Msk Case 83 Shoulder X Ray You Will Not Believe

Msk Case 83 Shoulder X Ray You Will Not Believe Youtube Dr. omer awan, physician and public health contributor for forbes breaks down this x ray case in a fun and interactive manner! come watch and learn! #e. 1 msk shoulder by mohamed emad shehata; shoulder and hip by mudit arora; z ocq 2017 by julie marthe grenier shoulder x ray by ahmed mohamed mohamed eid ali; annotated xrays by matt wong trauma ms by jose andres cordoba; musculoskeletal radiographic anatomy by samir benoudina; anatomy teaching upper limbs by jonathan adlam; shoulder x ray by.
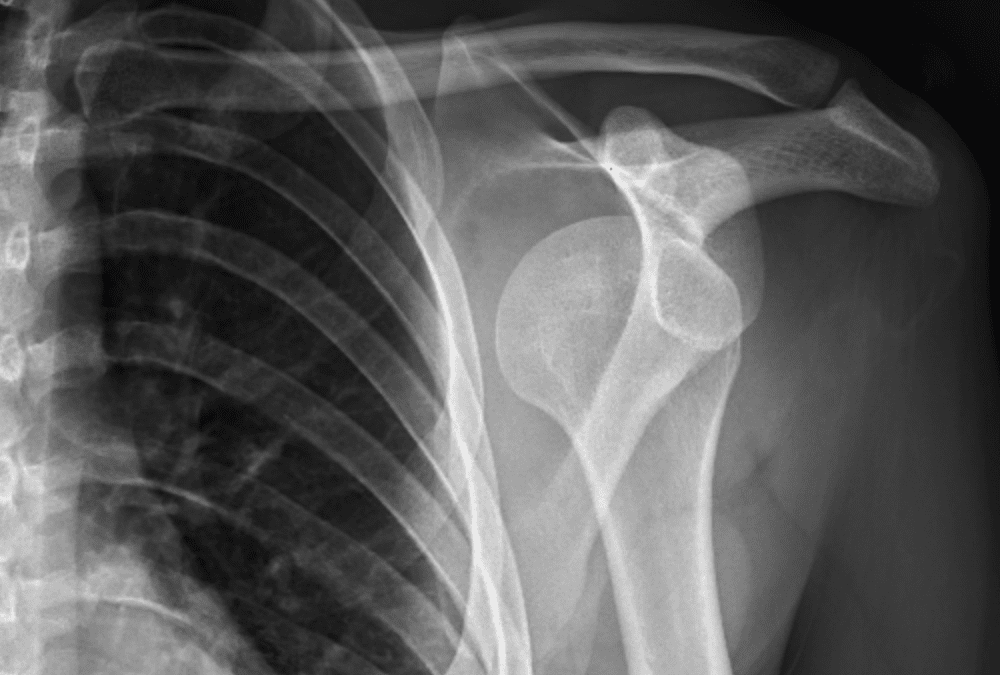
Msk Archives Casestacks This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged. musculoskeletal (msk) x ray interpretation can occasionally feature in osces and therefore it’s important to practice this skill to develop a structured approach. this guide provides a brief overview of msk x ray interpretation, including a structured approach you can apply. Initially described by lawrence 10, 11 in 1915, the axillary lateral x ray can be taken with the patient supine or erect. ideally, the arm is positioned in 70 to 90 degrees of abduction. the x ray beam is directed into the axilla from inferior to superior, and the x ray cassette is placed superior to the patient’s shoulder . Shoulder dislocation by bryan schnabel msk tute by henry lin; above the elbow by peter richter; normal rx by sabrina martel; shoulder mri by n seth; normal and variants of normal by tom molyneux; supervision 4 by richard hodgson; radiology test (2d year) by vasilii; x ray (non contrast) by vasilii; ms by albert guillemette; bcj: practical 1. Normal shoulder joint. the 'shoulder' joint is more accurately termed the glenohumeral joint. in the context of trauma there are 2 standard views used to assess this joint. these are the anterior posterior (ap) view, and the lateral or 'y view'. if the patient can tolerate holding the arm in abduction, an 'axial' view is an alternative to the.

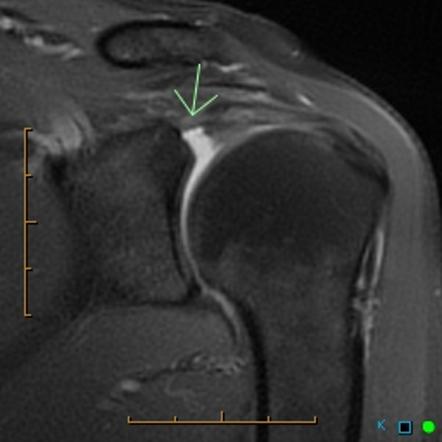
Playlist Viva Msk Shoulder Mri By Assoc Prof Craig Hacking Shoulder dislocation by bryan schnabel msk tute by henry lin; above the elbow by peter richter; normal rx by sabrina martel; shoulder mri by n seth; normal and variants of normal by tom molyneux; supervision 4 by richard hodgson; radiology test (2d year) by vasilii; x ray (non contrast) by vasilii; ms by albert guillemette; bcj: practical 1. Normal shoulder joint. the 'shoulder' joint is more accurately termed the glenohumeral joint. in the context of trauma there are 2 standard views used to assess this joint. these are the anterior posterior (ap) view, and the lateral or 'y view'. if the patient can tolerate holding the arm in abduction, an 'axial' view is an alternative to the. This brief tutorial discusses musculoskeletal x ray anatomy in general terms, and introduces some important concepts regarding musculoskeletal x ray interpretation. knowledge of normal bone, joint and soft tissue appearances enables accurate description of abnormalities seen on x ray. both normal and abnormal x rays are used to illustrate key. 1 of 157. download now. this document provides guidance on interpreting musculoskeletal x rays. it discusses evaluating bones, joints, soft tissues for fractures, structural anomalies, degenerative conditions. it emphasizes comparing two views, two joints, and looking for unexpected findings or artifacts. it also describes how to characterize.
Playlist Msk Trauma Shoulder And Humerus By Aman This brief tutorial discusses musculoskeletal x ray anatomy in general terms, and introduces some important concepts regarding musculoskeletal x ray interpretation. knowledge of normal bone, joint and soft tissue appearances enables accurate description of abnormalities seen on x ray. both normal and abnormal x rays are used to illustrate key. 1 of 157. download now. this document provides guidance on interpreting musculoskeletal x rays. it discusses evaluating bones, joints, soft tissues for fractures, structural anomalies, degenerative conditions. it emphasizes comparing two views, two joints, and looking for unexpected findings or artifacts. it also describes how to characterize.

Comments are closed.