Micro Module 4 Price Elasticity Of Demand 2 Cross Price Elasticity
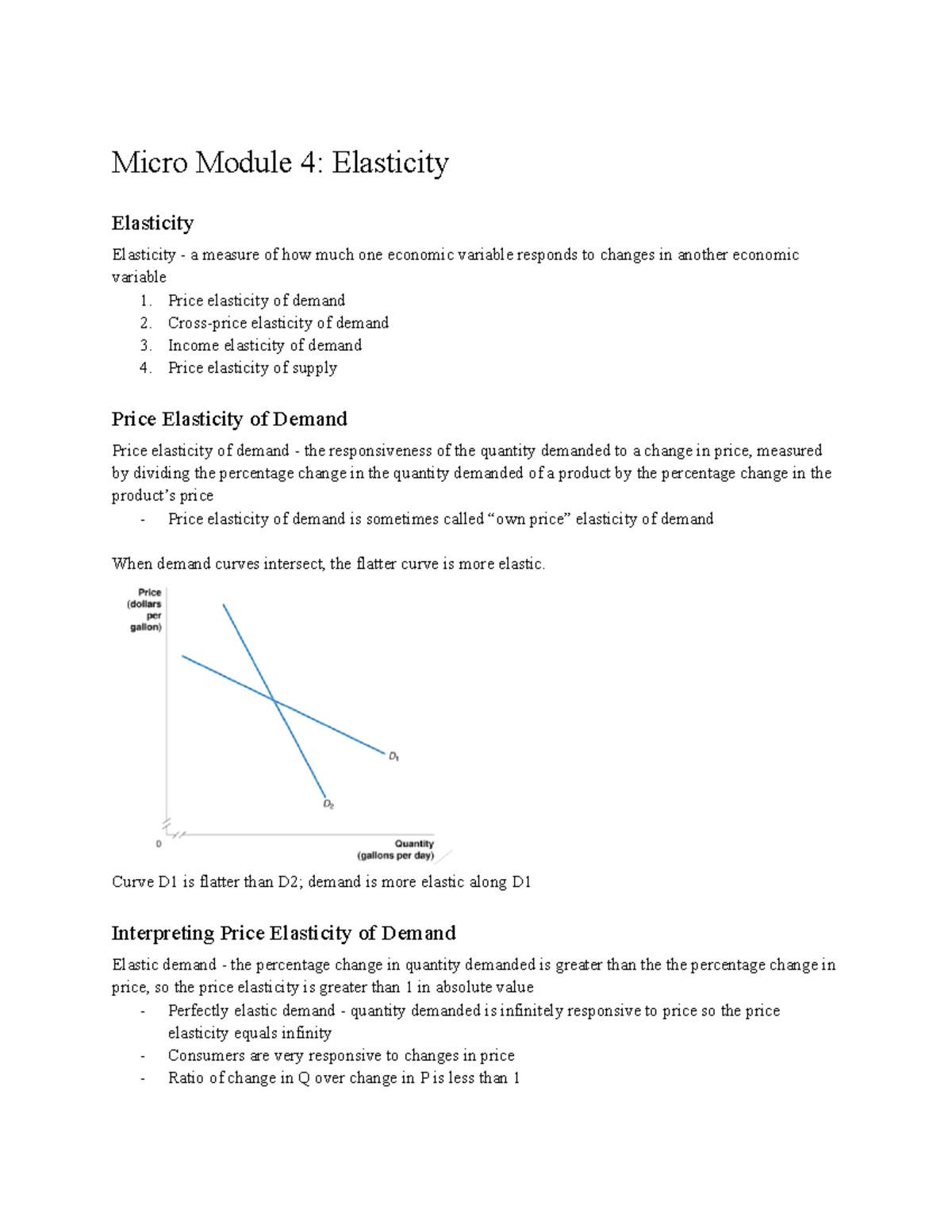
Micro Module 4 Price Elasticity Of Demand 2 Cross Price Elasticity Professor michael stone module 4 lecture notes micro module elasticity elasticity elasticity measure of how much one economic variable responds to changes in. Determinants of elasticity example. perfect inelasticity and perfect elasticity of demand. constant unit elasticity. total revenue and elasticity. more on total revenue and elasticity. elasticity and strange percent changes. price elasticity of demand and price elasticity of supply. elasticity in the long run and short run.

