Monopoly Market Structure Intelligent Economist
Monopoly Market Structure Intelligent Economist Advantages of a monopoly. 1. stability of prices. in a monopoly market structure, the prices are pretty stable. this is because there is only one firm involved in the market that sets the prices since there is no competing product. in other types of market structures prices are not stable and tend to be elastic as a result of the competition. A monopsony is a situation of the market wherein only one buyer exists in a particular area, typically along with many sellers. these sellers end up competing for the buyer’s purchases by lowering their prices. in the case of both monopsony and the much more well known situation of monopoly, market conditions are imperfect.
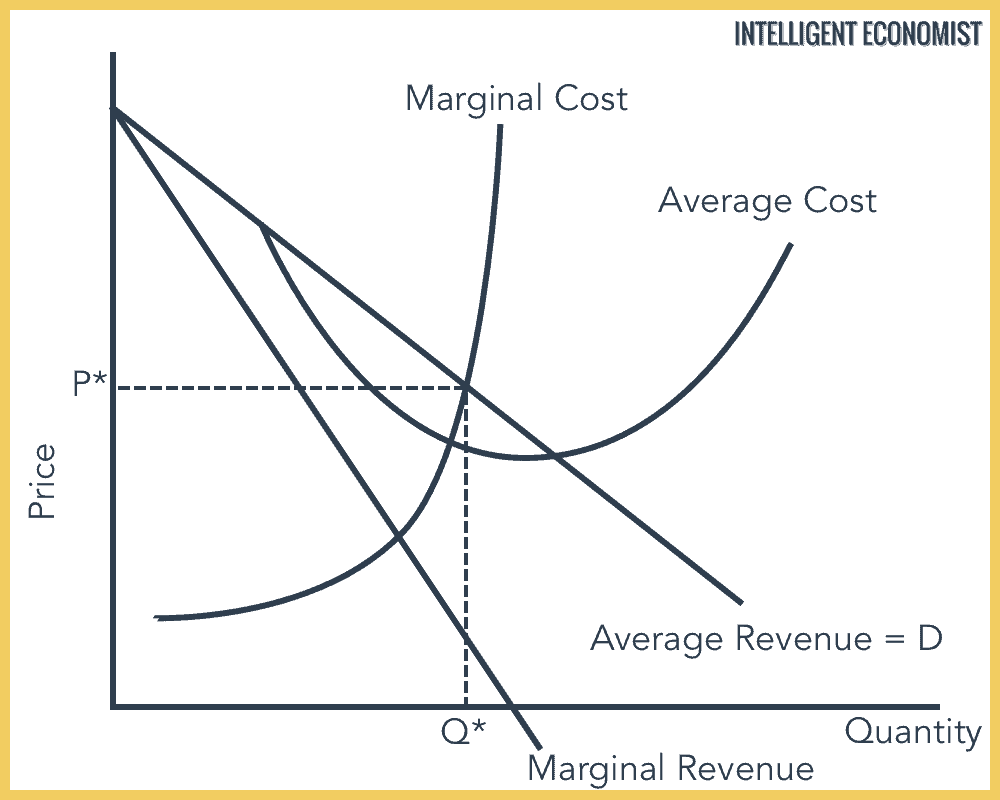
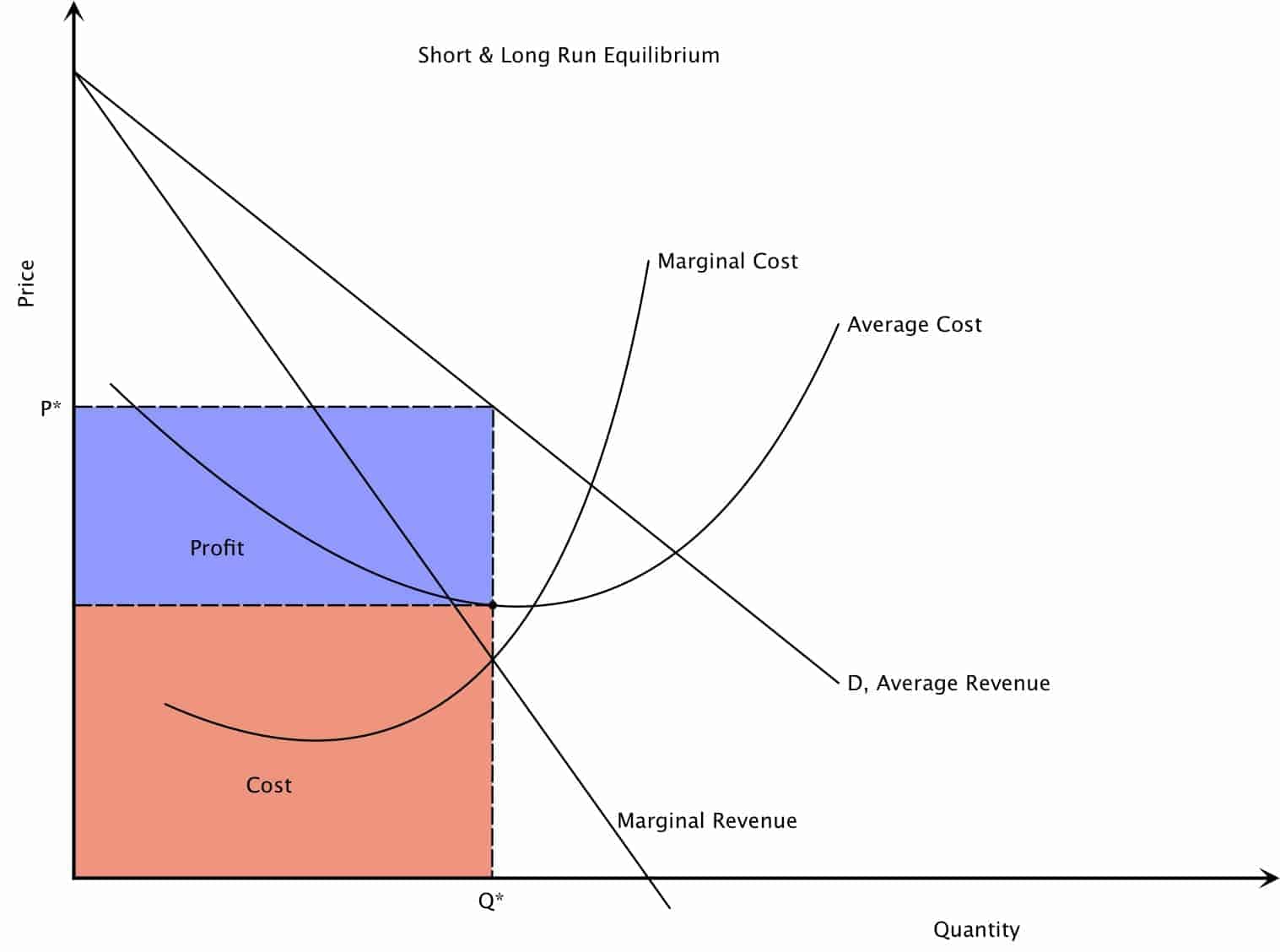
Monopoly Market Structure Intelligent Economist They use a great deal of intensive marketing and advertising. in this way, these firms can gain above market returns. the market structure of monopolistic competition was first labeled in the 1930s, by two economists: the american economist edward chamberlin, and the english economist joan robinson. 16. economic profit is equal to the difference between total revenues and economic costs. 17. the “citizen perspective” is that market power and competition can both be undesirable. 18. an example of a network externality is when the widespread adoption of a particular technology results in environmental damages. 19. Advantages of monopoly. economies of scale; if a firm is in a competitive market and produces at q2, its average costs will be ac2. a monopoly can increase output to q1 and benefit from lower long run average costs (ac1). in industries with high fixed costs, it can be more efficient to have a monopoly than several small firms. 2. research and. A pure monopoly is defined as a single seller of a product, i.e. 100% of market share. in the uk a firm is said to have monopoly power if it has more than 25% of the market share. for example, tesco @30% market share or google 90% of search engine traffic. monopoly diagram. a monopoly maximises profits where mr=mc (at point m).

