Muscle Contraction Cross Bridge Cycle Animation Channels For Pearson
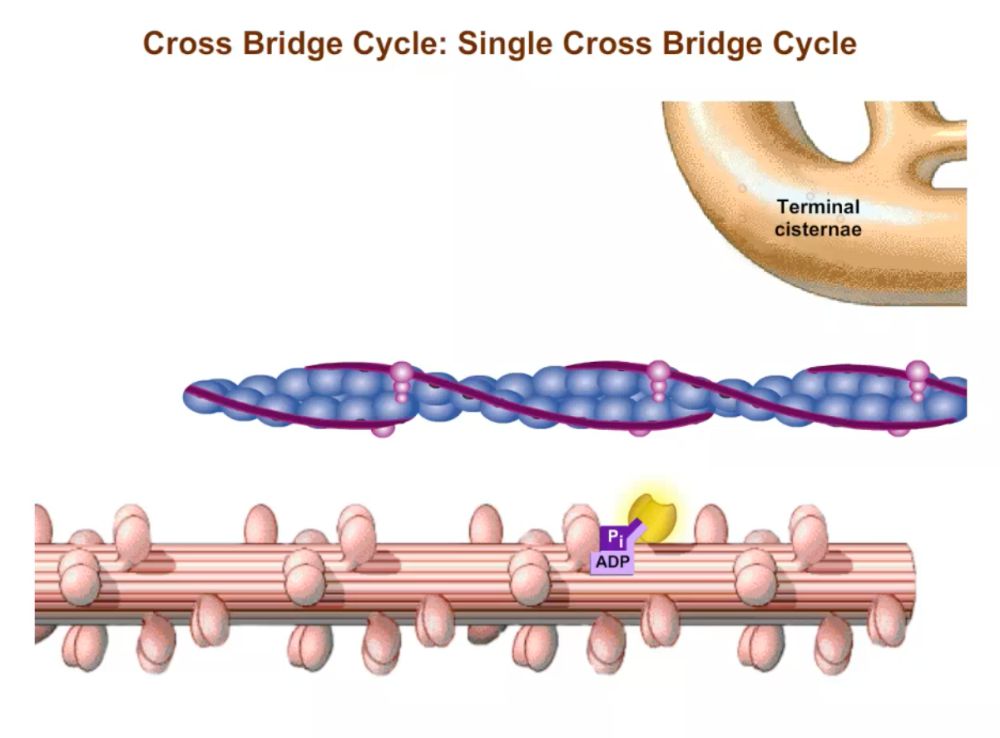
Cross Bridge Cycle Pearson Channels Muscle contraction cross bridge cycle, animation. We can see the mycin binding sites there on the acton, those are gonna become exposed. all right. now, we can talk about the mechanics of contraction once those mycin binding sites are exposed, the mycin is going to bind to the acton. we're gonna call that binding a cross bridge.

Muscle Contraction Cross Bridge Cycle Animation Youtube So the cross bridge cycle, we're going to say, is the interaction of the myosin head and the actin in a way that leads to the sarcomere shortening. and that's our goal. if we want a muscle to contract, we need that fundamental unit of muscle contraction, the sarcomere, to get shorter. so we have this cross bridge cycle broken up into 4 steps here. (usmle topics) molecular basis of the sliding filament theory (skeletal muscle contraction) the cross bridge cycle. purchase a license to download a non wa. 00:00 : introduction to video00:18 : sarcomeres are made up of myosin, actin.1:44 : atp is broken down to power muscle contraction1:59 : calcium allows for m. This is known as the sliding filament theory. cross bridge cycling forms the molecular basis for this sliding movement. – muscle contraction is initiated when muscle fibers are stimulated by a nerve impulse and calcium ions are released. – to trigger muscular contraction, the troponin units on the actin myofilaments are bound by calcium ions.

Muscle Contraction Cross Bridge Cycle Animation Channels For Pearson 00:00 : introduction to video00:18 : sarcomeres are made up of myosin, actin.1:44 : atp is broken down to power muscle contraction1:59 : calcium allows for m. This is known as the sliding filament theory. cross bridge cycling forms the molecular basis for this sliding movement. – muscle contraction is initiated when muscle fibers are stimulated by a nerve impulse and calcium ions are released. – to trigger muscular contraction, the troponin units on the actin myofilaments are bound by calcium ions. Your browser doesn't support html5 video. mark the new pause time. hour:. Muscle contraction the cross bridge cycle of muscle contraction with narration. this video will help the student understand cross bridge cycling and how it.

The Cross Bridges Of Muscles The Point Where The Muscle Strands Flip Your browser doesn't support html5 video. mark the new pause time. hour:. Muscle contraction the cross bridge cycle of muscle contraction with narration. this video will help the student understand cross bridge cycling and how it.

Muscle Contraction And Locomotion Boundless Biology

Comments are closed.