Medications 4 Week 6 Notes Hnn215 Oral Glycaemic Lowering Agents

Medications 4 Week 6 Notes Hnn215 Oral Glycaemic Lowering Agents Hnn215 week 6 2020; hnn215 week 5 2020; hnn215 week 4 2020; medications 4 week 6 notes. oral glycaemic lowering agents and insulin. Sulfonylureas oral glycaemic lowering agent. indication: type 2 diabetes mellitus increase insulin drug chart notes; drug class notes; hnn215 week 6 2020.
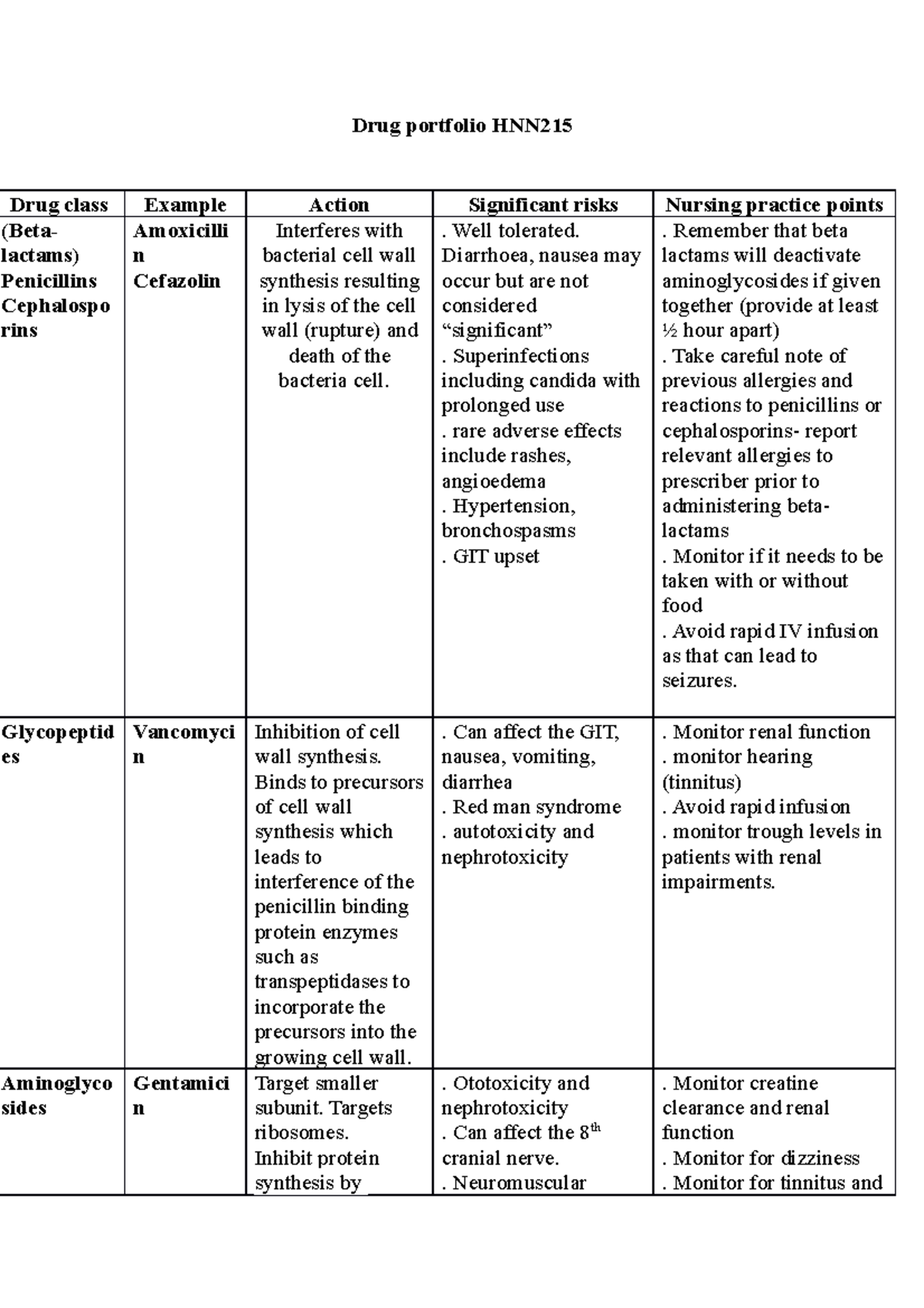
Drug Portfolio Hnn215 Drug Portfolio Hnn Drug Class Example Action Hnn215 – exam notes. important definitions: bio availability: the proportion of drug which enters the circulation when introduced into the body to have an active effect (the percentage of agent administered that reaches the systemic circulation) half life: time required for the activity of a substance taken into the body to lose one of its initial effectiveness (the time required for. Glycemic management — target glycated hemoglobin (a1c) levels in patients with type 2 diabetes should be tailored to the individual, balancing the anticipated reduction in microvascular complications over time with the immediate risks of hypoglycemia and other adverse effects of therapy. a reasonable goal of therapy is an a1c value of ≤7. Newer glucose lowering meds used alone or in combination four classes of oral glucose lowering meds 1. insulin secretagogues 2. biguanides 3. thiazolindinediones 4. alpha glucosidase inhibitors. In brief. the paradigms for oral pharmacological therapy in type 2 diabetes are shifting as we attain new insights into the optimal metabolic control in our patients. each drug category has unique advantages and disadvantages, and their proper use necessitates a full understanding of their mechanisms of action, glycemic and nonglycemic effects.

Hnn215 Exam Notes Weeks 1 6 Hnn215 Quality Use Of Medicines Newer glucose lowering meds used alone or in combination four classes of oral glucose lowering meds 1. insulin secretagogues 2. biguanides 3. thiazolindinediones 4. alpha glucosidase inhibitors. In brief. the paradigms for oral pharmacological therapy in type 2 diabetes are shifting as we attain new insights into the optimal metabolic control in our patients. each drug category has unique advantages and disadvantages, and their proper use necessitates a full understanding of their mechanisms of action, glycemic and nonglycemic effects. The major clinical effect of metformin is to decrease fasting glucose levels, thereby reducing a1c levels. the degree of clinical effect varies among patients, but most patients experience an a1c reduction of ~ 1.5 percentage points. 6 because metformin exerts its effects primarily by impairing hepatic gluconeogenesis, it is an antihyperglycemic agent rather than a hypoglycemic agent such as. The biguanide metformin is often selected as initial oral glucose lowering therapy. it counters insulin resistance and lowers blood glucose through several insulin dependent and independent mechanisms. sulfonylureas act on the pancreatic β cells to stimulate insulin secretion by binding to the transmembranal complex of sulfonylurea receptors.

Hnn215 Exam Notes Hnn215 Exam Notes Week 1 Medicines Used To Treat The major clinical effect of metformin is to decrease fasting glucose levels, thereby reducing a1c levels. the degree of clinical effect varies among patients, but most patients experience an a1c reduction of ~ 1.5 percentage points. 6 because metformin exerts its effects primarily by impairing hepatic gluconeogenesis, it is an antihyperglycemic agent rather than a hypoglycemic agent such as. The biguanide metformin is often selected as initial oral glucose lowering therapy. it counters insulin resistance and lowers blood glucose through several insulin dependent and independent mechanisms. sulfonylureas act on the pancreatic β cells to stimulate insulin secretion by binding to the transmembranal complex of sulfonylurea receptors.

Drug Class Hnn215 Summery Week 2 Drug Class Examples Action

Comments are closed.