Monopoly Definition Types Characteristics Examples Feedough

Monopoly Definition Types Characteristics Examples Feedough These different types of monopolies are listed below: private monopoly – a private monopoly is one that is owned by an individual or a group of individuals. these monopolies mainly aim for profits. public monopoly – a public monopoly is one that is owned by the government. these monopolies are set up for the welfare of the masses. A monopoly is a market structure that consists of a single seller or producer and no close substitutes. a monopoly limits available alternatives for its product and creates barriers for.
What Is Monopoly Defintion Types And Characteristics The Investors Book Characteristics. the three defining characteristics of a monopoly are existence of only one seller (and downward sloping demand curve), non existence of close substitutes (and low elasticity of demand) and very high barriers to entry. monopolist’s demand curve and marginal revenue. A legal monopoly is a monopoly that exists because of laws and regulations restrict competition. monopolists whose products are protected by intellectual property rights, such as trademarks, patents, and copyrights are good examples of legal monopolies. legal monopolies can also arise if the costs of complying with government regulations are. Monopoly meaning. a monopoly is a market where one firm (or manufacturer) is the sole supplier of certain goods or services. this firm faces no competition due to which it can set its own prices, thereby exercising full control over the market. the monopolist aims to generate high profits by selling products (or services) that do not have close. A monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular good. as a result, monopolies are characterized by a lack of competition within the market producing a good or service. monopoly: the graph shows a monopoly and the price (p) and change in price (p reg) as well as the output (q) and output change (q reg).
Monopoly Definition Types Characteristics Parsadi Monopoly meaning. a monopoly is a market where one firm (or manufacturer) is the sole supplier of certain goods or services. this firm faces no competition due to which it can set its own prices, thereby exercising full control over the market. the monopolist aims to generate high profits by selling products (or services) that do not have close. A monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular good. as a result, monopolies are characterized by a lack of competition within the market producing a good or service. monopoly: the graph shows a monopoly and the price (p) and change in price (p reg) as well as the output (q) and output change (q reg). Monopoly: definition and characteristics. monopoly in finance refers to a situation where a single entity or a group dominates an entire market, leading to limited competition and significant market power. understanding this concept is crucial for individuals and businesses as it affects consumer choices, business opportunities, and overall. The term pure monopoly refers to a market structure with a single firm producing all the market output. the firm is the sole producer of the goods or services, and there are no other substitutes.

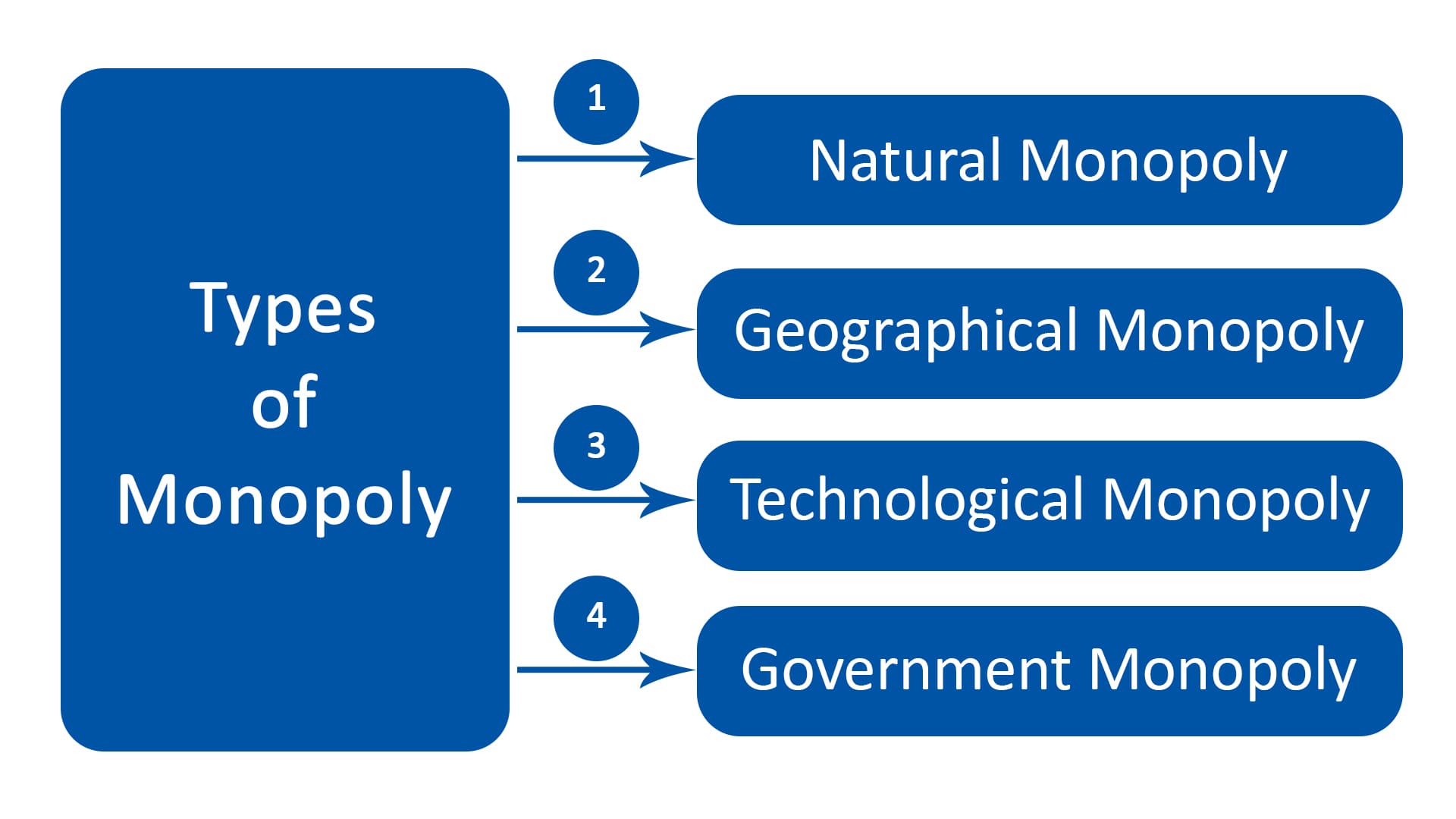
13 Types Of Monopoly 2024 Monopoly: definition and characteristics. monopoly in finance refers to a situation where a single entity or a group dominates an entire market, leading to limited competition and significant market power. understanding this concept is crucial for individuals and businesses as it affects consumer choices, business opportunities, and overall. The term pure monopoly refers to a market structure with a single firm producing all the market output. the firm is the sole producer of the goods or services, and there are no other substitutes.

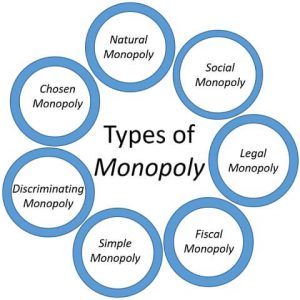
Types Of Monopoly Economics

What Is A Monopoly Definition And Examples Market Business 58 Off

Comments are closed.