspect of the neck and the superior half of the back. there are two trapezius muscles in the back, which when seen together, look like a trapezium. proximally, the trapezius originates. Your lat muscles are the largest muscles in the upper half of your body. they start below your shoulder blades and extend to your spine in your lower back. levator scapulae: these are smaller muscles that start at the side of your neck and extend to your shoulder blades. rhomboids: the rhomboid muscles connect your shoulder blades to your spine.

Comments are closed.