Midshaft Humerus Fracture

Humeral Shaft Fractures Trauma Orthobullets Learn about the epidemiology, anatomy, classification, presentation, imaging, and treatment of humeral shaft fractures. find out the common mechanisms, associated conditions, and complications of these fractures, especially midshaft humerus fractures. Learn about the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of nonstress fractures of the midshaft of the humerus in adults. this article is a limited summary of the clinical anatomy, pathophysiology, and management of this condition.

Humerus Fracture Physiotherapy The humerus (arm bone) is the upper arm's only long bone. humeral shaft fractures comprise 1 5% of all bony fractures (see image. oblique humeral shaft fracture). these injuries have a bimodal age distribution. in young people, humeral shaft fractures are mostly caused by high energy trauma. in older individuals, the damage may be caused by a low impact force.[1]. A comprehensive overview of humeral shaft fractures, including anatomy, classification, surgical approaches, indications, and outcomes. learn about the midshaft humerus fracture, a common injury that requires careful reduction and fixation. Traditionally, humeral shaft fractures have been described according to the following features: location proximal, middle, or distal. type of fracture line transverse, oblique, spiral, comminuted, or segmental. open or closed status. this article focuses on midshaft humerus fractures. no classification scheme for humeral shaft fractures has. The proximal end of your humerus is the top. the distal end is the bottom. so, if you have a proximal humerus fracture, your upper arm bone is broken near its top — the end that connects to your shoulder. similarly, if you have a distal humerus fracture that means your bone is broken at the bottom, closer to your elbow.
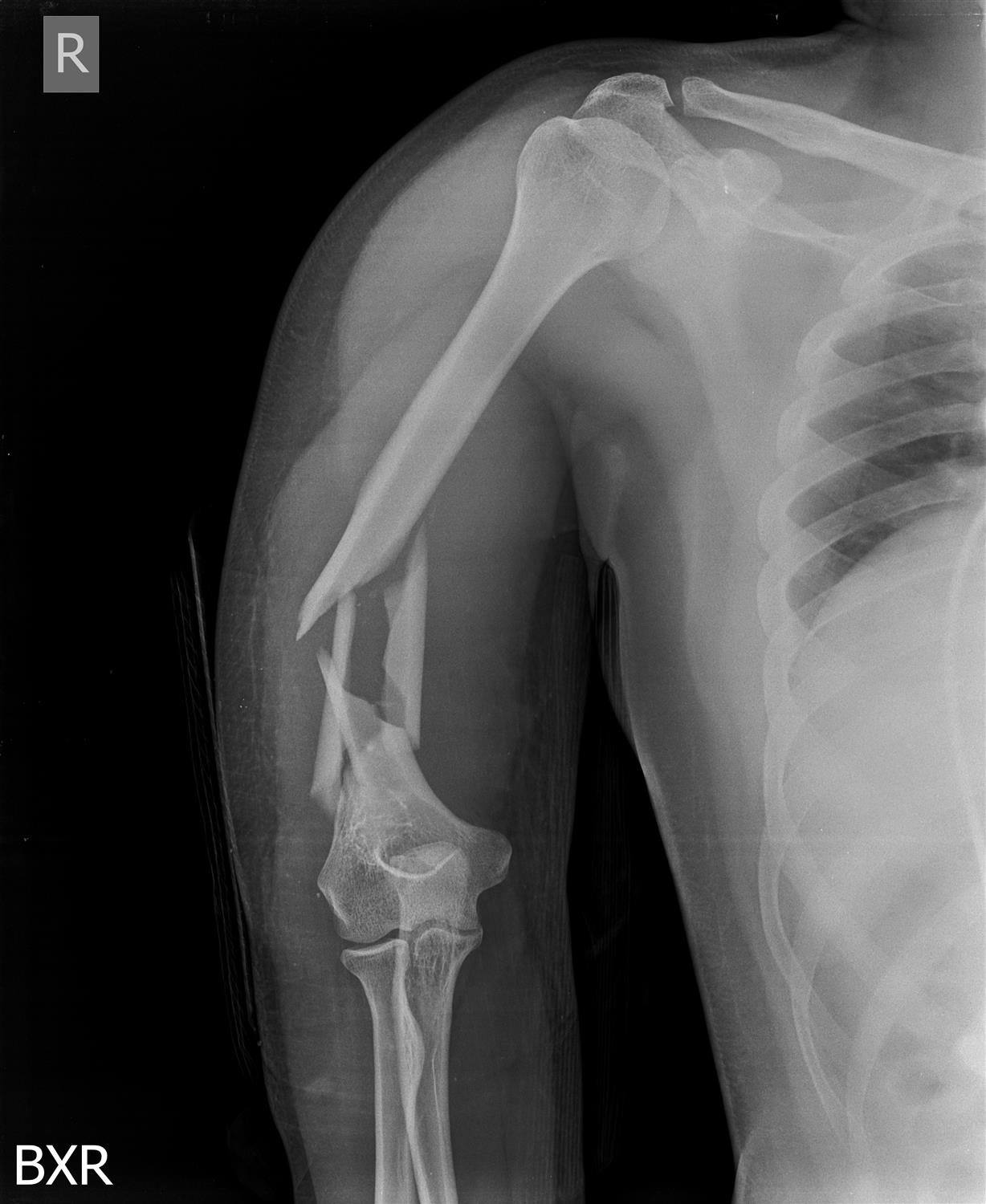
