Monopoly Price And Output For A Monopolist Economics Study Notes
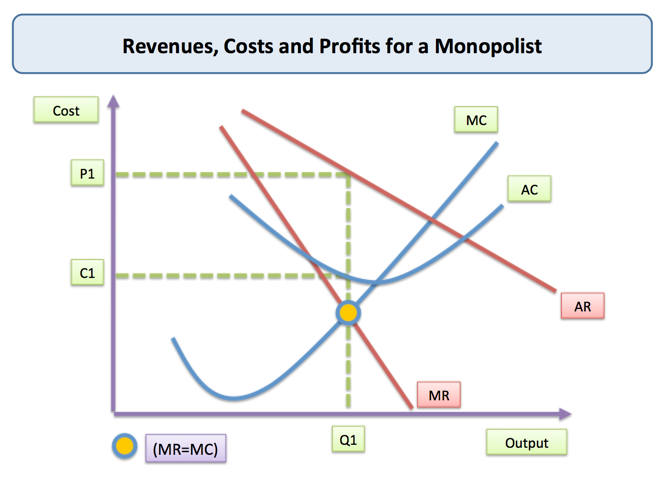
Monopoly Price And Output For A Monopolist Economics Study Notes Since a monopolist is the only rm in the market, it isn’t \small". to sell more units, the monopolist has to lower its price: p0(q) <0. a monopolist faces a downward sloping demand curve. we’re assuming here that the monopolist charges the same price, p(q), for each of the qunits sold. this is important, and we’ll revisit it soon. Monopoly price and output for a monopolist. level: a level. board: aqa, edexcel, ocr, ib. last updated 3 jul 2018. share : a pure monopolist in an industry is a single seller. it is rare for a firm to have a pure monopoly – except when the industry is state owned and has a legally protected monopoly.
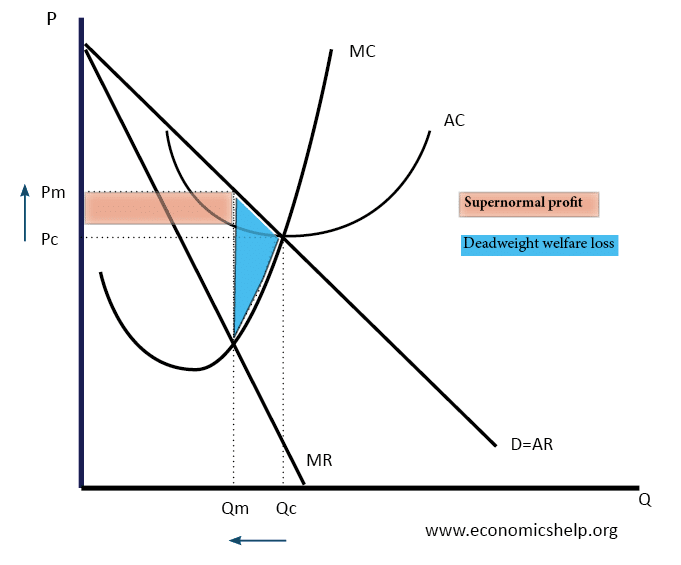
Diagram Of Monopoly Economics Help Profit maximization: mr = mc. monopolya monopolist is doesn’t take the price. s given.however, the monopolist is constrained by the dema. curve.a monopolist doesn’t have a supp. y curve.for a given demand curve, there is just one quantity the monopolist is willing t. Determine the price (p*) at which the firm will sell this quantity by locating it on the demand curve. the monopolist will maximize profit by producing q* units of output and charging p* as the price. c) diagrammatic analysis: a diagram of a monopoly market typically shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and marginal cost curve. Price making a monopoly seller in a goods market is the conceptual opposite from perfectly competitive firms. the monopolist does not face competition from other firms because he is the only seller. he is still constrained in his behavior, however, by consumers’ willingness to pay for his output, i.e., by the demand curve. The profit maximizing quantity will occur where mr = mc—or at the last possible point before marginal costs start exceeding marginal revenue. on figure 9.6, mr = mc occurs at an output of 5. step 2: the monopolist decides what price to charge. the monopolist will charge what the market is willing to pay.

