Muscle Contraction Cycle Muscle Contraction Muscular System Anatomy

Muscle Contraction Flow Chart Muscle contraction begins when the nervous system generates a signal. the signal, an impulse called an action potential, travels through a type of nerve cell called a motor neuron. the neuromuscular junction is the name of the place where the motor neuron reaches a muscle cell. skeletal muscle tissue is composed of cells called muscle fibers. Relaxing skeletal muscle fibers, and ultimately, the skeletal muscle, begins with the motor neuron, which stops releasing its chemical signal, ach, into the synapse at the nmj. the muscle fiber will repolarize, which closes the gates in the sr where ca was being released. atp driven pumps will move ca out of the sarcoplasm back into the sr.

Muscle Contraction Cycle Basic Anatomy And Physiology Muscular Excitation signalling of action potentials from the motor neuron are coupled with calcium release. thus, the excitation contraction coupling process begins with signaling from the nervous system at the neuromuscular junction (figure 10.3.1) and ends with calcium release for muscle contraction. figure 10.3.1 – motor end plate and innervation. Figure 10.11 skeletal muscle contraction (a) the active site on actin is exposed as calcium binds to troponin. (b) the myosin head is attracted to actin, and myosin binds actin at its actin binding site, forming the cross bridge. (c) during the power stroke, the phosphate generated in the previous contraction cycle is released. Muscle contraction is initiated with the depolarization of the sarcolemma caused by the sodium ions' entrance through the sodium channels associated with the ach receptors. figure 15.4.2 15.4. 2: this diagram represents the sequence of events that occurs when a motor neuron stimulates a muscle fiber to contract. The physiological concept of muscle contraction is based on two variables: length and tension. in physiology, muscle shortening and muscle contraction are not synonymous. tension within the muscle can be produced without changes in the length of the muscle, as when holding a dumbbell in the same position or holding a sleeping child in your arms. upon termination of muscle contraction, muscle.
Physiology Of Muscle Contraction Muscle contraction is initiated with the depolarization of the sarcolemma caused by the sodium ions' entrance through the sodium channels associated with the ach receptors. figure 15.4.2 15.4. 2: this diagram represents the sequence of events that occurs when a motor neuron stimulates a muscle fiber to contract. The physiological concept of muscle contraction is based on two variables: length and tension. in physiology, muscle shortening and muscle contraction are not synonymous. tension within the muscle can be produced without changes in the length of the muscle, as when holding a dumbbell in the same position or holding a sleeping child in your arms. upon termination of muscle contraction, muscle. The sliding filament model of contraction. when signaled by a motor neuron, a skeletal muscle fiber contracts as the thin filaments are pulled and then slide past the thick filaments within the fiber’s sarcomeres. this process is known as the sliding filament model of muscle contraction (figure 10.3.3). The energy released during atp hydrolysis changes the angle of the myosin head into a “cocked” position, ready to bind to actin if the sites are available. adp and pi remain attached; myosin is in its high energy configuration. figure 38.17.1 38.17. 1: cross bridge muscle contraction cycle: the cross bridge muscle contraction cycle, which.
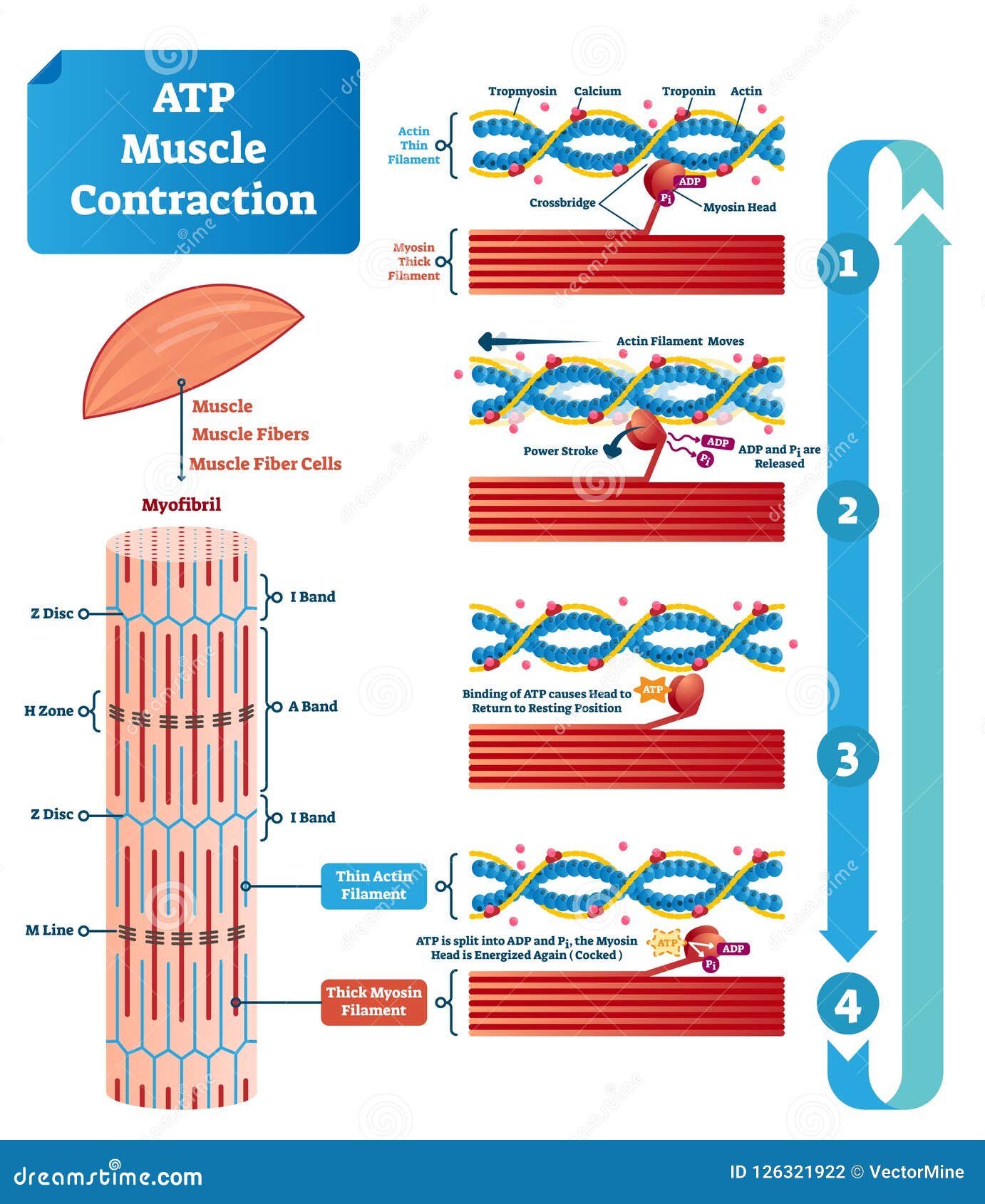
Atp Muscle Contraction Cycle Vector Illustration Labeled Educational The sliding filament model of contraction. when signaled by a motor neuron, a skeletal muscle fiber contracts as the thin filaments are pulled and then slide past the thick filaments within the fiber’s sarcomeres. this process is known as the sliding filament model of muscle contraction (figure 10.3.3). The energy released during atp hydrolysis changes the angle of the myosin head into a “cocked” position, ready to bind to actin if the sites are available. adp and pi remain attached; myosin is in its high energy configuration. figure 38.17.1 38.17. 1: cross bridge muscle contraction cycle: the cross bridge muscle contraction cycle, which.

5 Steps To The Contraction Cycle Skeletal Muscle Diagram Quizlet

Comments are closed.