Humeral Shaft Fractures Trauma Orthobullets Traditionally, humeral shaft fractures have been described according to the following features: location proximal, middle, or distal. type of fracture line transverse, oblique, spiral, comminuted, or segmental. open or closed status. this article focuses on midshaft humerus fractures. no classification scheme for humeral shaft fractures has. The proximal end of your humerus is the top. the distal end is the bottom. so, if you have a proximal humerus fracture, your upper arm bone is broken near its top — the end that connects to your shoulder. similarly, if you have a distal humerus fracture that means your bone is broken at the bottom, closer to your elbow. It connects to the shoulder blade at the top and the forearm at the bottom. the middle part of the humerus is called the humeral shaft. a break in this part is known as a humeral shaft fracture. muscles attached to the humerus help you move your shoulder and elbow. figure 1: skeleton model showing the humerus and how it attaches to the shoulder. Mid shaft humerus fractures occur in the middle of the upper arm bone, away from the shoulder and elbow joints. they are commonly caused by falls and may require surgery, physical therapy, or a sling to heal properly.
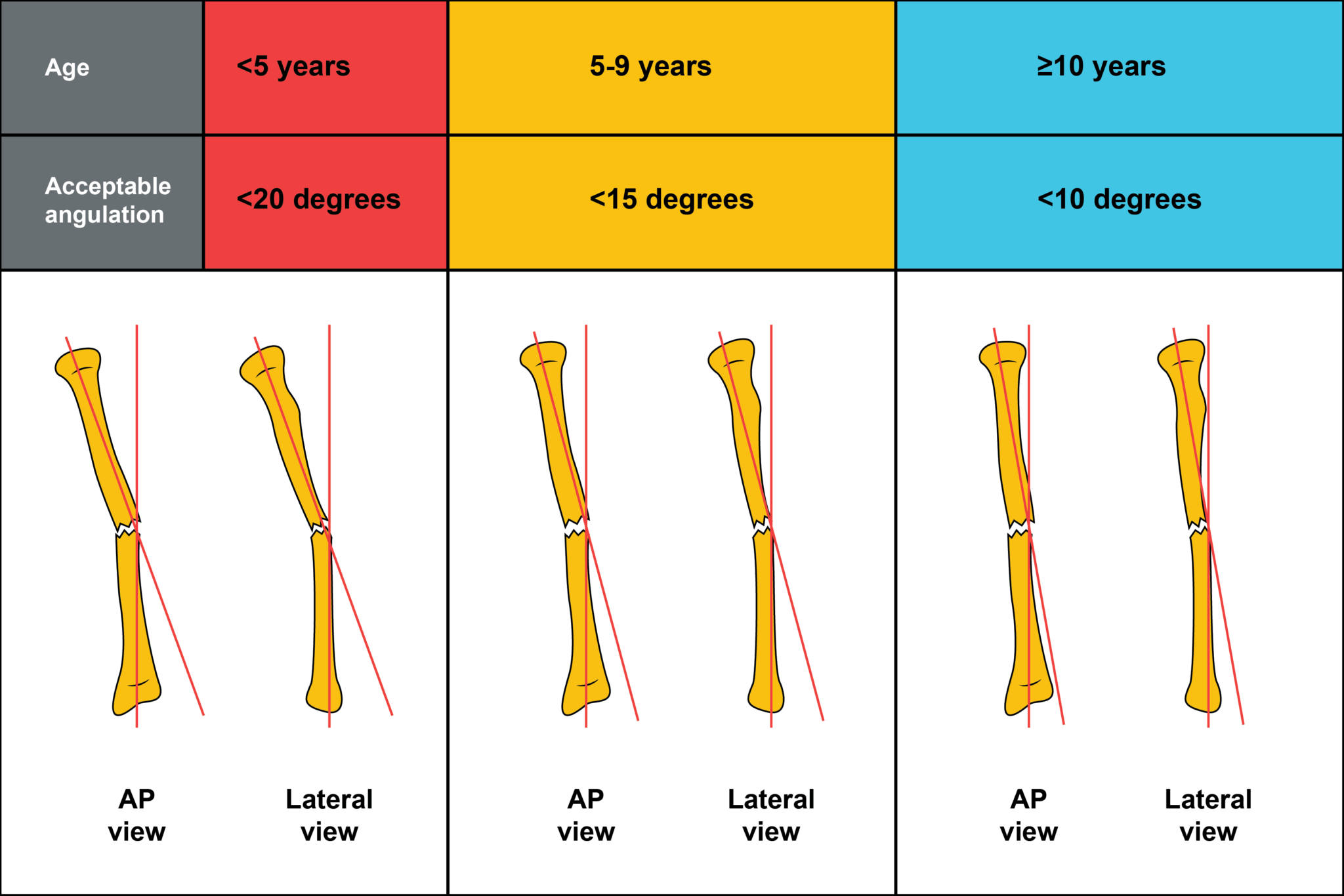
Midshaft Radius And Ulna Fractures Bipmd It connects to the shoulder blade at the top and the forearm at the bottom. the middle part of the humerus is called the humeral shaft. a break in this part is known as a humeral shaft fracture. muscles attached to the humerus help you move your shoulder and elbow. figure 1: skeleton model showing the humerus and how it attaches to the shoulder. Mid shaft humerus fractures occur in the middle of the upper arm bone, away from the shoulder and elbow joints. they are commonly caused by falls and may require surgery, physical therapy, or a sling to heal properly.

Humeral Fracture Spiral Midshaft Image Radiopaedia Org

Comments are closed.