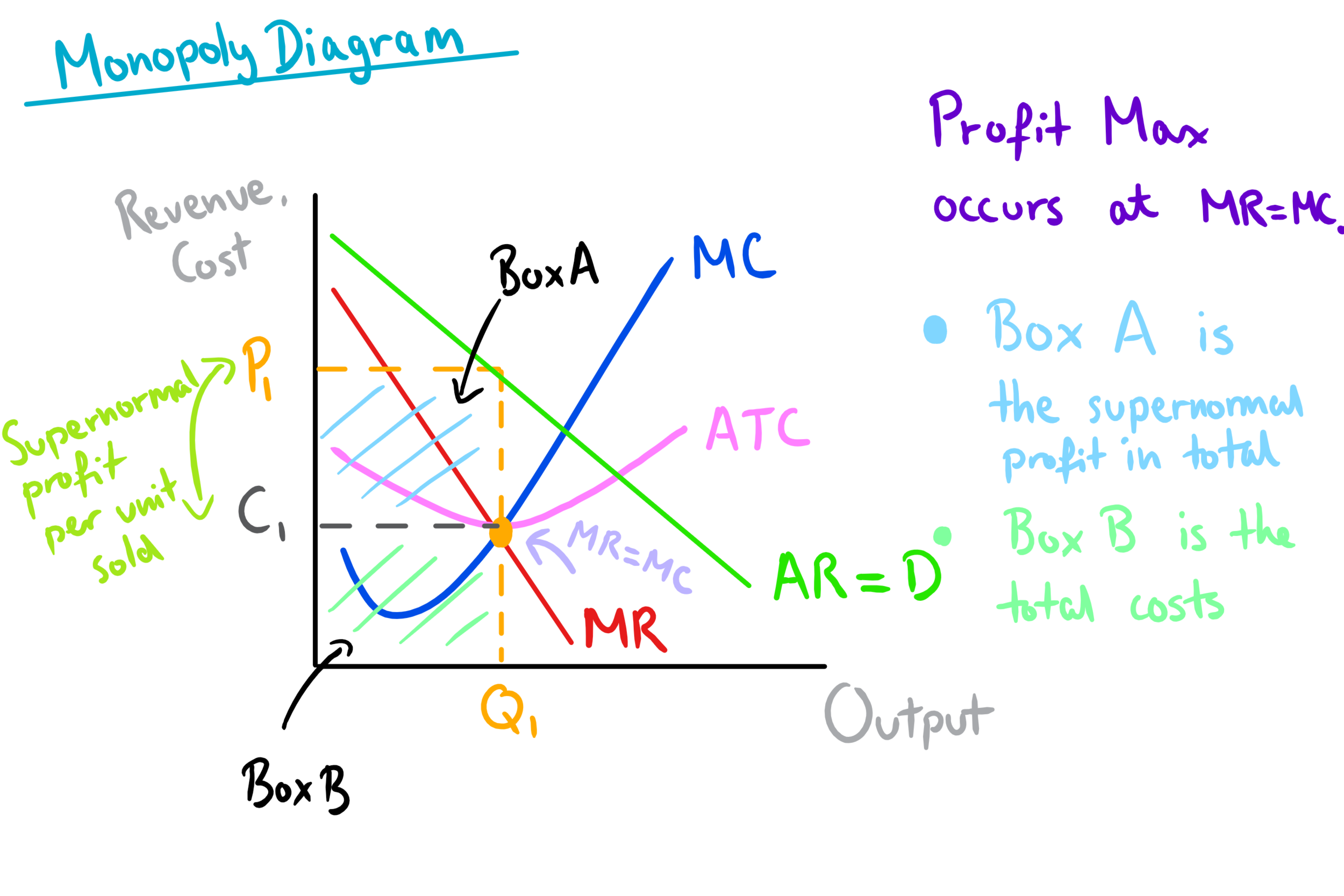
Draw The Graph For A Monopoly With Demand Marginal Revenue And Price making a monopoly seller in a goods market is the conceptual opposite from perfectly competitive firms. the monopolist does not face competition from other firms because he is the only seller. he is still constrained in his behavior, however, by consumers’ willingness to pay for his output, i.e., by the demand curve. The profit maximizing quantity will occur where mr = mc—or at the last possible point before marginal costs start exceeding marginal revenue. on figure 9.6, mr = mc occurs at an output of 5. step 2: the monopolist decides what price to charge. the monopolist will charge what the market is willing to pay. Because a monopolist must cut the price of every unit in order to increase sales, total revenue does not always increase as output rises. in this case, total revenue reaches a maximum of $25 when 5 units are sold. beyond 5 units, total revenue begins to decline. figure 10.4 demand, elasticity, and total revenue. To calculate profit for a monopoly. profit = total revenue – total cost. total revenue = 25*30 = 750. total cost = 5 * 25 = 125. therefore, total profit for this section is = 625 (assuming there is no fixed cost) monopoly diagram. supply and demand equations. how to work out output, price and profit from monopoly equations, such as p1=55 q1.

Monopoly Diagram A Level Economics Because a monopolist must cut the price of every unit in order to increase sales, total revenue does not always increase as output rises. in this case, total revenue reaches a maximum of $25 when 5 units are sold. beyond 5 units, total revenue begins to decline. figure 10.4 demand, elasticity, and total revenue. To calculate profit for a monopoly. profit = total revenue – total cost. total revenue = 25*30 = 750. total cost = 5 * 25 = 125. therefore, total profit for this section is = 625 (assuming there is no fixed cost) monopoly diagram. supply and demand equations. how to work out output, price and profit from monopoly equations, such as p1=55 q1.

A Draw A Graph For A Monopoly With Demand Marginal Revenue And
Monopolies Mr Banks Economics Hub Resources Tutoring Exam Prep

Comments are closed.