Minocycline Teeth
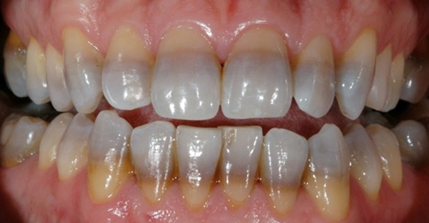
Tooth Staining Awareness Of Oral Health Effects Of Tetracycline And Minocycline works by keeping the number of bacteria from growing. lowering the amount of bacteria helps to reduce inflammation and swelling in your mouth, and the amount of bleeding around the teeth. minocycline is placed in deep gum pockets next to your teeth in order to reduce the depth of the pockets. this medicine will be applied by your. Minocycline stains teeth differently to tetracycline and doxycycline. tetracyclines stain teeth through their ability to form a complex with calcium ions, 2 via chelation, and this complex is preferential deposited in dentine and to lesser extent enamel. 12 given the mechanisms by which minocycline stains teeth it can stain teeth at any age.
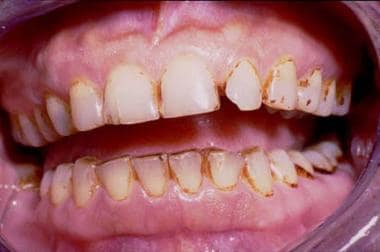
Minocycline Teeth Minocycline is used to treat pimples and red bumps (non nodular inflammatory lesions) that occur with moderate to severe acne vulgaris in patients 12 years of age and older. minocycline capsules are used to treat bacterial infections in many different parts of the body. it is also used to treat anthrax infection and other infections in patients. A drug dose of more than 3 grams or when use exceeds 10 days often can cause teeth staining. minocycline and doxycycline react with the glycoproteins of the dental pellicle, a protein film that coats the tooth enamel to help prevent the deposition of salivary calcium phosphate, which increases one’s risk of periodontitis. Redness, blistering, peeling, or loosening of the skin, including inside the mouth. severe diarrhea, fever. unusual vaginal discharge, itching, or odor. side effects that usually do not require medical attention (report to your care team if they continue or are bothersome): change in tooth color. diarrhea. Summary:. the overall prevalence of staining has been reported to be 3 4% for tetracycline and 3 6% for minocycline. prevention of tetracycline or minocycline induced teeth staining or discoloration is most easily done by avoiding tetracycline use during periods of mineralization (or calcification), which generally occurs in children up to the age of 8 years old.
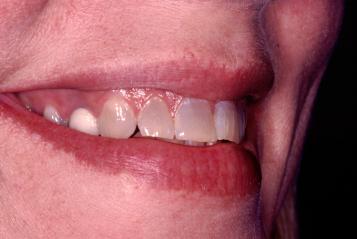
Minocycline Discoloration Of Teeth Redness, blistering, peeling, or loosening of the skin, including inside the mouth. severe diarrhea, fever. unusual vaginal discharge, itching, or odor. side effects that usually do not require medical attention (report to your care team if they continue or are bothersome): change in tooth color. diarrhea. Summary:. the overall prevalence of staining has been reported to be 3 4% for tetracycline and 3 6% for minocycline. prevention of tetracycline or minocycline induced teeth staining or discoloration is most easily done by avoiding tetracycline use during periods of mineralization (or calcification), which generally occurs in children up to the age of 8 years old. The prevalence of tooth discoloration attributed to minocycline use is estimated to be within the range of 3% to 6%. [20] [21] notably, hepatotoxicity is a potential concern associated with minocycline usage, and therefore a risk of exacerbating preexisting renal failure should also be considered. The two differ in that minocycline can affect fully erupted teeth 7,9,10 whereas tetracycline affects the unerupted, uncalcified dentition leading to avoidance of the drug during childhood. 7.

Comments are closed.