Monopoly Power In Markets Reference Library Economics Tutor2u
Monopoly Power In Markets Reference Library Economics Tutor2u A near pure monopoly occurs when one firm has a market share in excess of 90 percent. but more realistically, a near pure monopoly can exist when one seller has more than three quarters of a market defined in a certain way. monopoly power enjoyed by a firm depends in part on how the market is defined. many businesses have local monopoly power. In this revision video i explore the concept of monopoly power in markets. what is monopoly? reference library. study notes, videos, interactive activities and.

Monopoly Power In Markets Reference Library Economics Tutor2u Monopoly. natural monopoly. local monopoly. supernormal profit. oligopoly. this video tutorial looks at examples of industries where one or more firms has significant monopoly (market) power. it is an introduction to monopoly ahead of the the main analysis of price, output and profit in monopolistic markets. Some of the key potential advantages and drawbacks of monopoly power in markets are discussed in this updated revision video together with some of the diagra. Monopoly power. a pure monopoly is defined as a single supplier. while there only a few cases of pure monopoly, monopoly ‘power’ is much more widespread, and can exist even when there is more than one supplier – such in markets with only two firms, called a duopoly, and a few firms, an oligopoly. according to the 1998 competition act. In economics, monopsony power refers to the market power that a single buyer or a group of buyers can exercise over the sellers in a market. it's the flip side of monopoly power, which is the market power exerted by a single seller over buyers. this revision video looks at monopsony power. in economics, monopsony power refers to the market.

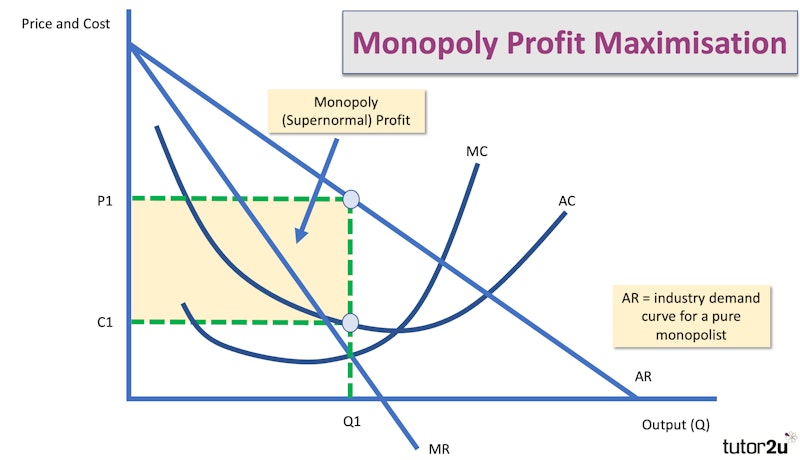
Monopoly Power And Economic Welfare Reference Library Economics Monopoly power. a pure monopoly is defined as a single supplier. while there only a few cases of pure monopoly, monopoly ‘power’ is much more widespread, and can exist even when there is more than one supplier – such in markets with only two firms, called a duopoly, and a few firms, an oligopoly. according to the 1998 competition act. In economics, monopsony power refers to the market power that a single buyer or a group of buyers can exercise over the sellers in a market. it's the flip side of monopoly power, which is the market power exerted by a single seller over buyers. this revision video looks at monopsony power. in economics, monopsony power refers to the market. A pure monopoly is defined as a single seller of a product, i.e. 100% of market share. in the uk a firm is said to have monopoly power if it has more than 25% of the market share. for example, tesco @30% market share or google 90% of search engine traffic. monopoly diagram. a monopoly maximises profits where mr=mc (at point m). 25% market share combined, so they are said to have monopoly power. there are very few examples of pure monopolies, but several firms have monopoly power. monopoly power is influenced by factors such as: o barriers to entry: the higher the barriers to entry, the easier it is for firms to maintain monopoly power.

Comments are closed.