Monopoly Meaning Types Characteristics How To Measure
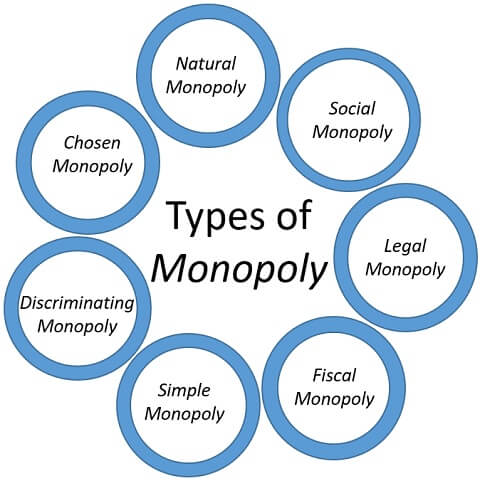
What Is Monopoly Defintion Types And Characteristics The Investors Book Monopoly meaning. a monopoly is a market where one firm (or manufacturer) is the sole supplier of certain goods or services. this firm faces no competition due to which it can set its own prices, thereby exercising full control over the market. the monopolist aims to generate high profits by selling products (or services) that do not have close. These different types of monopolies are listed below: private monopoly – a private monopoly is one that is owned by an individual or a group of individuals. these monopolies mainly aim for profits. public monopoly – a public monopoly is one that is owned by the government. these monopolies are set up for the welfare of the masses.
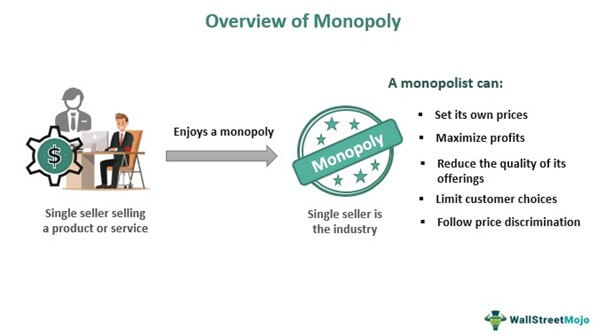
Monopoly Meaning Types Characteristics How To Measure A monopoly is a market structure that consists of a single seller or producer and no close substitutes. a monopoly limits available alternatives for its product and creates barriers for. The characteristics of a monopoly are as follows: 1. creates barriers to entry, limiting new companies from joining the market and minimizing competition. 2. economies of scale leads to the. Legal monopolies. a legal monopoly is a monopoly that exists because of laws and regulations restrict competition. monopolists whose products are protected by intellectual property rights, such as trademarks, patents, and copyrights are good examples of legal monopolies. legal monopolies can also arise if the costs of complying with. A monopolist is a price maker and not a price taker. in fact, his price fixing power is absolute. he is in a position to fix the price for the product as he likes. he can vary the price from buyer to buyer. thus, in a competitive industry, there is single ruling price, while in a monopoly there may be price differentials.
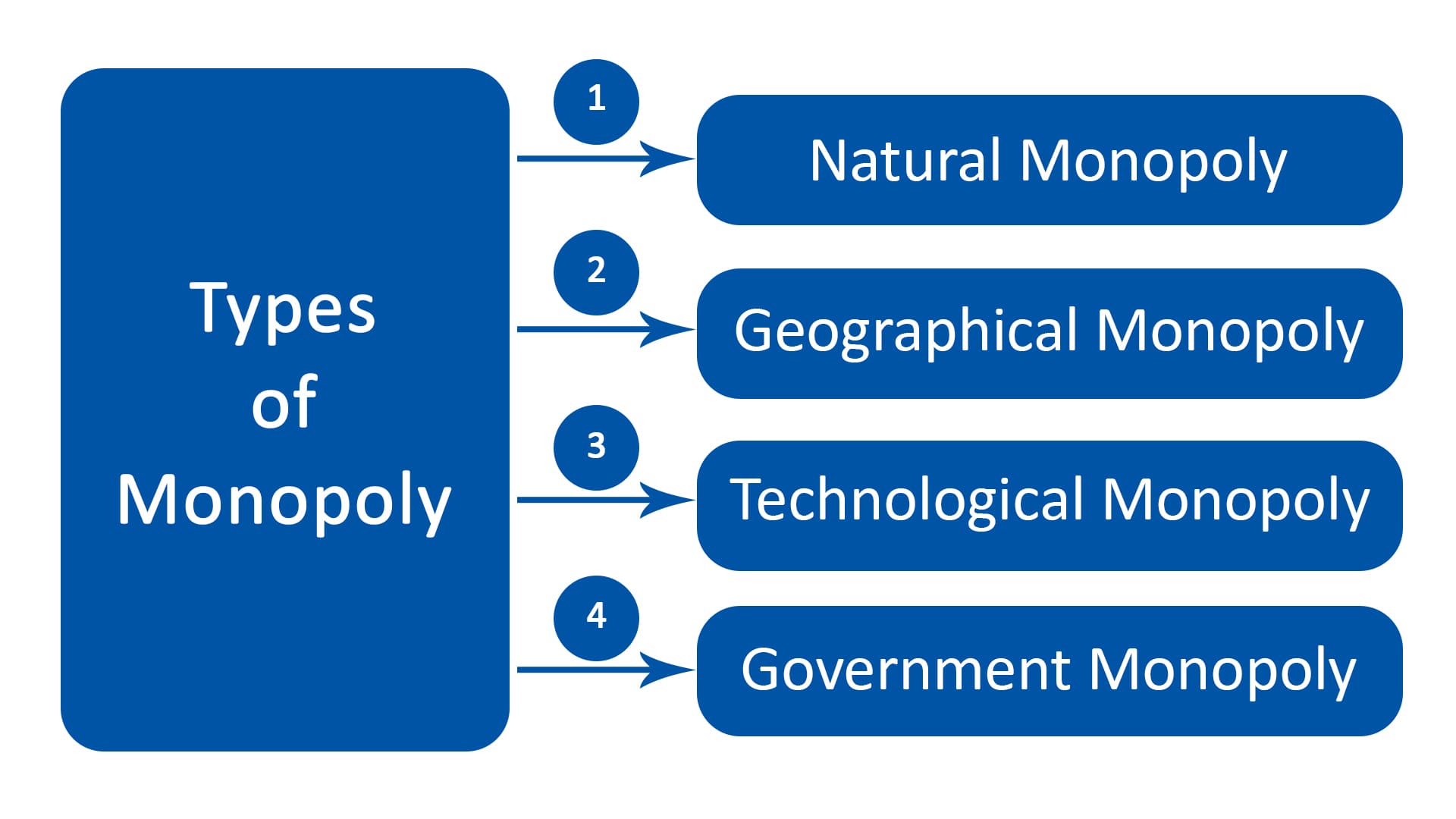
