Monopoly And Monopoly Power Aqa Economics Specification Topic 4 1 Mr

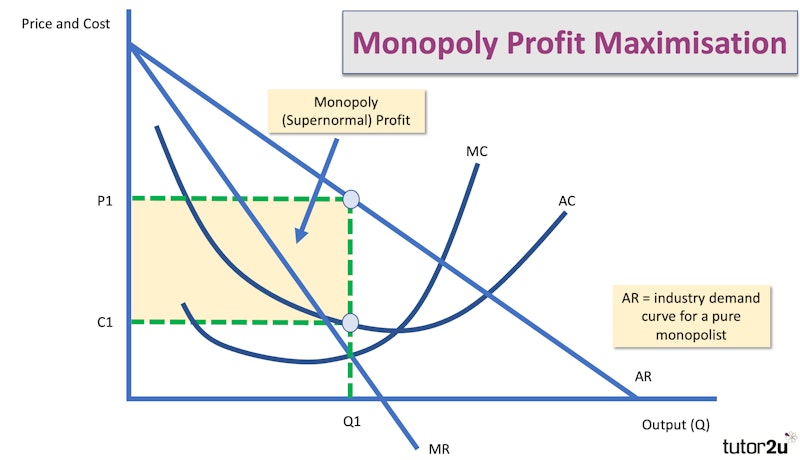
Monopoly And Monopoly Power Aqa Economics Specification Topic 4 1 Mr A monopoly has price setting power this makes it unlike a competitive market where the ar and mr curve would be the same and perfectly horizontal in a monopoly market, the ar and mr curves are different notice also that the ar curve is downward sloping this means the monopolist can change the price at the cost of demand for example, if the monopoly firm raises the price, they will. This page is about 'market structure, static efficiency, dynamic efficiency and resource allocation' taken from aqa economics syllabus topic 4.1. learn economics alongside the aqa a level economics specification. revise exactly what you need to know for the exam.

Monopoly And Monopoly Power Aqa Economics Specification Topic 4 1 Mr A monopoly is a market structure in which there is a single seller. there are no substitute products. the firm has complete market power and is able to set prices and control output. this allows the firm to maximise supernormal profit in the short run. there is no long run erosion of supernormal profit as competitors are unable to enter the. Aqa students should know: monopoly power and profits: the idea of monopoly power, which describes a scenario in which one company has a great influence over a specific market or industry, should be understood by students. because there is a lack of competition, monopolistic businesses frequently have the capacity to charge higher prices and. This editable and downloadable powerpoint covers many different aspects of monopoly and monopoly power. monopoly power is the market power that a single firm has when it's the only supplier of a particular good or service. in this situation, the firm has the ability to set prices without worrying about competition from other firms. If a consumer is willing to pay £18 to watch a movie and the price is £15, their consumer surplus is £3. producer surplus is the difference between the amount that the producer is willing to sell a product for and the price they actually do. e.g. if a producer is willing to sell a laptop for £450 and the price is £595, their producer.

A Level Economics Monopoly And Monopoly Power Teaching Resources This editable and downloadable powerpoint covers many different aspects of monopoly and monopoly power. monopoly power is the market power that a single firm has when it's the only supplier of a particular good or service. in this situation, the firm has the ability to set prices without worrying about competition from other firms. If a consumer is willing to pay £18 to watch a movie and the price is £15, their consumer surplus is £3. producer surplus is the difference between the amount that the producer is willing to sell a product for and the price they actually do. e.g. if a producer is willing to sell a laptop for £450 and the price is £595, their producer. Here are two methods to explain why there is a welfare loss (also known as a deadweight loss) in monopoly: method 1 . to show there is welfare loss from monopoly, we need to compare two outcomes: 1. the monopoly profit maximising outcome. the monopoly chooses its output level where mr=mc. then it prices on the average revenue curve. 2. 4.1.5.6 monopoly and monopoly power. a pure monopoly is a sole seller in a market. firms operating in monopolistically competitive and oligopolistic markets are price makers and have varying degrees of monopoly power. monopoly power is influenced by factors such as barriers to entry, the number of competitors, advertising and the degree of.
Monopoly Power In Markets Reference Library Economics Tutor2u Here are two methods to explain why there is a welfare loss (also known as a deadweight loss) in monopoly: method 1 . to show there is welfare loss from monopoly, we need to compare two outcomes: 1. the monopoly profit maximising outcome. the monopoly chooses its output level where mr=mc. then it prices on the average revenue curve. 2. 4.1.5.6 monopoly and monopoly power. a pure monopoly is a sole seller in a market. firms operating in monopolistically competitive and oligopolistic markets are price makers and have varying degrees of monopoly power. monopoly power is influenced by factors such as barriers to entry, the number of competitors, advertising and the degree of.

Monopoly And Monopoly Power Aqa Economics Specification Topic 4 1 Mr

4 1 5 6 Monopoly And Monopoly Power Aqa A Level Economics Teaching

Comments are closed.