Metastatic Lung Radiopaedia

Metastatic Lung Radiopaedia Pulmonary metastases are usually asymptomatic or can present with hemoptysis, dyspnea, and pneumothorax. symptoms more commonly arise from the primary tumor, extrapulmonary metastates or systemic effects 5. pulmonary thrombotic microangiopathy is an exception, causing hypoxemia, pulmonary hypertension, cor pulmonale, rapid decline and death 10. Cannonball metastases refer to multiple large, well circumscribed, round pulmonary metastases that appear not unsurprisingly like cannonballs. the french terms " envolée de ballons " and " lâcher de ballons ", which translate to "balloons release", are also used to describe this same appearance. metastases with such an appearance are.

Metastatic Lung Radiopaedia Most pulmonary metastases occurring as single or multiple nodules are asymptomatic. when present, symptoms are nonspecific and include cough, hemoptysis, and shortness of breath. the most common clinical manifestation of lymphatic spread of tumor is dyspnea. the dyspnea is typically insidious in onset but tends to progress rapidly. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer related mortality in the united states, and accurate staging plays a vital role in determining prognosis and treatment. the recently revised eighth edition of the tnm staging system for lung cancer defines new t and m descriptors and updates stage groupings on the basis of substantial differences in survival. there are new t descriptors that are based. Metastatic seeding to the pleura (cancers of the lung, breast, pancreas, and stomach) [4] frequently occurs, due to hematogenous dissemination with extension to the pleura, with lymphangitic spread, or originating from established hepatic metastases. radiologically, pleural metastases may appear