Material Hardship Far More Common Among Black And Latinx Families
Material Hardship Far More Common Among Black And Latinx Families Of note, maternal racial and ethnic group membership was not a consistent predictor of material hardship pattern. families with black, non latinx mothers (vs. white non latinx) faced higher risk of the mostly moderate (rr=1.638) and worsening (rr=1.674) material hardship patterns compared to mostly limited but did not face differences in risk. Material hardship far more common among share. facebook twitter print email. helping families meet basic needs enables parents to promote children’s healthy.

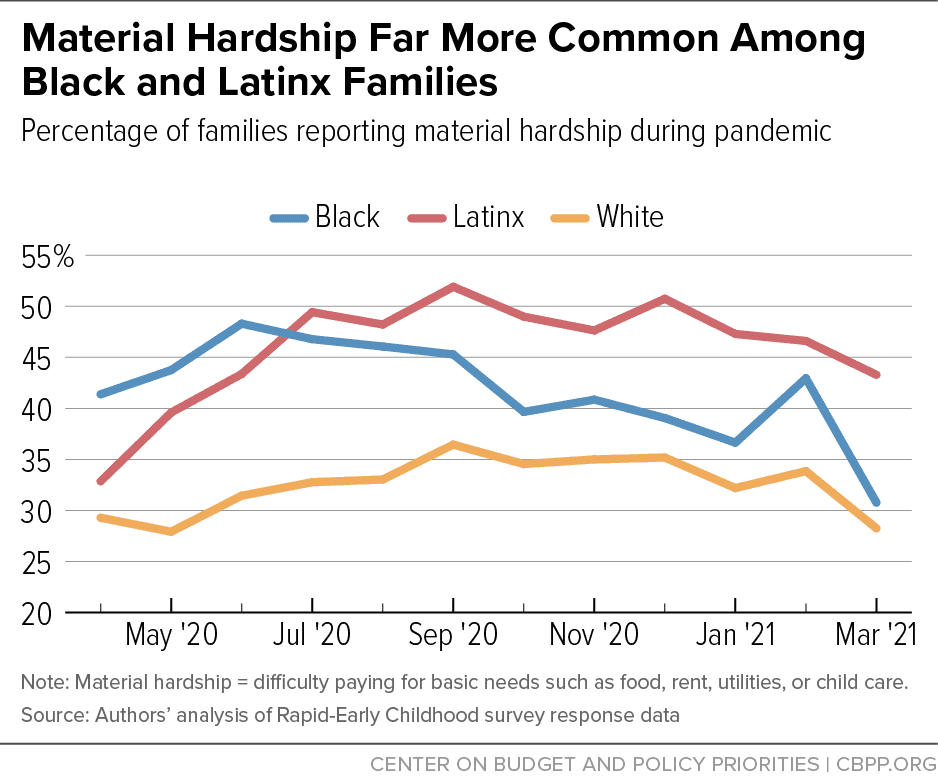
Material Hardship Far More Common Among Black And Latinx Families Latinx families were among the hardest hit by covid, both health wise (they faced some of the highest rates of disease burden and covid related mortality) 9 and socioeconomically (via job loss 10 and reduction in work hours). 11 we show data on four hardship measures—housing quality hardship, bill paying hardship, food insecurity, and (an. According to the 2021 sipp, about 1 in 3 (34.8%) hispanic and about 1 in 4 (24.3%) non hispanic people in the united states lived in a household that experienced material hardship in 2020. differences in material hardship were striking among hispanic origin groups (figure 1). half of those of dominican (50.5%) and salvadoran (49.2%) origin. Results. we found that differences in income to poverty ratio account for differences in cps contact between black and white families. differences in cps contact between black and latinx families were not explained by economic wellbeing measures alone but were ameliorated when differences in income poverty, material hardship, and a full set of family characteristics were considered. Material hardship has emerged as a direct measure of deprivation in the united states and an important complement to income poverty, providing different evidence about the ways in which deprivation may affect wellbeing. this study addresses gaps in our knowledge about deprivation as the first to examine patterns of material hardship over time. using data from the fragile families and child.

High Hardship Among Black And Latinx Lgbtq Renters Underscores Need For Results. we found that differences in income to poverty ratio account for differences in cps contact between black and white families. differences in cps contact between black and latinx families were not explained by economic wellbeing measures alone but were ameliorated when differences in income poverty, material hardship, and a full set of family characteristics were considered. Material hardship has emerged as a direct measure of deprivation in the united states and an important complement to income poverty, providing different evidence about the ways in which deprivation may affect wellbeing. this study addresses gaps in our knowledge about deprivation as the first to examine patterns of material hardship over time. using data from the fragile families and child. We measured income poverty and material hardship when children were age 1 and measured any cps contact by age five. our final sample included 3,517 families, including 1,848 black, 614 white, and 1,055 latinx families. The demonstrated presence of material hardship among families with incomes up to 400% of fpl (e.g., see karpman et al., 2018b ; rodems & shaefer, 2020 ) sug.

Women Donors Network The Pandemic Isn T Behind Black Latinx We measured income poverty and material hardship when children were age 1 and measured any cps contact by age five. our final sample included 3,517 families, including 1,848 black, 614 white, and 1,055 latinx families. The demonstrated presence of material hardship among families with incomes up to 400% of fpl (e.g., see karpman et al., 2018b ; rodems & shaefer, 2020 ) sug.

Facts Myths And Misinformation On Covid 19 Protecting Black Latinx

Comments are closed.