Market Structure Chart Economics
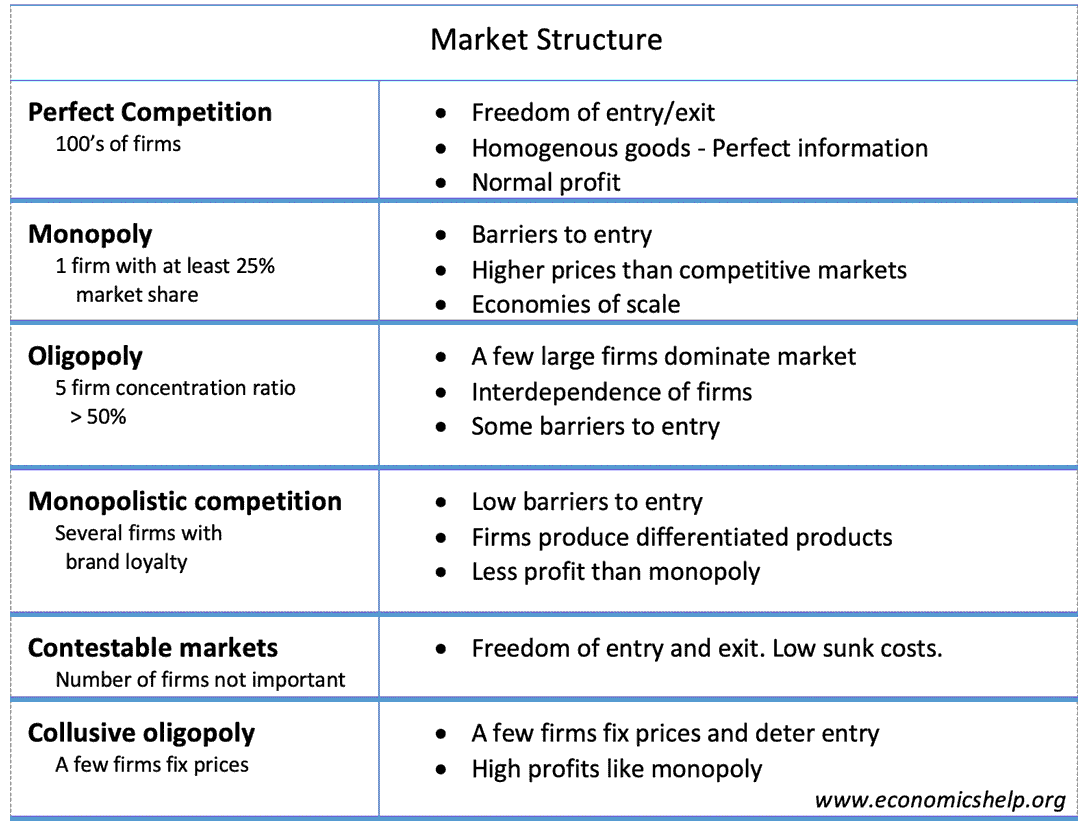
Types Of Market Structure Economics Help There are four basic types of market structure in economics: perfect competition, imperfect competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. perfect competition describes a market structure where a large number of small firms compete against each other with homogeneous products. meanwhile, monopolistic competition refers to a type of market structure. Duopoly – where two firms dominate the market. for example, pepsi and coca cola. android vs apple. a duopoly falls between a monopoly and oligopoly. different types of market structure 1. perfect competition (many firms) 2. monopoly (one firm), oligopoly (a few firms) monopolistic competition, contestable markets and collusion.

Tony Kim S Economics Comapring Market Structures Gain a deeper understanding of market structures with our collection of essential diagrams for economics students. our web page provides a comprehensive overview of market structure concepts, including perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. explore these diagrams and their applications to real world scenarios, and learn how they can help you analyze and. Market demand and market supply determine the market price and quantity. the demand for a firm’s product is perfectly elastic (i.e. one firm’s product is a perfect substitute for another firm’s product). in perfect competition, the firm’s marginal revenue equals the market price. if mr = mc, economic profit is maximized. A market structure helps us to understand what differentiates markets from one another. in economics, market structure is the number of firms producing identical products which are homogeneous. the types of market structures include the following: monopolistic competition, also called competitive market, where there is a large number of firms. Market structure makes it easier to understand the characteristics of diverse markets. the main body of the market is composed of suppliers and demanders. both parties are equal and indispensable. the market structure determines the price formation method of the market.

Key Summary On Market Structures Economics Tutor2u A market structure helps us to understand what differentiates markets from one another. in economics, market structure is the number of firms producing identical products which are homogeneous. the types of market structures include the following: monopolistic competition, also called competitive market, where there is a large number of firms. Market structure makes it easier to understand the characteristics of diverse markets. the main body of the market is composed of suppliers and demanders. both parties are equal and indispensable. the market structure determines the price formation method of the market. Economic profit is equal to the difference between total revenues and economic costs. 17. the “citizen perspective” is that market power and competition can both be undesirable. 18. an example of a network externality is when the widespread adoption of a particular technology results in environmental damages. 19. It is common to differentiate these markets across the following seven distinct features. the industry’s buyer structure. the turnover of customers. the extent of product differentiation. the nature of costs of inputs. the number of players in the market. vertical integration extent in the same industry. the largest player’s market share.

The Four Major Types Of Market Structure Symphysis Economic profit is equal to the difference between total revenues and economic costs. 17. the “citizen perspective” is that market power and competition can both be undesirable. 18. an example of a network externality is when the widespread adoption of a particular technology results in environmental damages. 19. It is common to differentiate these markets across the following seven distinct features. the industry’s buyer structure. the turnover of customers. the extent of product differentiation. the nature of costs of inputs. the number of players in the market. vertical integration extent in the same industry. the largest player’s market share.

Comments are closed.