Maxwells Equations Explained
Ppt Maxwell S Equations Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id Maxwell's equations, or maxwell–heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, electric and magnetic circuits. the equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such. Maxwell's equations are a set of 4 complicated equations that describe the world of electromagnetics. these equations describe how electric and magnetic fields propagate, interact, and how they are influenced by objects. james clerk maxwell [1831 1879] was an einstein newton level genius who took a set of known experimental laws (faraday's law.
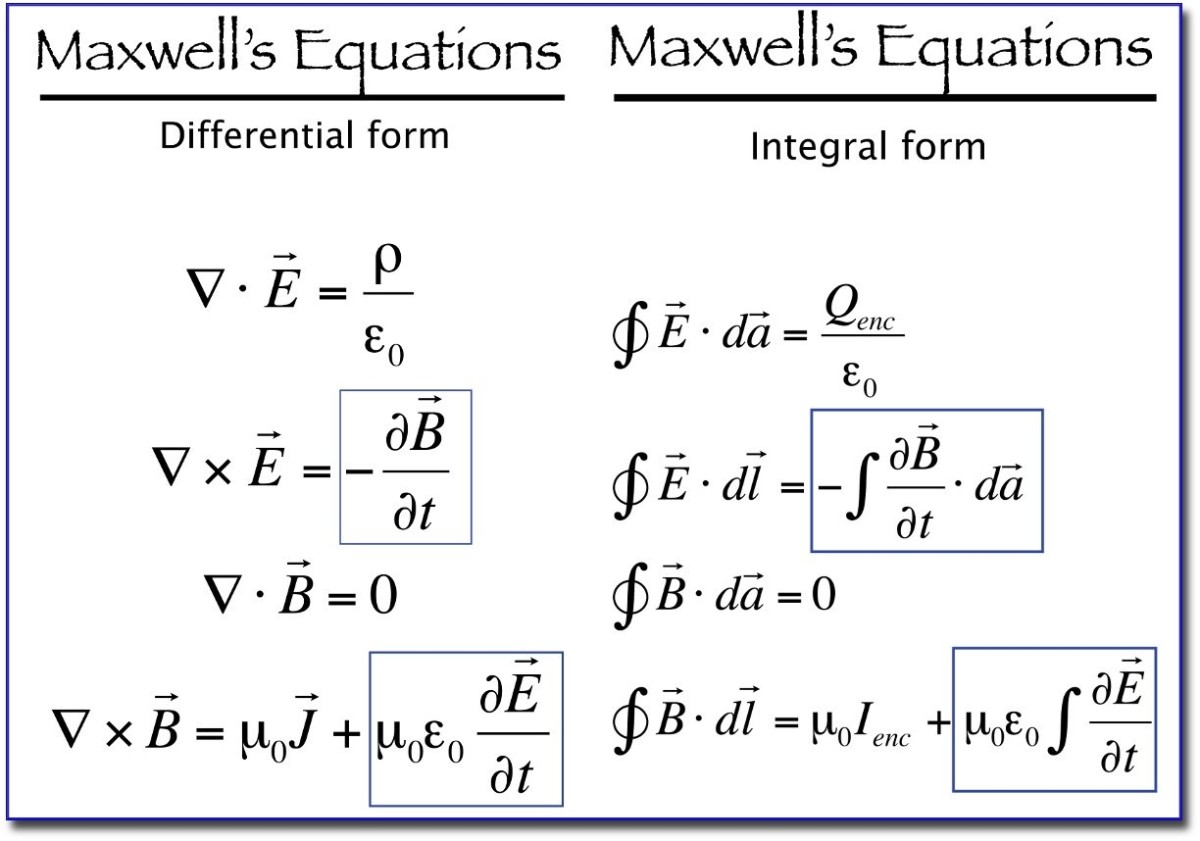
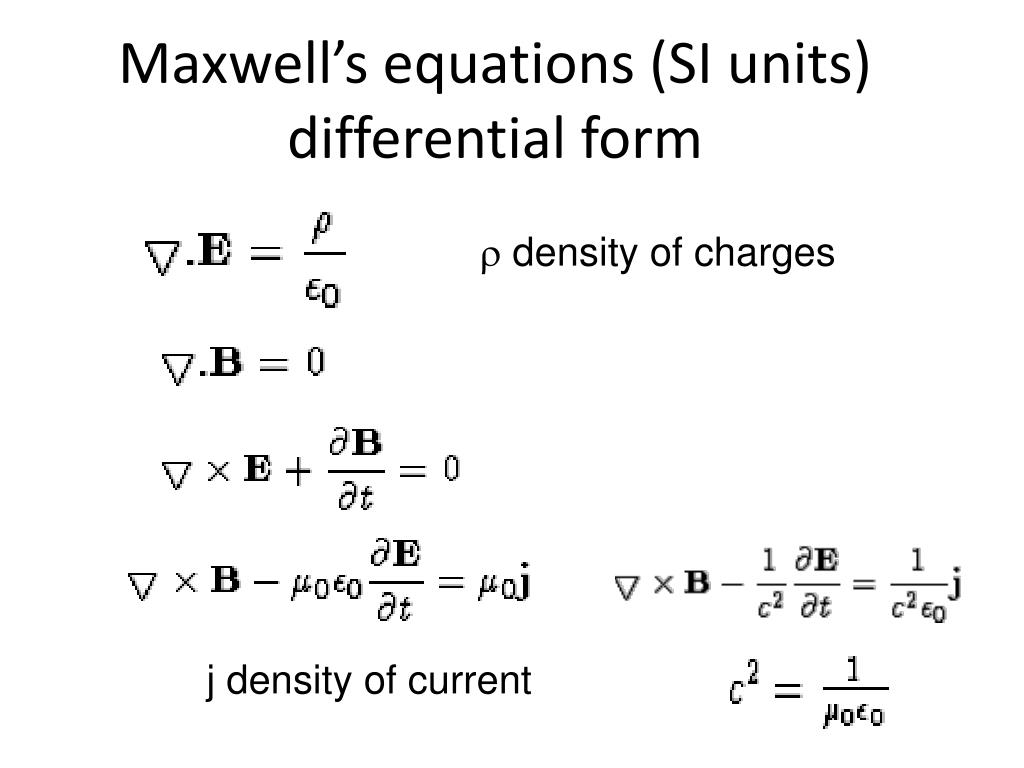
Maxwell S Equations And Displacement Current Owlcation Until maxwell’s work, the known laws of electricity and magnetism were those we have studied in chapters 3 through 17.in particular, the equation for the magnetic field of steady currents was known only as \begin{equation} \label{eq:ii:18:1} \flpcurl{\flpb}=\frac{\flpj}{\epso c^2}. \end{equation} maxwell began by considering these known laws and expressing them as differential equations, as. Magnetic fields are generated by moving charges or by changing electric fields. this fourth of maxwell’s equations, equation 16.2.17, encompasses ampère’s law and adds another source of magnetic fields, namely changing electric fields. maxwell’s equations and the lorentz force law together encompass all the laws of electricity and magnetism. Maxwell’s equations, four equations that, together, form a complete description of the production and interrelation of electric and magnetic fields. the physicist james clerk maxwell, in the 19th century, based his description of electromagnetic fields on these four equations, which express experimental