Muscle Contraction Cycle Basic Anatomy And Physiology Muscular

Muscle Contraction Diagram Labelled Stock Image C043 4842 Muscle contraction begins when the nervous system generates a signal. the signal, an impulse called an action potential, travels through a type of nerve cell called a motor neuron. the neuromuscular junction is the name of the place where the motor neuron reaches a muscle cell. skeletal muscle tissue is composed of cells called muscle fibers. The physiological concept of muscle contraction is based on two variables: length and tension. in physiology, muscle shortening and muscle contraction are not synonymous. tension within the muscle can be produced without changes in the length of the muscle, as when holding a dumbbell in the same position or holding a sleeping child in your arms. upon termination of muscle contraction, muscle.

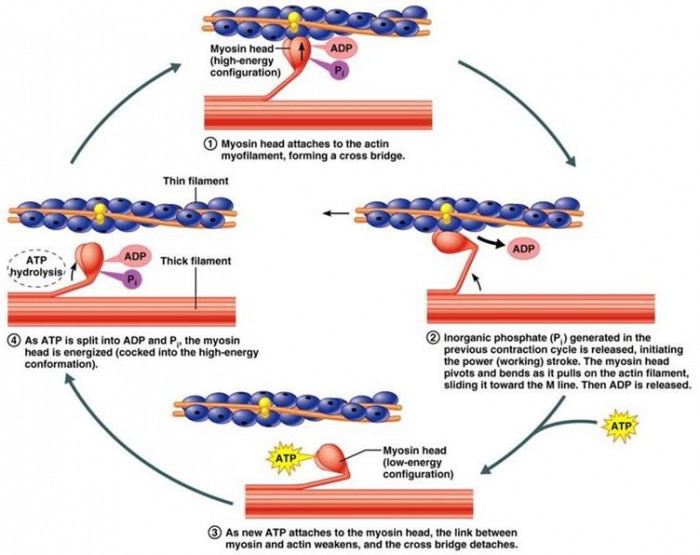
38 17 Muscle Contraction And Locomotion Atp And Muscle Contraction Muscle contraction is initiated with the depolarization of the sarcolemma caused by the sodium ions' entrance through the sodium channels associated with the ach receptors. figure 15.4.2 15.4. 2: this diagram represents the sequence of events that occurs when a motor neuron stimulates a muscle fiber to contract. Treppe. when a skeletal muscle has been dormant for an extended period and then stimulated to contract, with all other things being equal, the initial contractions generate about one half the force of later contractions. the muscle tension increases in a graded manner that to some looks like a set of stairs. Relaxing skeletal muscle fibers, and ultimately, the skeletal muscle, begins with the motor neuron, which stops releasing its chemical signal, ach, into the synapse at the nmj. the muscle fiber will repolarize, which closes the gates in the sr where ca was being released. atp driven pumps will move ca out of the sarcoplasm back into the sr. As organs that contain cells that can contract, muscles can generate force and movement. skeletal muscle works in conjunction with the bones of the skeleton to create body movements. additionally, it is also associated with the diaphragmatic, esophageal, and eye muscles. thus, skeletal muscle serves a variety of purposes, including moving of the body, breathing, and swallowing. in contrast to.
Physiology Of Skeletal Muscle Contraction Earth S Lab Relaxing skeletal muscle fibers, and ultimately, the skeletal muscle, begins with the motor neuron, which stops releasing its chemical signal, ach, into the synapse at the nmj. the muscle fiber will repolarize, which closes the gates in the sr where ca was being released. atp driven pumps will move ca out of the sarcoplasm back into the sr. As organs that contain cells that can contract, muscles can generate force and movement. skeletal muscle works in conjunction with the bones of the skeleton to create body movements. additionally, it is also associated with the diaphragmatic, esophageal, and eye muscles. thus, skeletal muscle serves a variety of purposes, including moving of the body, breathing, and swallowing. in contrast to. Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. Skeletal muscle is found throughout the body and functions to contract in response to a stimulus. skeletal muscle serves many purposes, including producing movement, sustaining body posture and position, maintaining body temperature, storing nutrients, and stabilizing joints. in contrast to smooth and cardiac muscle contraction, most skeletal muscle contraction is under voluntary control.

Comments are closed.