Marking The Bones Placement
Anatomy Bone Markings Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf Outside of projections, several bone markings fall into the category of depressions and openings. bony landmarks in this category form basins, channels and holes that house nerves, vessels, tendons and muscles. below, we explore some examples. jugular foramen. foramen jugulare. 2 the brain : can you name the main anatomical areas of the brain? 3 the cell : learn the anatomy of a typical human cell. 4 the skull : do you know the bones of the skull? 5 the axial skeleton : how about the bones of the axial skeleton? 6 the heart : name the parts of the human heart.
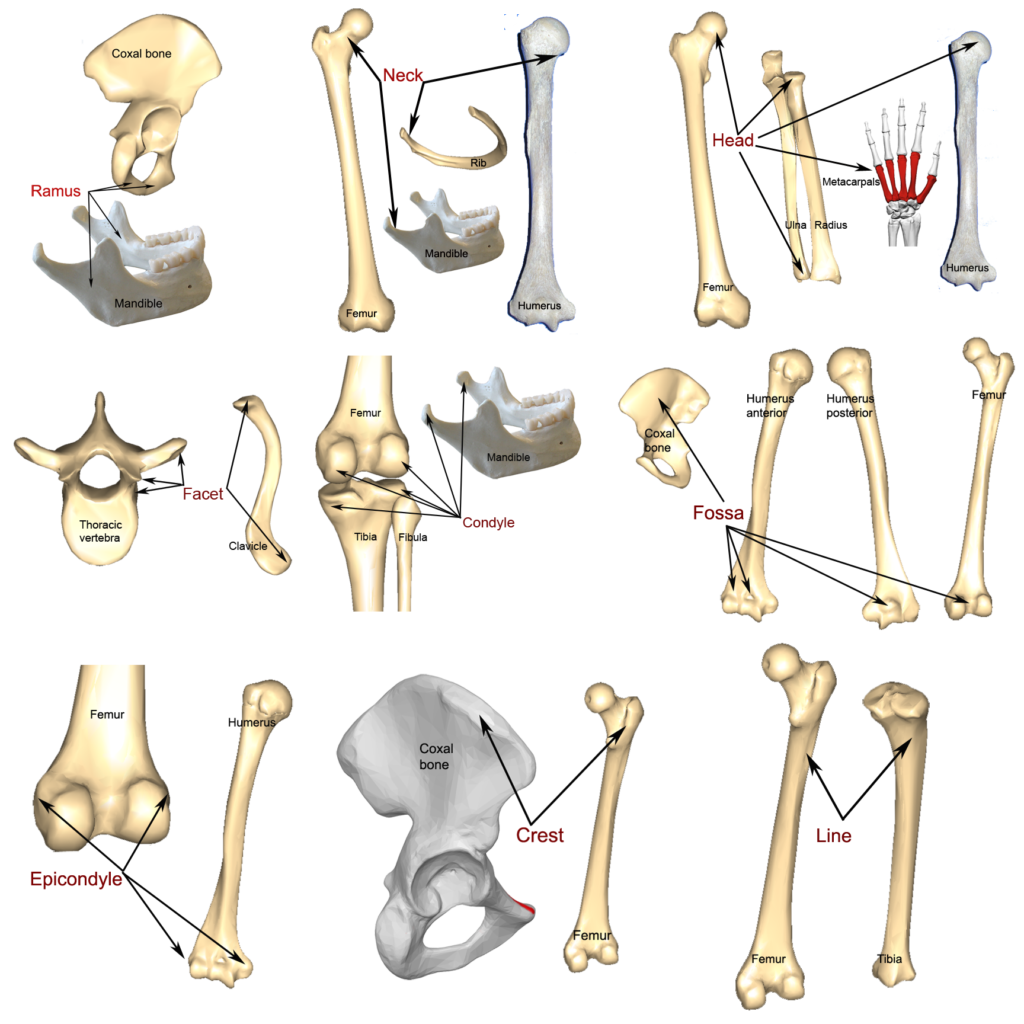
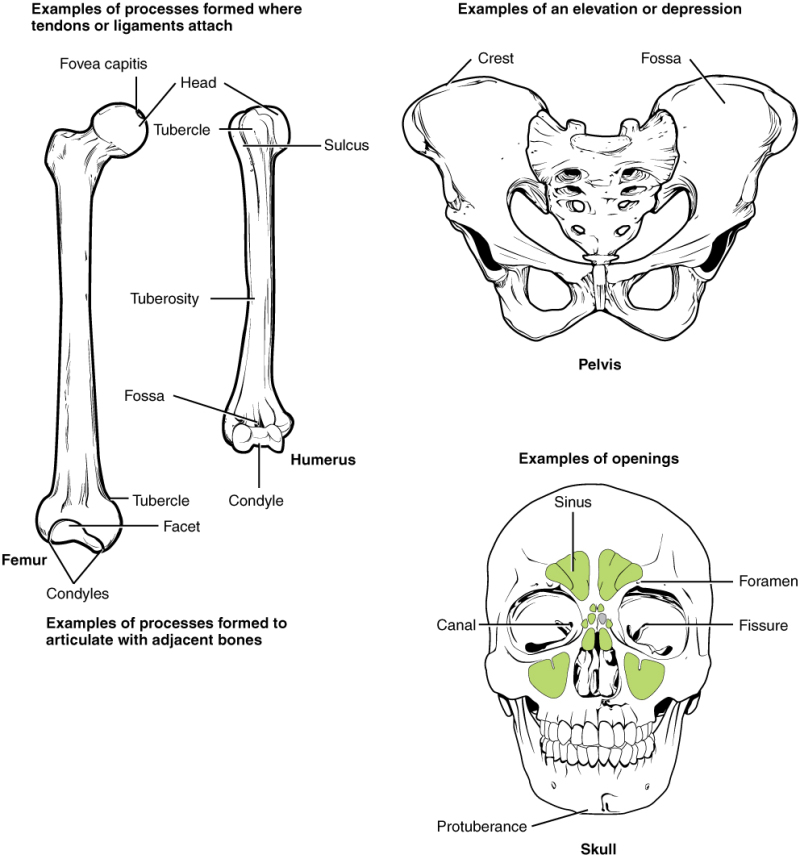
Bone Markings Processes And Cavities Human Anatomy And Physiology This online quiz is called the 206 bones of the skeleton. it was created by member suki baker and has 28 questions. Table 7.2 describes the bone markings, which are illustrated in (figure 7.2.1). there are three general classes of bone markings: (1) articulations, (2) projections, and (3) holes. as the name implies, an articulation is where two bone surfaces come together (articulus = “joint”). these surfaces tend to conform to one another, such as one. Introduction. bone markings are crucial for identifying bones and understanding anatomy. these distinctive features benefit various professionals, including clinicians and forensic scientists. bone markings are easily overlooked but serve essential functions like facilitating joint movement, locking bones in place, and supporting and protecting. Compact bone is the denser, stronger of the two types of osseous tissue (figure 6.3.6). it makes up the outer cortex of all bones and is in immediate contact with the periosteum. in long bones, as you move from the outer cortical compact bone to the inner medullary cavity, the bone transitions to spongy bone.

