Market Equilibrium Transition To New Equilibrium Tutor2u

Market Equilibrium Transition To New Equilibrium Reference Library Not every market clears immediately. transition to a new equilibrium. in many cases we see shifts in both demand and supply in which case the final effect on price and quantity depends on the direction of the shifts in the curves and also the scale of the changes. here is an example in the analysis diagram below. shift in demand and supply. Equilibrium means ‘at rest’ or ‘a state of balance’ i.e. a situation where there is no tendency for change. the concept is used in both microeconomics (e.g. equilibrium prices in a market) and also in macroeconomics (e.g. equilibrium national income). market equilibrium is a state in which the quantity of a good or service that is being supplied is equal to the quantity that is being.
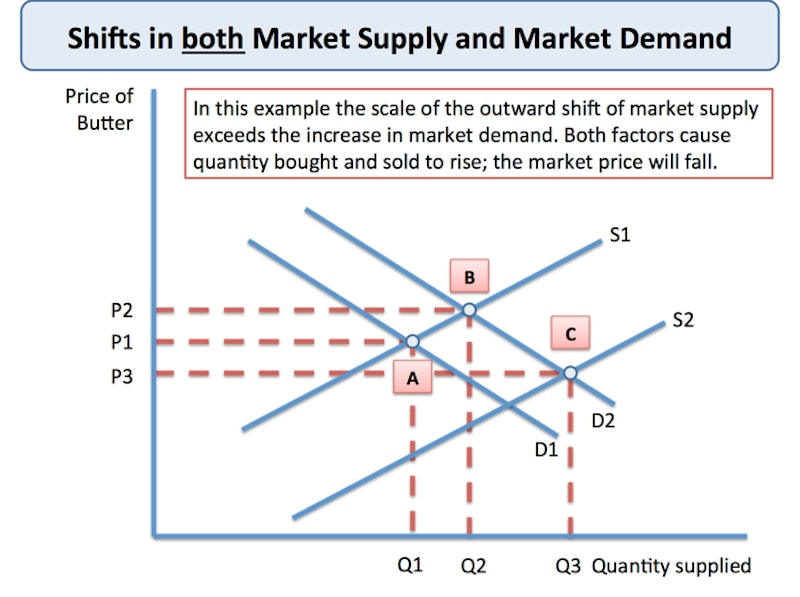
Market Equilibrium Transition To New Equilibrium Reference Library The demand for and supply of fresh fish in a local market is shown in the table below. the original equilibrium price is £6 per kg. if market demand rises by 80 kg at each and every price, then the new equilibrium price will be £8 with 300kg bought and sold. this change in market equilibrium from an increase in demand is illustrated below. The new market equilibrium will be at q3 and p1. movements to a new equilibrium. increase in demand; if there was an increase in income the demand curve would shift to the right (d1 to d2). initially, there would be a shortage of the good. therefore the price and quantity supplied will increase leading to a new equilibrium at q2, p2. 2. This is a brief revision video introducing students to the concept of market equilibrium, a state of balance between market demand and market supply.#aqaeco. The word “equilibrium” means “balance.”. if a market is at its equilibrium price and quantity, then it has no reason to move away from that point. however, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity. (4).

Market Equilibrium Tutor2u Business This is a brief revision video introducing students to the concept of market equilibrium, a state of balance between market demand and market supply.#aqaeco. The word “equilibrium” means “balance.”. if a market is at its equilibrium price and quantity, then it has no reason to move away from that point. however, if a market is not at equilibrium, then economic pressures arise to move the market toward the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity. (4). Equilibrium. equilibrium in a market occurs when demand = supply. at this point, the price is called the equilibrium or market clearing price. this is the price at which sellers are clearing (selling) their stock at an acceptable rate. a graph showing a market in equilibrium with a market clearing price at p & quantity at q. The answer is "both." like the two blades of a scissors, supply and demand work together to determine price. when you combine the supply and demand curves, there is a point where they intersect; this point is called the market equilibrium. the price at this intersection is the equilibrium price, and the quantity is the equilibrium quantity.

Market Equilibrium Tutor2u Equilibrium. equilibrium in a market occurs when demand = supply. at this point, the price is called the equilibrium or market clearing price. this is the price at which sellers are clearing (selling) their stock at an acceptable rate. a graph showing a market in equilibrium with a market clearing price at p & quantity at q. The answer is "both." like the two blades of a scissors, supply and demand work together to determine price. when you combine the supply and demand curves, there is a point where they intersect; this point is called the market equilibrium. the price at this intersection is the equilibrium price, and the quantity is the equilibrium quantity.

Comments are closed.