Mitochondria Biogenesis And Mtor

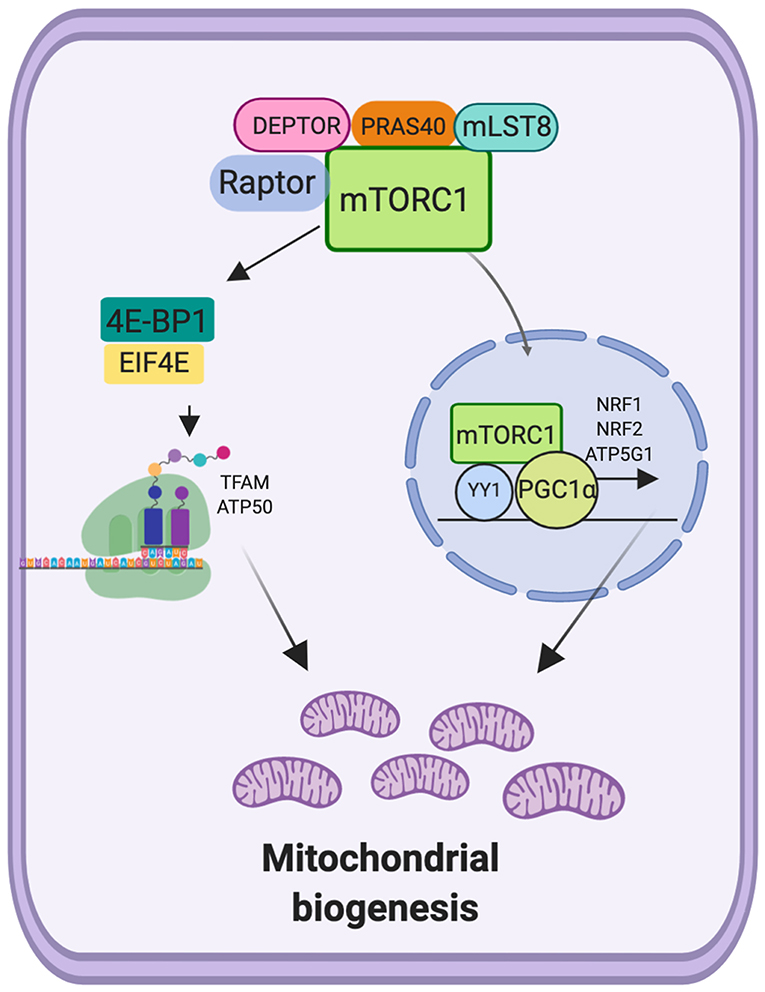
Mitochondria Biogenesis And Mtor In addition to stimulation of mitochondrial biogenesis by antagonizing 4e bp dependent translational repression of mitochondria related mrnas, mtorc1 inhibits mitochondrial degradation by suppressing autophagy (figures s6b–s6d). these findings suggest coordination of translational and autophagy programs that underpin important biological. We demonstrate that mtorc1 controls mitochondrial activity and biogenesis by selectively promoting translation of nucleus encoded mitochondria related mrnas via inhibition of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4e (eif4e) binding proteins (4e bps).

Mitochondria Biogenesis And Mtor Mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mtorc1) as a regulator of mitochondrial functions. mtorc1 can be activated by growth factor, and can regulate the mitochondrial biogenesis, mitophagy, fission and fusion processes, glutaminolysis, and mitochondrial oncometabolites generation. The observation that mtor inhibition leads to mitochondrial hyperfusion could provide an explanation for the cytostatic action of mtor inhibitors (benjamin et al., 2011). it has previously been suggested that the induction of mitochondrial hyperfusion during starvation renders mitochondria refractive to autophagy and protects cells against. Mtor activity is central to energy homeostasis, inasmuch as it coordinates protein synthesis, cell growth and proliferation, generation of metabolic intermediates, and mitochondrial biogenesis and functions (fig. 1). accordingly, dysregulation of mtor signaling and mitochondrial dysfunction underpin aging and diseases such as cancer, diabetes. That means the regulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis by mtor occurs antagonistically. mitophagy and cardiovascular disease. atherosclerosis. atherosclerosis (as) is, a chronic.
Frontiers Mtorc1 As A Regulator Of Mitochondrial Functions And A Mtor activity is central to energy homeostasis, inasmuch as it coordinates protein synthesis, cell growth and proliferation, generation of metabolic intermediates, and mitochondrial biogenesis and functions (fig. 1). accordingly, dysregulation of mtor signaling and mitochondrial dysfunction underpin aging and diseases such as cancer, diabetes. That means the regulation of mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis by mtor occurs antagonistically. mitophagy and cardiovascular disease. atherosclerosis. atherosclerosis (as) is, a chronic. Betz, c. et al. feature article: mtor complex 2 akt signaling at mitochondria associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (mam) regulates mitochondrial physiology. proc. natl acad. sci. usa 110. Translation augments mitochondrial biogenesis, respiration, and energy production to drive cell growth and proliferation (gandin et al., 2016; morita et al., 2013). strikingly, the selected mrnas also encode a protein relevant to mitochondrial fission, mitochondrial fission process protein 1 (mtfp1), also called mtp18. (larsson et al., 2012).
Mechanistic Target Of Rapamycin Complex 1 Mtorc1 As A Regulator Of Betz, c. et al. feature article: mtor complex 2 akt signaling at mitochondria associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (mam) regulates mitochondrial physiology. proc. natl acad. sci. usa 110. Translation augments mitochondrial biogenesis, respiration, and energy production to drive cell growth and proliferation (gandin et al., 2016; morita et al., 2013). strikingly, the selected mrnas also encode a protein relevant to mitochondrial fission, mitochondrial fission process protein 1 (mtfp1), also called mtp18. (larsson et al., 2012).

The Link Of Mtor Signaling With Podocyte Mitochondrial Function Mtor

Comments are closed.