Mbti 16 Types Chart
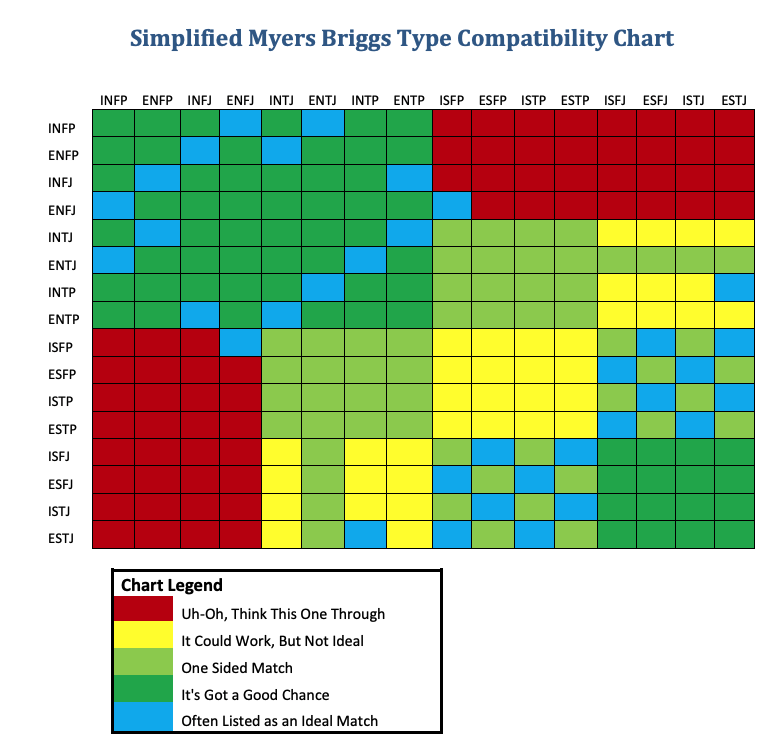
Mbti 16 Types Chart Esfp a esfp t. spontaneous, energetic and enthusiastic people – life is never boring around them. extensive, research backed profiles of 16 personality types: learn how different personalities approach romantic relationships, career choices, friendships, parenthood, and more. The 16 mbti ® personality types the myers briggs ® system consists of four preference pairs that reflect different aspects of personality—opposite ways to direct and receive energy through extraversion (e) or introversion (i), take in information with sensing (s) or intuition (n), come to conclusions using thinking (t) or feeling (f), and.

