Microeconomics Unit 3 Complete Summary Production Perfect Competition

Ap Micro Microeconomics Unit 3 Production Cost Perfect Competition Review This video covers all of the key points of unit 3 from the ap microeconomics course exam description (ced). short costs, long run cost, accounting vs economi. Lastly, the model of perfect competition is dissected to illustrate an idealized market structure where numerous small firms compete against each other, leading to significant implications for prices and production levels.this comprehensive unit provides a logical progression through key microeconomic concepts that influence the real world.
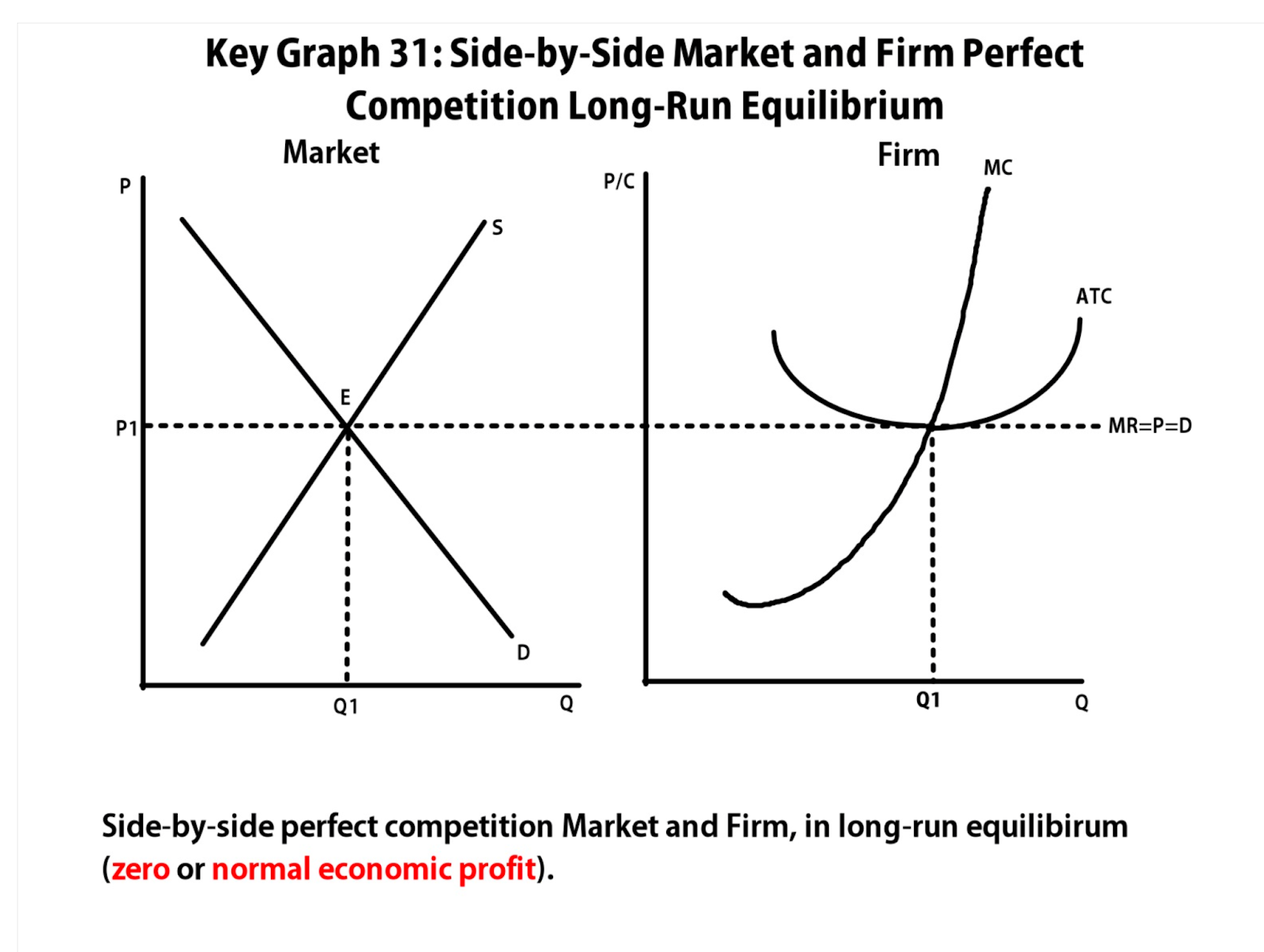
Unit 3 Production Cost And The Perfect Competition Model Guide Quiz. unit test. production, cost, and the perfect competition model: quiz 1. production, cost, and the perfect competition model: quiz 2. firms’ short run decisions to produce and long run decisions to enter or exit a market. increasing, decreasing, and constant cost industries. Q chat. unit 3 focuses on firm behavior and culminates with an introduction to the perfect competition model, which will form a basis of comparison for other market structures in the next unit. this unit builds on the idea of supply, which was introduced in the previous unit, and explores in more detail what drives the decisions that firms make. Ap microeconomics unit 3: production, cost, and the perfect competition model. in this unit, you'll apply the supply and demand concepts you learned in unit 2 to individual firms to uncover production and cost curves. then, you'll build on top of this to derive perfect competition. note: for best results, click to highlight and copy paste this. Mr = mc. three characteristics of mr=mc rule: rule applies to all markets structures (pc, monopolies, etc.) the rule applies only if price is above avc. rule can be restated p = mc for perfectly competitive firms (because mr = p) side by side graph for perfectly completive industry and firm.

Ap Micro Microeconomics Unit 3 Production Cost Perfect Competition Ap microeconomics unit 3: production, cost, and the perfect competition model. in this unit, you'll apply the supply and demand concepts you learned in unit 2 to individual firms to uncover production and cost curves. then, you'll build on top of this to derive perfect competition. note: for best results, click to highlight and copy paste this. Mr = mc. three characteristics of mr=mc rule: rule applies to all markets structures (pc, monopolies, etc.) the rule applies only if price is above avc. rule can be restated p = mc for perfectly competitive firms (because mr = p) side by side graph for perfectly completive industry and firm. Or you can use the buttons at the top of this page to pick a specific ap microeconomics and unit 1: basic economic concepts, unit 2: supply and demand, unit 3: production, cost, and the perfect competition model, unit 4: imperfect competition, unit 5: factor markets, unit 6: market failure and the role of government to explore all the flashcard. Total cost divided by quantity of output produced. on average, how much does each individual unit of output cost to produce. atc is u shaped because afc and avc move in opposite directions as output rises. atc= tc q. u shaped average total cost curve. atc falls at low levels of output, then rises at higher levels.

Comments are closed.