Meiosis Ii Stages And Significance Of Meiosis Ii Cell Division

Meiosis Ii Phases And Significance Of Meiosis Ii Cell Division The four stages of meiosis ii are as follows: . prophase ii – it immediately sets off after the cytokinesis when the daughter cells are formed. the chromosomes begin to condense accompanied by the dissolution of the nuclear membrane and the disappearance of the golgi apparatus and er complex. metaphase ii – the chromosomes are connected to. Its goal is to make daughter cells with exactly half as many chromosomes as the starting cell. to put that another way, meiosis in humans is a division process that takes us from a diploid cell—one with two sets of chromosomes—to haploid cells—ones with a single set of chromosomes. in humans, the haploid cells made in meiosis are sperm.
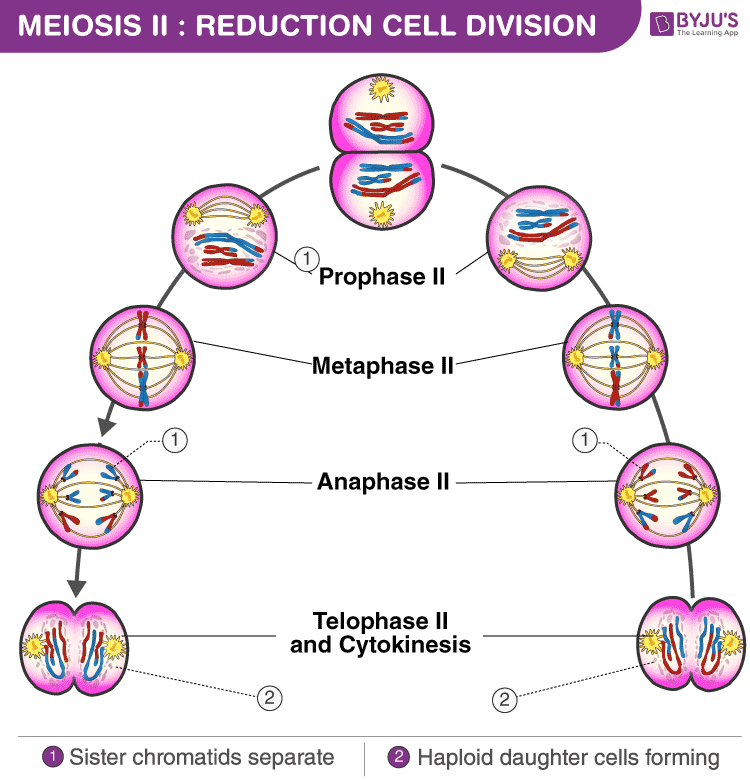
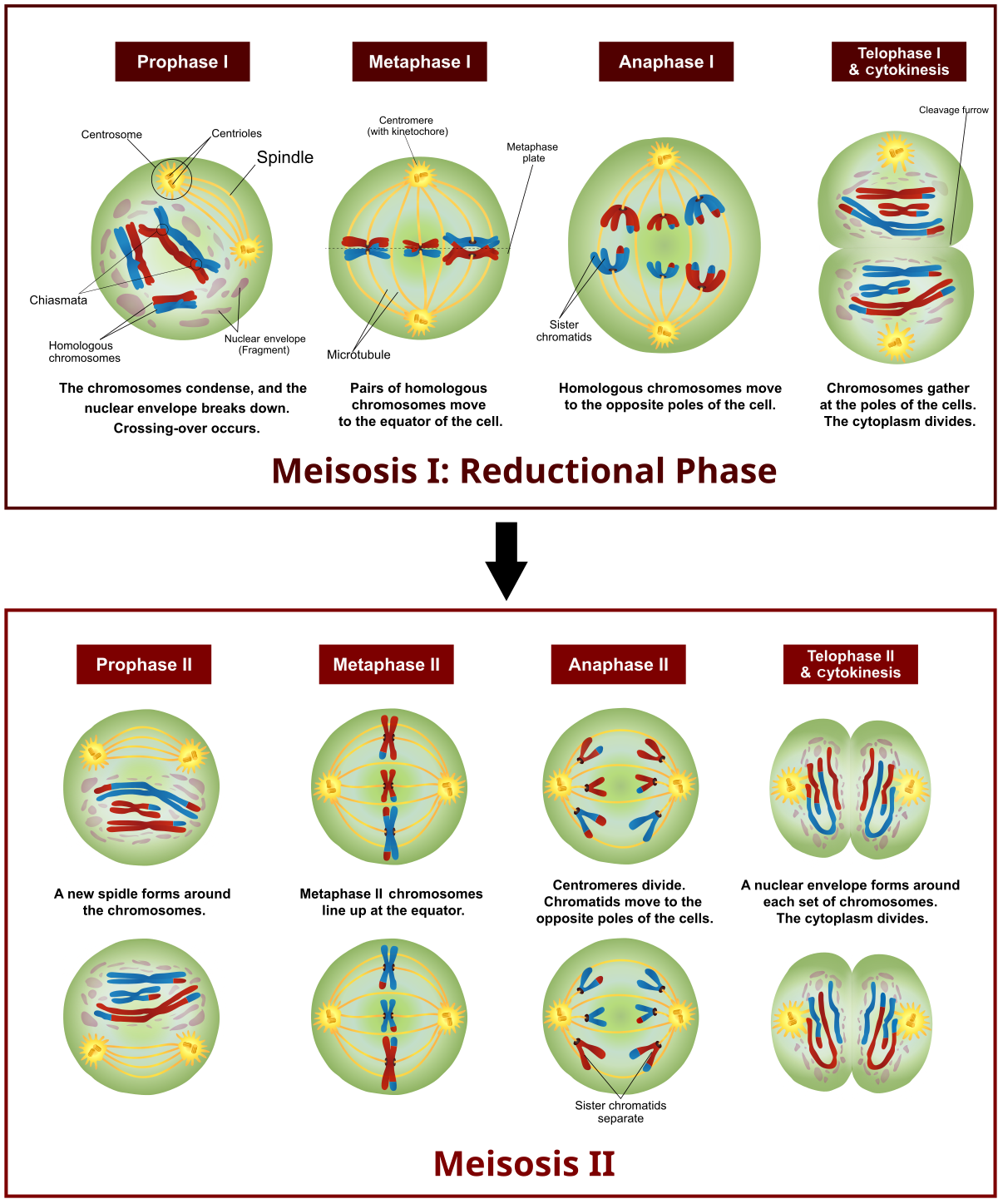
Meiosis Ii Stages And Significance Of Meiosis Ii Cell Division Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half (2n to n), leading to the formation of four non identical daughter cells. it is crucial for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. meiosis involves two divisions, so it’s typically broken down into meiosis i and meiosis ii. Meiosis stages diagram. meiosis involves two successive stages or phases of cell division, meiosis i and meiosis ii. each stage includes a period of nuclear division or karyokinesis and a cytoplasmic division or cytokinesis. although not a part of meiosis, the cells before entering meiosis i undergo a compulsory growth period called interphase. Telophase ii. as in the previous telophase i, the cell is now divided into two and the chromosomes are on opposite ends of the cell. cytokinesis or plasma division occurs, and new nuclear envelopes are formed around the chromosomes. results of meiosis ii. at the end of meiosis ii, there are 4 cells, each haploid, and each with only 1 copy of. Meiosis ii is a process that helps cells divide and create gametes, which are needed for sexual reproduction. it starts with prophase ii, where the nuclear envelope dissolves and chromosomes condense. then, in metaphase ii, chromosomes line up along the cell's middle. during anaphase ii, sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. finally, in telophase ii, the nuclear.