How The Myers Briggs Type Indicator Works 16 Personality The development of the myers briggs test. the mbti tool was developed by isabel briggs myers and her mother katharine cook briggs in 1942. the mbti is rooted in carl jung’s theory of psychological types, which proposed four essential psychological functions: judging (thinking and feeling) and perceiving (sensation and intuition). Free personality test, type descriptions, relationship and career advice | 16personalities. take the test. “it’s so incredible to finally be understood.”. only 10 minutes to get a “freakishly accurate” description of who you are and why you do things the way you do. take the test. 782k . This article discusses how the myers briggs types were created, what the 16 different mbti types are, and how this personality typing system works. the development of the myers briggs test both myers and briggs were fascinated by jung's theory of psychological types and recognized that the theory could have real world applications. What makes the mbti assessment unique from many other personality surveys is the ethical requirement of the interpretive feedback session to verify a best fit type. the value of a verification process is explained in detail. people often ask to take the mbti test. learn the reasons why the mbti is an assessment, instrument, tool, or inventory.
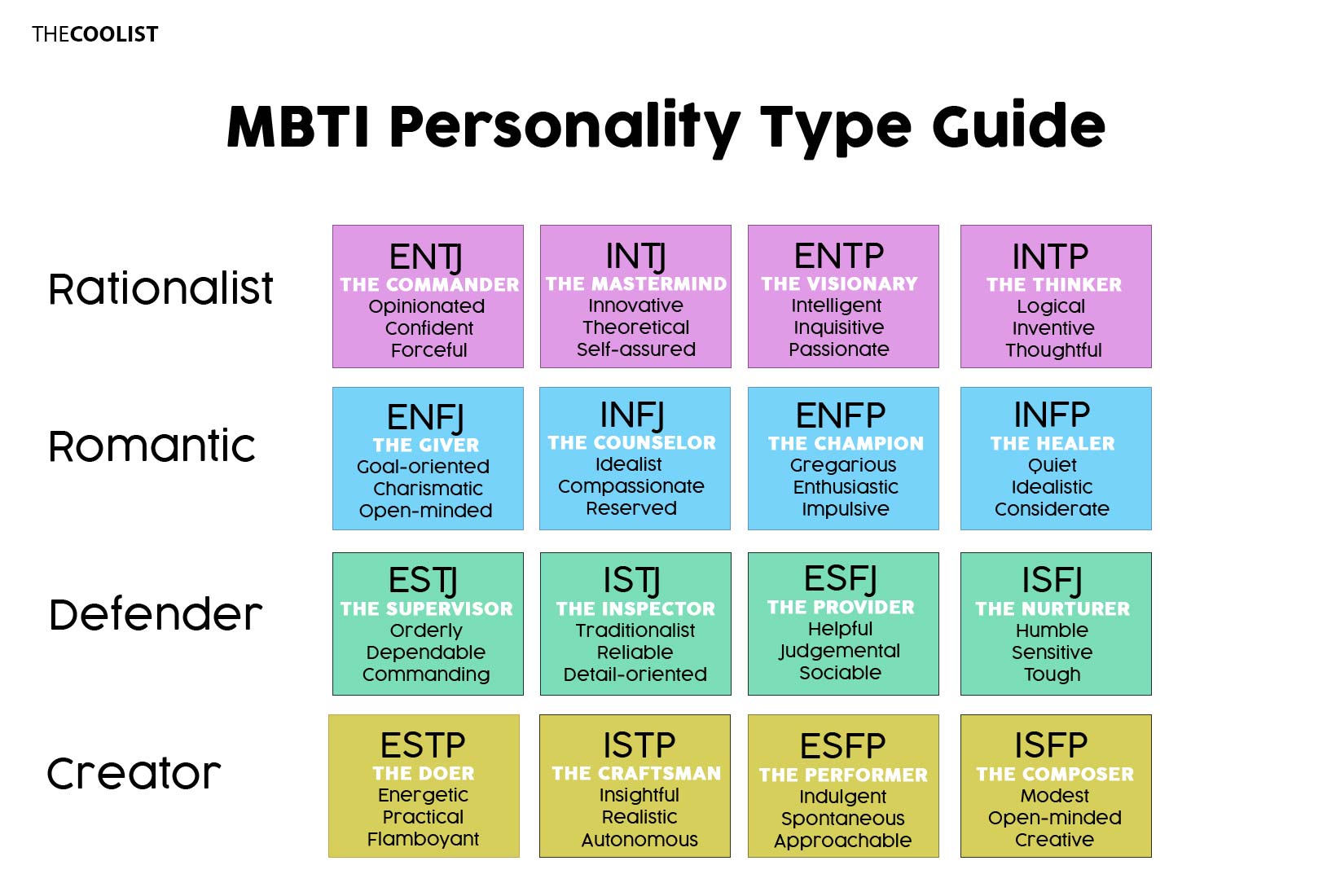
16 Different Personality Types Behaviors Characteristics Social Skills This article discusses how the myers briggs types were created, what the 16 different mbti types are, and how this personality typing system works. the development of the myers briggs test both myers and briggs were fascinated by jung's theory of psychological types and recognized that the theory could have real world applications. What makes the mbti assessment unique from many other personality surveys is the ethical requirement of the interpretive feedback session to verify a best fit type. the value of a verification process is explained in detail. people often ask to take the mbti test. learn the reasons why the mbti is an assessment, instrument, tool, or inventory. The 16 personality types were created by isabel myers and katharine briggs, developers of the mbti® assessment. myers and briggs created their personality typology to help people discover their own strengths and gain a better understanding of how people are different. when you discover your own personality type, you'll understand more clearly. The 16 mbti personality types. the myers briggs type indicator ® (mbti ®) step i is based on carl jung’s theory of psychological type. it indicates your personality preferences in four dimensions: where you focus your attention – extraversion (e) or introversion (i) the way you take in information – sensing (s) or intuition (n).

16 Personality Types By Myers Briggs Mbm The 16 personality types were created by isabel myers and katharine briggs, developers of the mbti® assessment. myers and briggs created their personality typology to help people discover their own strengths and gain a better understanding of how people are different. when you discover your own personality type, you'll understand more clearly. The 16 mbti personality types. the myers briggs type indicator ® (mbti ®) step i is based on carl jung’s theory of psychological type. it indicates your personality preferences in four dimensions: where you focus your attention – extraversion (e) or introversion (i) the way you take in information – sensing (s) or intuition (n).

Comments are closed.