Mean Median And Mode Of Grouped Data Frequency Distribution Tables Statistics
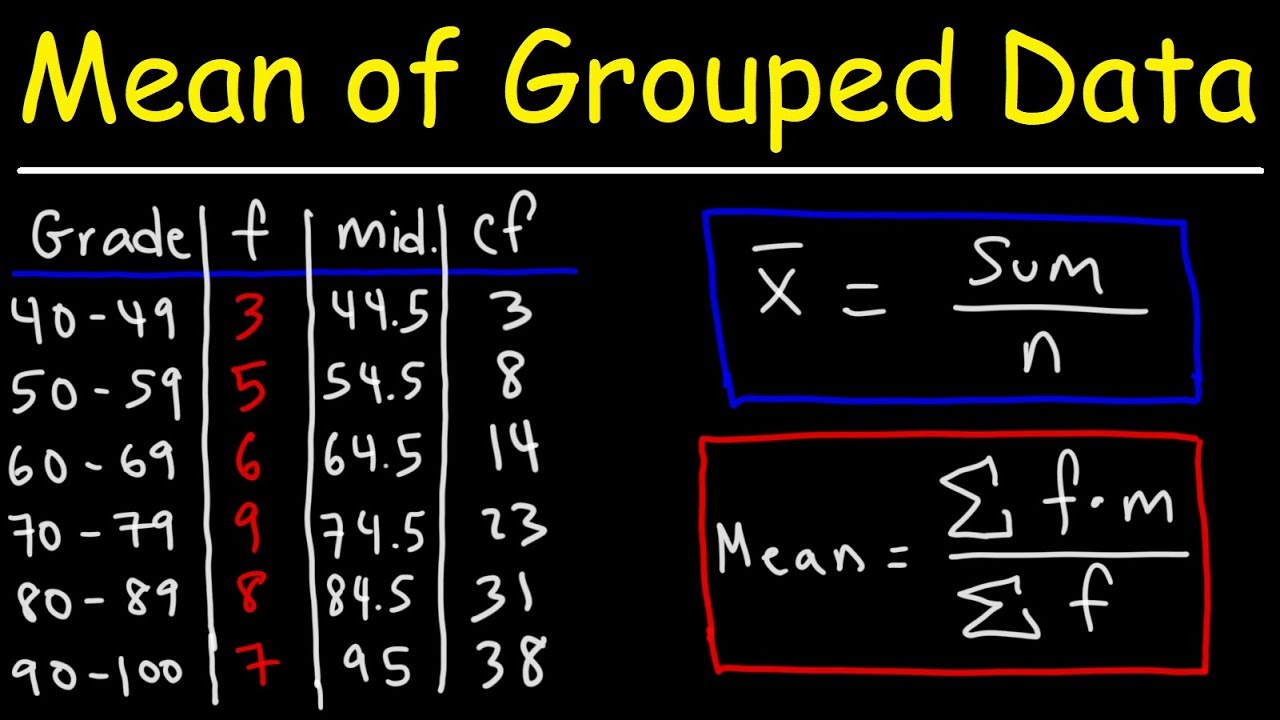
Mean Median And Mode Of Grouped Data Frequency Distribution Tables For grouped data, we cannot find the exact mean, median and mode, we can only give estimates. to estimate the mean use the midpoints of the class intervals: estimated mean = sum of (midpoint × frequency) sum of frequency. to estimate the median use: estimated median = l (n 2) − b g × w. where:. The median is a better measure of the "center" than the mean because 49 of the values are 30,000 and one is 5,000,000. the 5,000,000 is an outlier. the 30,000 gives us a better sense of the middle of the data. another measure of the center is the mode. the mode is the most frequent value.

Mean Median And Mode Grouped Data Youtube Here, the total frequency n = ∑f = 50. n 2 = 50 2 = 25. the median is (n 2)th value = 25th value. now, 25th value occurs in the cumulative frequency 28, whose corresponding x value is 7. so, the median = 7. (iii) mode : by observing the given data set, the number 8 occurs more number of times. that is 13 times. Example 1: whole numbers. sort these 20 20 items into the grouped frequency table. using the set of data, account for each item with a tally mark in the table. 2 fill in the frequency column. add up the tally marks and fill in the frequency column. 3 find the cumulative frequency and the relative frequency, if needed. Estimated mean from a grouped frequency table. when the data has been grouped together and put into a grouped frequency table, you cannot find the actual mean because you only have a range of possible values. instead you can find an estimate for the mean using the midpoints of each group. you can add more columns to the grouped frequency table. The following table shows the frequency distribution of the diameters of 40 bottles. (lengths have been measured to the nearest millimeter) find the mean of the data. step 1: find the midpoint of each interval. step 2: multiply the frequency of each interval by its mid point. step 3: get the sum of all the frequencies (f) and the sum of all the fx.
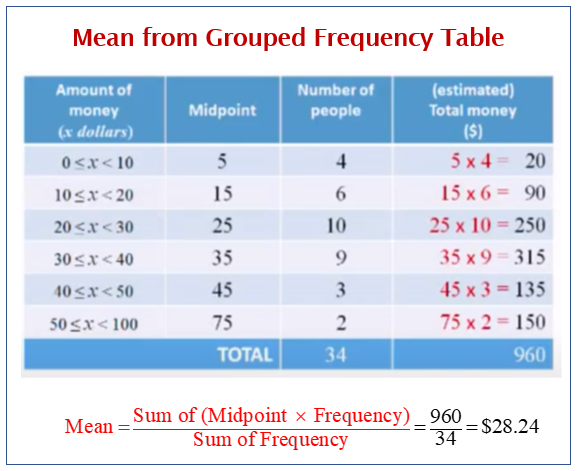
Grouped Frequency Tables Examples Solutions Videos Worksheets Estimated mean from a grouped frequency table. when the data has been grouped together and put into a grouped frequency table, you cannot find the actual mean because you only have a range of possible values. instead you can find an estimate for the mean using the midpoints of each group. you can add more columns to the grouped frequency table. The following table shows the frequency distribution of the diameters of 40 bottles. (lengths have been measured to the nearest millimeter) find the mean of the data. step 1: find the midpoint of each interval. step 2: multiply the frequency of each interval by its mid point. step 3: get the sum of all the frequencies (f) and the sum of all the fx. Ungrouped frequency distribution: a table that shows the number of data points for each individual value. this is sometimes called just a “frequency distribution.” this is the type shown in example 1 above. grouped frequency distribution: a table that shows the number of data points that fall within a range of values, called a class. Median of grouped data = l w [ (n 2 – c) f] where: l: lower limit of median class. w: width of median class. n: total frequency. c: cumulative frequency up to median class. f: frequency of median class. note: the median class is the class that contains the value located at n 2. in the example above, there are n = 23 total values.

Comments are closed.