Microeconomics Market Power Monopoly And Monopsony Pptx

Microeconomics Market Power Monopoly And Monopsony Pptx 1 of 41. download now. microeconomics market power monopoly and monopsony.pptx download as a pdf or view online for free. Chapter 10 monopoly and monopsony | ppt. ai enhanced description. yesica adicondro. follow. this document discusses monopoly and monopoly power. it begins by reviewing perfect competition and then defines monopoly as a market with one seller and many buyers of a unique product where there are barriers to entry.
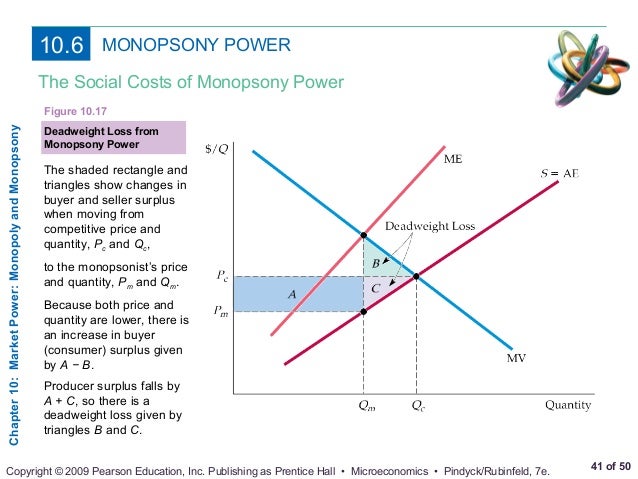
Em Sofyan Monopoly And Monopsony Market Market where there is only one buyer and one seller bilateral monopoly is rare, however, markets with a small number of sellers with monopoly power selling to a market with few buyers with monopsony power is more common even with bargaining, in general, monopsony and monopoly power will counteract each other chapter 10. Monopoly in microeconomics. 1) a monopoly is a market structure with a single seller of a product without close substitutes. 2) the key characteristics of a monopoly are that it is the sole price maker and faces a downward sloping demand curve, unlike competitive firms which are price takers. 3) barriers to entry, such as government licenses. Chapter 10 outline. sep 20, 2012. 520 likes | 1.01k views. chapter 10 outline. 10.1 monopoly 10.2 monopoly power 10.3 sources of monopoly power 10.4 the social costs of monopoly power 10.5 monopsony 10.6 monopsony power 10.7 limiting market power: the antitrust laws. market power: monopoly and monopsony. 10.1 monopoly 10.2 monopoly power 10.3 sources of monopoly power 10.4 the social costs of monopoly power 10.5 monopsony 10.6 monopsony power 10.7 limiting market power: the antitrust laws c h a p t e r 10 prepared by: fernando quijano, illustrator market power: monopoly and monopsony chapter outline.
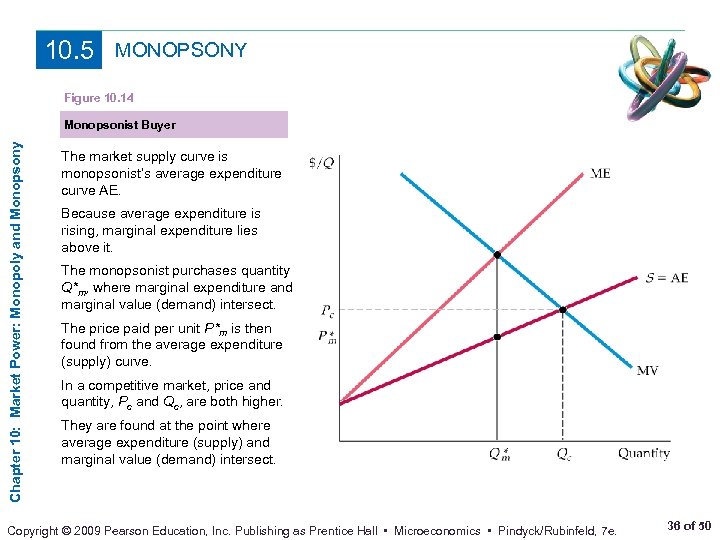
Chapter 10 Market Power Monopoly And Monopsony Prepared Chapter 10 outline. sep 20, 2012. 520 likes | 1.01k views. chapter 10 outline. 10.1 monopoly 10.2 monopoly power 10.3 sources of monopoly power 10.4 the social costs of monopoly power 10.5 monopsony 10.6 monopsony power 10.7 limiting market power: the antitrust laws. market power: monopoly and monopsony. 10.1 monopoly 10.2 monopoly power 10.3 sources of monopoly power 10.4 the social costs of monopoly power 10.5 monopsony 10.6 monopsony power 10.7 limiting market power: the antitrust laws c h a p t e r 10 prepared by: fernando quijano, illustrator market power: monopoly and monopsony chapter outline. 1 monopsony 1 14.01 principles of microeconomics, fall 2007 chia hui chen november 14, 2007 lecture 24 monopoly and monopsony outline 1. chap 10: monopsony 2. chap 10: monopoly power 3. chap 11: price discrimination 1 monopsony a monopsony is a market in which there is a single buyer. typically, a monop. Prices set about 25% above mc. d e mc mc p mc ©2005 pearson education, inc. chapter 10 55 sources of monopoly power the less elastic the demand curve, the more monopoly power a firm has the firm’s elasticity of demand is determined by: 1) elasticity of market demand 2) number of firms in market 3) the interaction among firms ©2005 pearson.

Buec 311 Market Power Monopoly And Monopsony W17 Handout Pptx Market 1 monopsony 1 14.01 principles of microeconomics, fall 2007 chia hui chen november 14, 2007 lecture 24 monopoly and monopsony outline 1. chap 10: monopsony 2. chap 10: monopoly power 3. chap 11: price discrimination 1 monopsony a monopsony is a market in which there is a single buyer. typically, a monop. Prices set about 25% above mc. d e mc mc p mc ©2005 pearson education, inc. chapter 10 55 sources of monopoly power the less elastic the demand curve, the more monopoly power a firm has the firm’s elasticity of demand is determined by: 1) elasticity of market demand 2) number of firms in market 3) the interaction among firms ©2005 pearson.

Comments are closed.