as nodules or plaquelike formations on plain. Radiography. the most common radiographic pattern of pulmonary metastasis is the presence of multiple nodules, ranging in size from 3 mm to 15 cm or more. the nodules are more common in the lung bases (because of higher blood flow than upper lobes) and in the outer third of the lungs in the subpleural region.
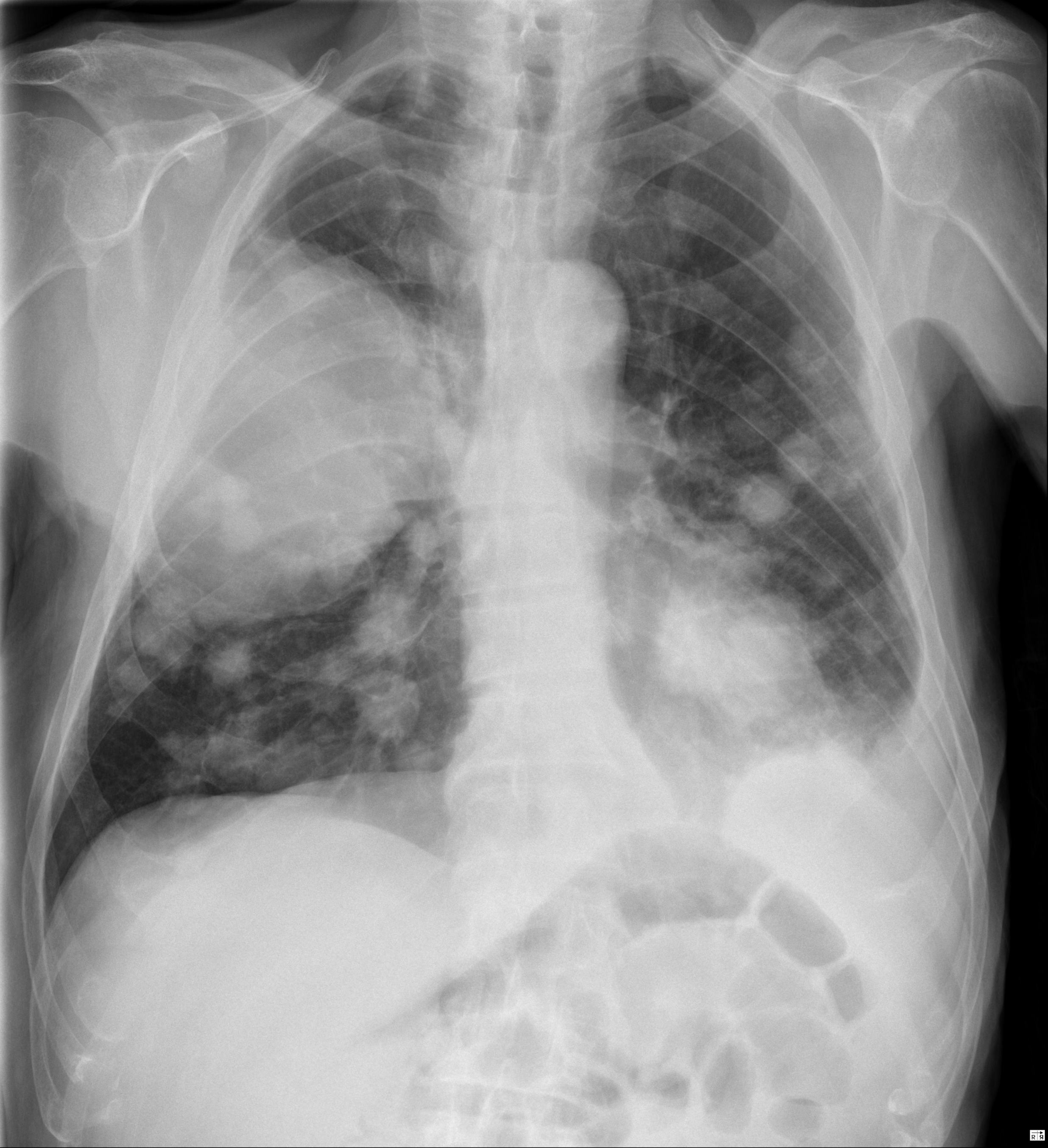
Advanced Metastatic Lung Cancer Image Radiopaedia Org Metastatic seeding to the pleura (cancers of the lung, breast, pancreas, and stomach) [4] frequently occurs, due to hematogenous dissemination with extension to the pleura, with lymphangitic spread, or originating from established hepatic metastases. radiologically, pleural metastases may appear as nodules or plaquelike formations on plain. Radiography. the most common radiographic pattern of pulmonary metastasis is the presence of multiple nodules, ranging in size from 3 mm to 15 cm or more. the nodules are more common in the lung bases (because of higher blood flow than upper lobes) and in the outer third of the lungs in the subpleural region. Metastatic pulmonary calcification (mpc) is a consequence of calcium deposition in pulmonary parenchyma . the most common cause is chronic renal failure [ 1 , 2 ], but mpc can also occur in a variety of disorders, including primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism, intravenous calcium therapy and massive osteolysis from metastases or multiple. Lung is a common site of metastases; usually multiple, bilateral, sharply outlined, rapidly growing, more pleomorphic and necrotic than lung primaries. may appear as multiple discrete nodules in periphery of lung or as lymphangitic carcinomatosis (peribronchial and perivascular patterns via lymphatics) rarely appear as intralymphatic.