Cross Price Elasticity Of Demand Economics Tutor2u Then, those values can be used to determine the price elasticity of demand: [latex]\displaystyle\text{price elasticity of demand}=\frac{6.9\text{ percent}}{ 15.5\text{ percent}}= 0.45[ latex] the elasticity of demand between these two points is 0.45, which is an amount smaller than 1. that means that the demand in this interval is inelastic. Terms in this set (10) what is elasticity? elasticity refers to the degree to which individuals, consumers or producers change their demand or the amount supplied in response to price or income changes. important terms: • elastic: e > 1. • inelastic: e < 1. The cross price elasticity of demand is computed similarly: the initial quantity of sprockets demanded is 9 and the subsequent quantity demanded is 10 (q1 = 9, q2 = 10). using the midpoint formula, we can calculate the percent change in the quantity of sprockets demanded: the percent change in the quantity of sprockets demanded is 10.5%. Cross elasticity of demand. cross elasticity of demand (xed) measures the percentage change in quantity demand for a good after a change in the price of another. for example: if there is an increase in the price of tea by 10%. and the quantity demanded for coffee increases by 2%, then the cross elasticity of demand = 2 10 = 0.2.
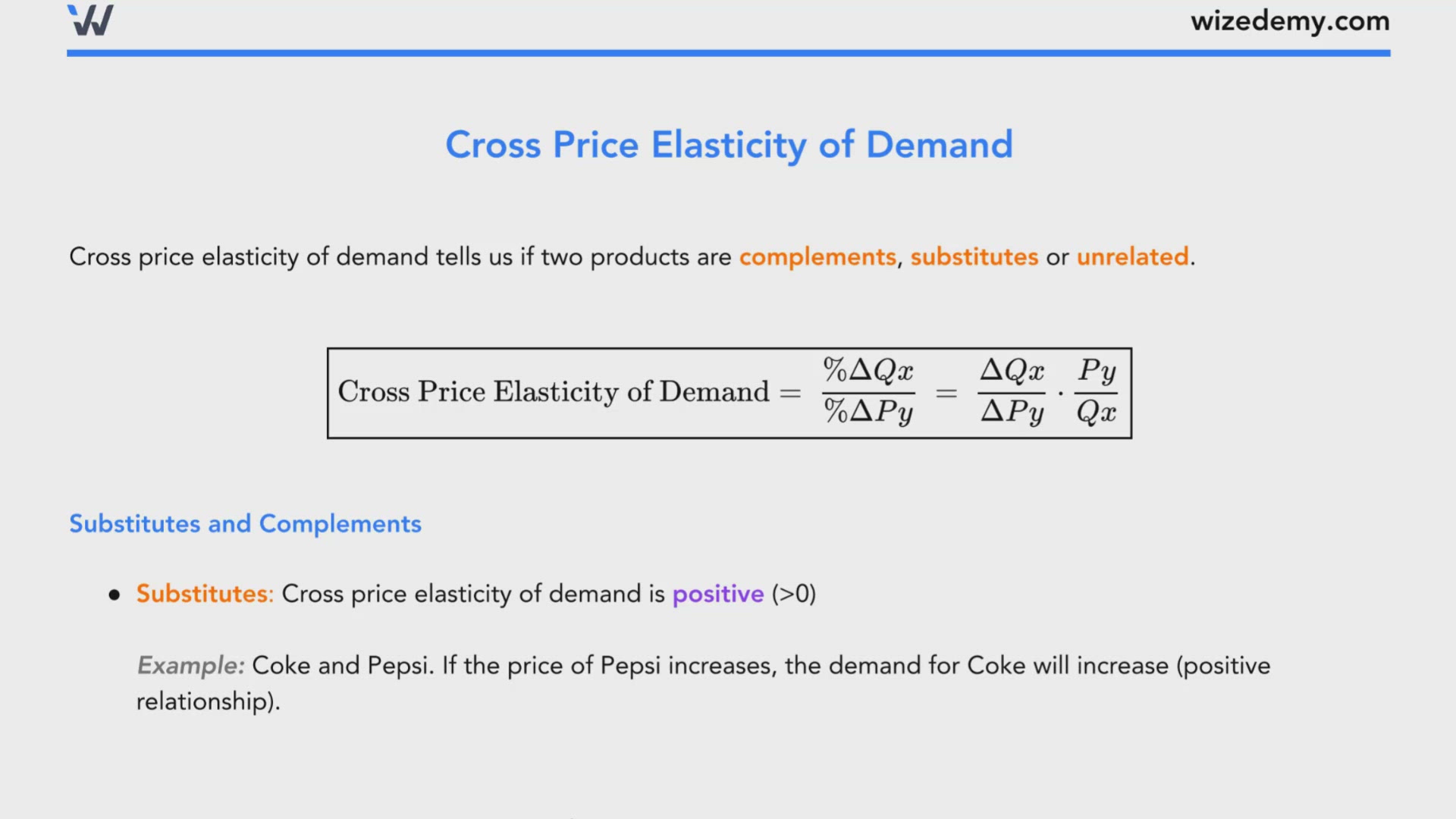
Cross Price Elasticity Wize University Microeconomics Textbook Wizeprep The cross price elasticity of demand is computed similarly: the initial quantity of sprockets demanded is 9 and the subsequent quantity demanded is 10 (q1 = 9, q2 = 10). using the midpoint formula, we can calculate the percent change in the quantity of