Measure Of Exterior Angle Of A Triangle Geogebra

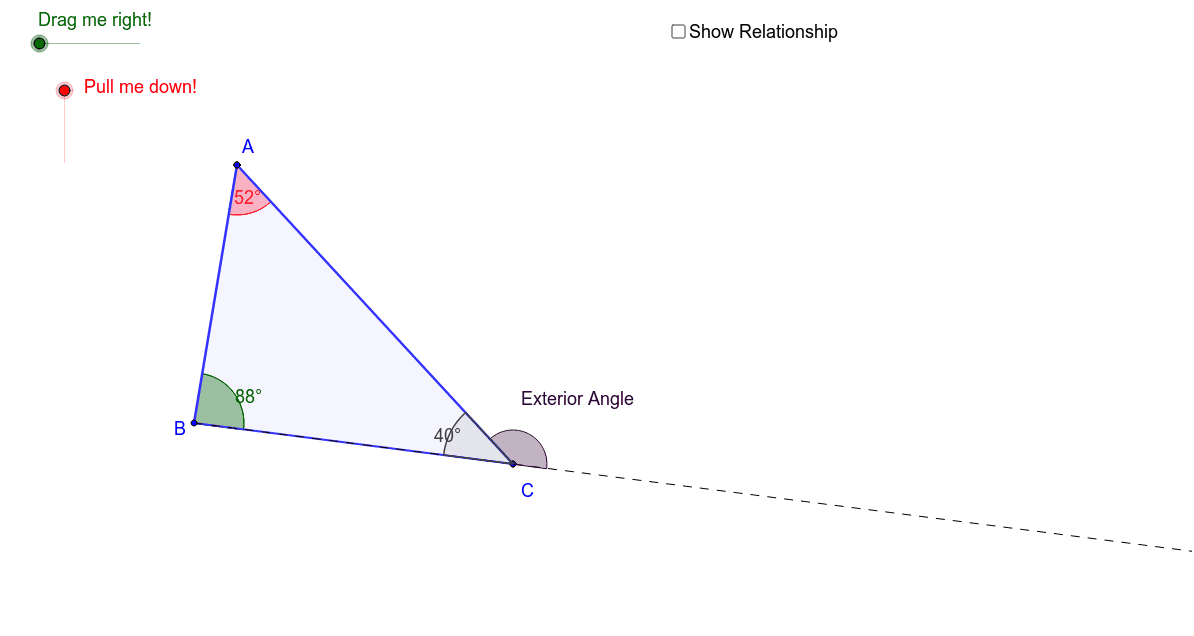
Measure Of Exterior Angle Of A Triangle Geogebra Explore the relationship between the sum of the two remote interior angles and the exterior angle of the third angle in a triangle by dragging sliders and making observations. drag the two sliders to transform the angle measures for angle a and b of the triangle. compare the sum of these angles to the exterior angle at c in the triangle. This demonstrates that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two remote interior angles. google classroom geogebra.
Exterior Angle Of A Triangle Geogebra The exterior angles of a triangle, quadrilateral, and pentagon are shown, respectively, in the applets below. you can control the size of a colored exterior angle by using the slider with matching color. feel free to move the vertices of these polygons anywhere you'd like. note: for the quadrilateral & pentagon, the last two applets work best. Topic: angles this worksheet is a demonstration illustrating why the exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the two opposite interior angles. click fold to fold the top part of the triangle over, then rearrange to rotate and translate the combined interior angle until it overlaps the exterior angle. Are the exterior angles of a triangle always obtuse? no, the exterior angles of a triangle may not always be obtuse (more than 90°). however, the sum of all the three exterior angles should always be 360°. for example, if two exterior angles of a triangle are 165° (obtuse) and 141° (obtuse), the third one is 54° (acute). Learn about the angle sum and exterior angles of triangles with interactive geogebra applets and exercises.
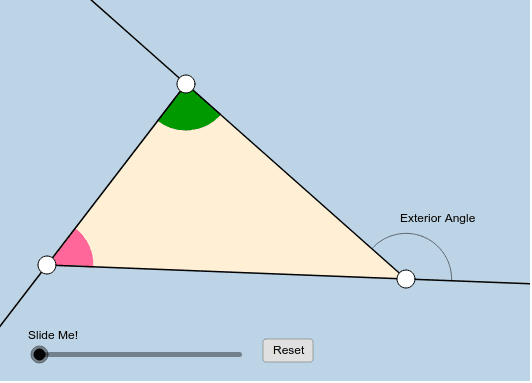
Triangle Exterior Angle Geogebra Are the exterior angles of a triangle always obtuse? no, the exterior angles of a triangle may not always be obtuse (more than 90°). however, the sum of all the three exterior angles should always be 360°. for example, if two exterior angles of a triangle are 165° (obtuse) and 141° (obtuse), the third one is 54° (acute). Learn about the angle sum and exterior angles of triangles with interactive geogebra applets and exercises. An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles. every triangle has six exterior angles (two at each vertex are equal in measure). the exterior angles, taken one at each vertex, always sum up to 360 ° 360\degree 360°. an exterior angle is supplementary to its adjacent triangle interior angle. The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two non adjacent interior angles. (non adjacent interior angles may also be referred to as remote interior angles.) facts: • an exterior ∠ is equal to the addition of the two Δ angles not right next to it. 140º = 60º 80º; 120º = 80º 40º;.

Comments are closed.