Monopoly Definition Types Characteristics Parsadi Legal monopolies. a legal monopoly is a monopoly that exists because of laws and regulations restrict competition. monopolists whose products are protected by intellectual property rights, such as trademarks, patents, and copyrights are good examples of legal monopolies. legal monopolies can also arise if the costs of complying with. A monopolist is a price maker and not a price taker. in fact, his price fixing power is absolute. he is in a position to fix the price for the product as he likes. he can vary the price from buyer to buyer. thus, in a competitive industry, there is single ruling price, while in a monopoly there may be price differentials. Define what is meant by a natural monopoly. monopoly is at the opposite end of the spectrum of market models from perfect competition. a monopoly firm has no rivals. it is the only firm in its industry. there are no close substitutes for the good or service a monopoly produces. not only does a monopoly firm have the market to itself, but it. A monopoly is an industry or sector in which one company dominates. it is a market structure characterized by a single seller or producer who dominates the market by selling the same product and eliminating the competition. in law, a monopoly is a business entity with considerable market power that enables it to charge high prices and depletes.

13 Types Of Monopoly 2024 Define what is meant by a natural monopoly. monopoly is at the opposite end of the spectrum of market models from perfect competition. a monopoly firm has no rivals. it is the only firm in its industry. there are no close substitutes for the good or service a monopoly produces. not only does a monopoly firm have the market to itself, but it. A monopoly is an industry or sector in which one company dominates. it is a market structure characterized by a single seller or producer who dominates the market by selling the same product and eliminating the competition. in law, a monopoly is a business entity with considerable market power that enables it to charge high prices and depletes.

Comments are closed.