Mastoidectomy Facial Recess Approach And Cochleostomy Techniques

Mastoidectomy Facial Recess Approach And Cochleostomy Techniques Facial recess approach. dr. jackler and ms. gralapp retain copyright for all of their original illustrations which appear in this online atlas. we encourage use of our illustrations for educational purposes, but copyright permission should be sought before publication or commercial use. to request permission for publication or commercial use. 1 the three main approaches for ci are the classic approach, which uses the fr; the suprameatal approach (sma), which does not require mastoidectomy and uses the creation of a tunnel over the facial nerve (fn) to enter the middle ear; and the endomeatal approach (ema), which is based on the completion of a groove in the posterior wall of.
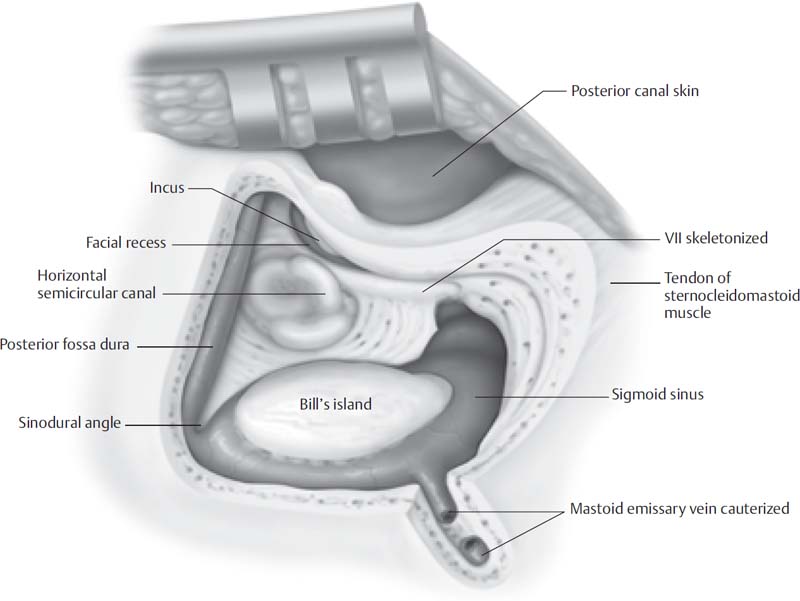
The Translabyrinthine Approach To The Skull Base Neupsy Key Mastoidectomy is one of the key steps in placing a cochlear implant to rehabilitate acquired or congenital sensorineural hearing loss. a mastoidectomy allows the surgeon access to the middle ear through the facial recess. the implant electrode array is placed through the facial recess into a cochleostomy, which is drilled inferior and slightly. Standard ci surgery includes a mastoidectomy and facial recess approach to the middle ear and cochlea. knowledge of facial recess anatomy is crucial for safe and adequate cochlear visualization and ideal cochleostomy position. anteriorly, thinning of the posterior external auditory canal is the first step in creation of an ideal facial recess. These techniques would also require the opening of the middle ear by raising of the eardrum, increasing the risk of harming it. at the time, the sma and veria were proposed as the safest approaches to fn; however, our analyses show that the safest approach for the facial nerve would be the pericanal approach with a distance of 2.17 mm. Abstract. posterior tympanotomy or facial recess approach is the routine approach for cochlear implantation based on the knowledge of facial recess and facial nerve course anatomy. the surgical landmarks are lateral semicircular canal, incus and mastoid segment of facial nerve. the tips and tricks for a large enough posterior tympanotomy to.

Cochlear Implant Electrode Misplaced In The Carotid Canal Cochlear These techniques would also require the opening of the middle ear by raising of the eardrum, increasing the risk of harming it. at the time, the sma and veria were proposed as the safest approaches to fn; however, our analyses show that the safest approach for the facial nerve would be the pericanal approach with a distance of 2.17 mm. Abstract. posterior tympanotomy or facial recess approach is the routine approach for cochlear implantation based on the knowledge of facial recess and facial nerve course anatomy. the surgical landmarks are lateral semicircular canal, incus and mastoid segment of facial nerve. the tips and tricks for a large enough posterior tympanotomy to. In 1961, dr house introduced the mastoidectomy with posterior tympanotomy approach (mpta) for cochlear implantation. 28 since then, the mpta has stood the test of time and become the most commonly used approach. as the name implies, a mastoidectomy is performed followed by a posterior tympanotomy, which opens the facial recess exposing the. Supralabyrinthine approaches to cochlear implantation have not found wide acceptance due to technical limitations with exposure of the scala tympani and postoperative healing. thus, standard mastoidectomy techniques are typically used. the mastoidectomy incision design and device placement are critical for prevention of complications.

Ppt Cortical Mastoidectomy And Combined Approach Tympanoplasty Cat In 1961, dr house introduced the mastoidectomy with posterior tympanotomy approach (mpta) for cochlear implantation. 28 since then, the mpta has stood the test of time and become the most commonly used approach. as the name implies, a mastoidectomy is performed followed by a posterior tympanotomy, which opens the facial recess exposing the. Supralabyrinthine approaches to cochlear implantation have not found wide acceptance due to technical limitations with exposure of the scala tympani and postoperative healing. thus, standard mastoidectomy techniques are typically used. the mastoidectomy incision design and device placement are critical for prevention of complications.

Mastoidectomy Ento Key

Comments are closed.