laws. Maxwell's equations are a set of four differential equations that form the theoretical basis for describing classical electromagnetism: gauss's law: electric charges produce an electric field. the electric flux across a closed surface is proportional to the charge enclosed. gauss's law for magnetism: there are no magnetic monopoles. the magnetic flux across a closed surface is.

A Plain Explanation Of Maxwell S Equations Fosco Connect Maxwell’s equations, four equations that, together, form a complete description of the production and interrelation of electric and magnetic fields. the physicist james clerk maxwell, in the 19th century, based his description of electromagnetic fields on these four equations, which express experimental laws. Maxwell's equations are a set of four differential equations that form the theoretical basis for describing classical electromagnetism: gauss's law: electric charges produce an electric field. the electric flux across a closed surface is proportional to the charge enclosed. gauss's law for magnetism: there are no magnetic monopoles. the magnetic flux across a closed surface is. Maxwell's equations represent one of the most elegant and concise ways to state the fundamentals of electricity and magnetism. from them one can develop most of the working relationships in the field. because of their concise statement, they embody a high level of mathematical sophistication and are therefore not generally introduced in an. Gauss's law and ampere's law together…. ∂ αfαβ = μ 0jβ. no one's law and faraday's law together…. ∂ αfβγ ∂ βfγα ∂ γfαβ = 0. the new symbols are matrices. 4 gradient…. 4 current density (usually just called 4 current)…. electromagnetic field tensor, contravariant form…. electromagnetic field tensor, covariant.

Comments are closed.