sprockets demanded: the percent change in the quantity of sprockets demanded is 10.5%. Cross elasticity of demand. cross elasticity of demand (xed) measures the percentage change in quantity demand for a good after a change in the price of another. for example: if there is an increase in the price of tea by 10%. and the quantity demanded for coffee increases by 2%, then the cross elasticity of demand = 2 10 = 0.2. Next, we take the results of our calculations and plug them into the formula for price elasticity of supply: price elasticity of supply = % change in quantity % change in price = 26.1 7.4 = 3.53. again, as with the elasticity of demand, the elasticity of supply is not followed by any units. Figure 4.4: price and its impact on elasticity of demand. another implication is the concept of the elasticity equation and slope. students often believe that the slope of the demand curve is elasticity, but this is not true. consider this re write of the equation for price elasticity of demand:.
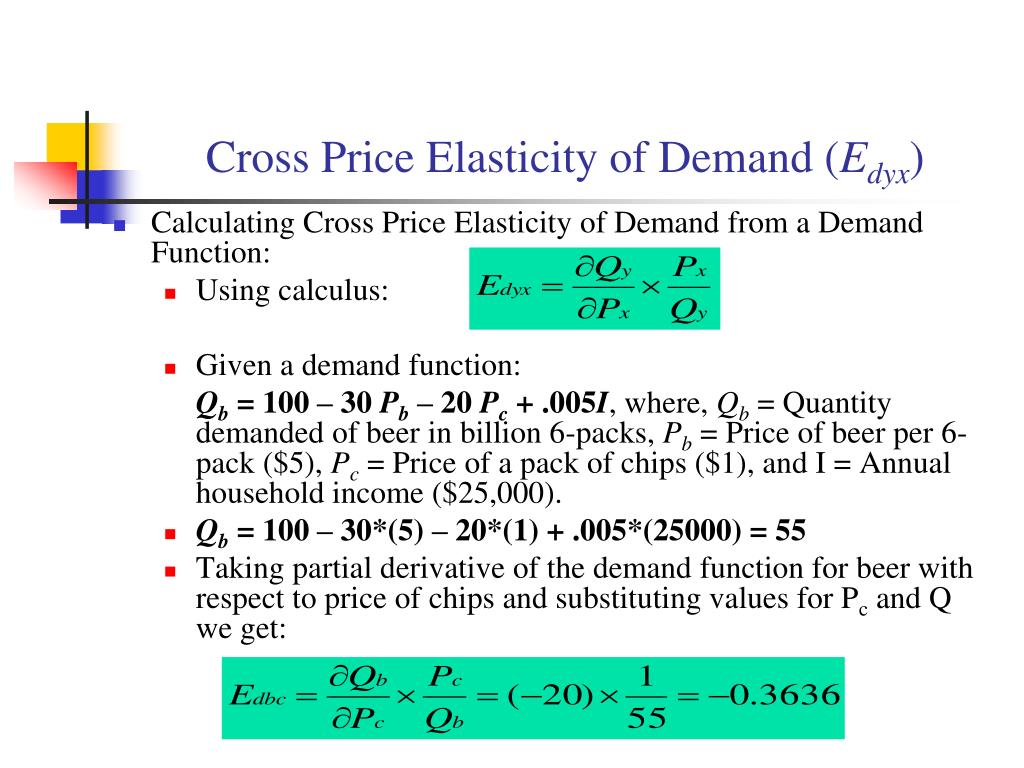
Cross Price Elasticity Of Demand Formula Next, we take the results of our calculations and plug them into the formula for price elasticity of supply: price elasticity of supply = % change in quantity % change in price = 26.1 7.4 = 3.53. again, as with the elasticity of demand, the elasticity of supply is not followed by any units. Figure 4.4: price and its impact on elasticity of demand. another implication is the concept of the elasticity equation and slope. students often believe that the slope of the demand curve is elasticity, but this is not true. consider this re write of the equation for price elasticity of demand:.

Comments are closed.