Monopoly Market Structure Intelligent Economist Advantages of monopoly. economies of scale; if a firm is in a competitive market and produces at q2, its average costs will be ac2. a monopoly can increase output to q1 and benefit from lower long run average costs (ac1). in industries with high fixed costs, it can be more efficient to have a monopoly than several small firms. 2. research and. A pure monopoly is defined as a single seller of a product, i.e. 100% of market share. in the uk a firm is said to have monopoly power if it has more than 25% of the market share. for example, tesco @30% market share or google 90% of search engine traffic. monopoly diagram. a monopoly maximises profits where mr=mc (at point m). Gain a deeper understanding of market structures with our collection of essential diagrams for economics students. our web page provides a comprehensive overview of market structure concepts, including perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. explore these diagrams and their applications to real world scenarios, and learn how they can help you analyze and. A monopoly is a market structure with a single seller or producer that assumes a dominant position in an industry or a sector. monopolies are discouraged in free market economies because they.

Monopoly Market Structure Intelligent Economist Gain a deeper understanding of market structures with our collection of essential diagrams for economics students. our web page provides a comprehensive overview of market structure concepts, including perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. explore these diagrams and their applications to real world scenarios, and learn how they can help you analyze and. A monopoly is a market structure with a single seller or producer that assumes a dominant position in an industry or a sector. monopolies are discouraged in free market economies because they.

Comments are closed.