Metastatic Lung Cancer Image Radiopaedia Org Metastatic pulmonary calcification (mpc) is a consequence of calcium deposition in pulmonary parenchyma . the most common cause is chronic renal failure [ 1 , 2 ], but mpc can also occur in a variety of disorders, including primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism, intravenous calcium therapy and massive osteolysis from metastases or multiple. Lung is a common site of metastases; usually multiple, bilateral, sharply outlined, rapidly growing, more pleomorphic and necrotic than lung primaries. may appear as multiple discrete nodules in periphery of lung or as lymphangitic carcinomatosis (peribronchial and perivascular patterns via lymphatics) rarely appear as intralymphatic.

Metastatic Pulmonary Calcification Radiology Reference Article
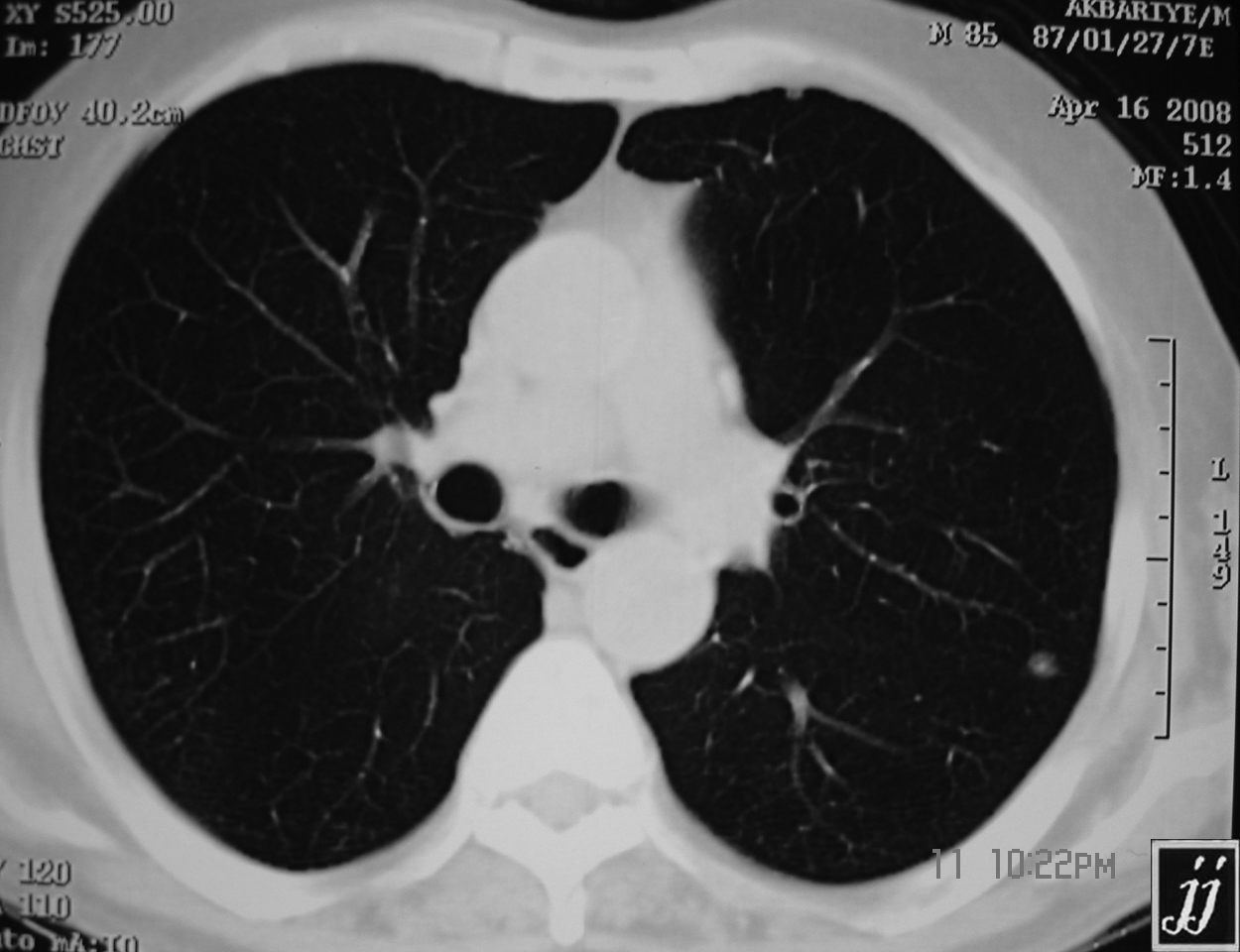
Lung Metastasis Radiopaedia

Comments are closed.