Bone Markings Processes And Cavities Human Anatomy And Physiology Introduction. bone markings are crucial for identifying bones and understanding anatomy. these distinctive features benefit various professionals, including clinicians and forensic scientists. bone markings are easily overlooked but serve essential functions like facilitating joint movement, locking bones in place, and supporting and protecting. Compact bone is the denser, stronger of the two types of osseous tissue (figure 6.3.6). it makes up the outer cortex of all bones and is in immediate contact with the periosteum. in long bones, as you move from the outer cortical compact bone to the inner medullary cavity, the bone transitions to spongy bone. They are usually classified into five types of bones that include the flat, long, short, irregular, and sesamoid bones. the human bones have a number of important functions in the body. most importantly, they are responsible for somatic rigidity, structural outline, erect posture and movement (e.g. bipedal gait). Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces, while spongy (cancellous) bone has open spaces and supports shifts in weight distribution. compact bone. compact bone is the denser, stronger of the two types of bone tissue (figure 6.12). it can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones, where it provides.

Anatomy Bone Markings Anatomical Charts Posters They are usually classified into five types of bones that include the flat, long, short, irregular, and sesamoid bones. the human bones have a number of important functions in the body. most importantly, they are responsible for somatic rigidity, structural outline, erect posture and movement (e.g. bipedal gait). Compact bone is dense so that it can withstand compressive forces, while spongy (cancellous) bone has open spaces and supports shifts in weight distribution. compact bone. compact bone is the denser, stronger of the two types of bone tissue (figure 6.12). it can be found under the periosteum and in the diaphyses of long bones, where it provides.

Table Lists Types Of Bone Markings Along With Illustrations And

Comments are closed.