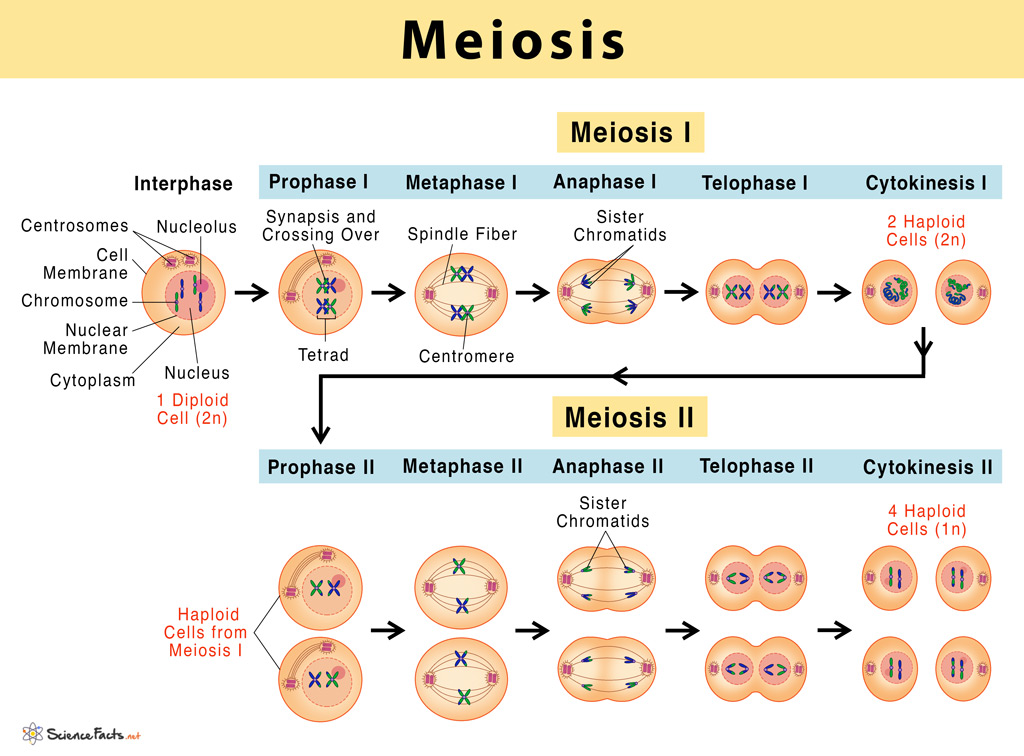
Meiosis Definition Stages Purpose With Diagram Telophase ii. as in the previous telophase i, the cell is now divided into two and the chromosomes are on opposite ends of the cell. cytokinesis or plasma division occurs, and new nuclear envelopes are formed around the chromosomes. results of meiosis ii. at the end of meiosis ii, there are 4 cells, each haploid, and each with only 1 copy of. Meiosis ii is a process that helps cells divide and create gametes, which are needed for sexual reproduction. it starts with prophase ii, where the nuclear envelope dissolves and chromosomes condense. then, in metaphase ii, chromosomes line up along the cell's middle. during anaphase ii, sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. finally, in telophase ii, the nuclear. Meiosis: phases, stages, applications with diagram. meiosis is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing eukaryotes, resulting in four daughter cells (gametes), each of which has half the number of chromosomes as compared to the original diploid parent cell. the haploid cells become gametes, which by union with another haploid cell during. Meiosis consists of a reduction division and an equational division. two divisions, meiosis i and meiosis ii, are required to produce gametes (figure 3). meiosis i is a unique cell division that.
20 Meiosis And Sexual Reproduction Openstax Biology Meiosis: phases, stages, applications with diagram. meiosis is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing eukaryotes, resulting in four daughter cells (gametes), each of which has half the number of chromosomes as compared to the original diploid parent cell. the haploid cells become gametes, which by union with another haploid cell during. Meiosis consists of a reduction division and an equational division. two divisions, meiosis i and meiosis ii, are required to produce gametes (figure 3). meiosis i is a unique cell division that.

Meiosis Ii Stages And Significance Of Meiosisii Cell

Stages Of Meiosis Vector Illustration Meiosis Cell Division

Comments are closed.