Marginal Utility Consumer Choice Marginal Utility Consumer Choice
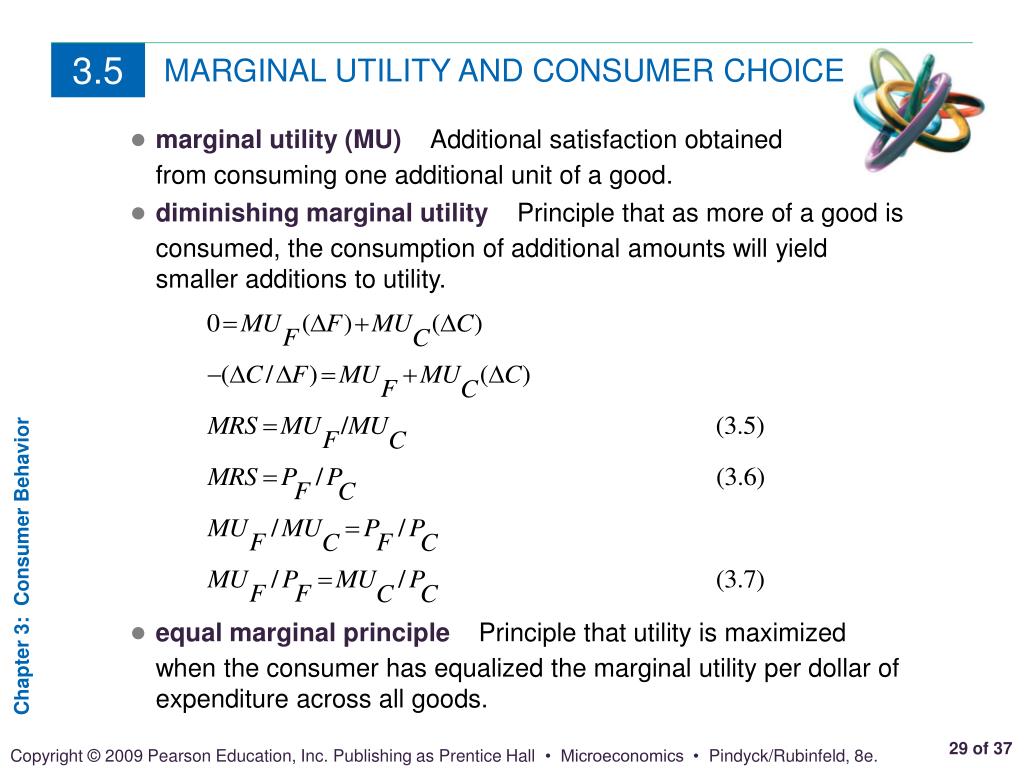
Ppt Chapter 3 Outline Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 3195763 Marginal utility tells how much marginal value or satisfaction a consumer gets from consuming an additional unit of a good. microeconomic theory states that consumer choice is made on margins. 5 consumer choice 5.1 consumption choices total utility and diminishing marginal utility. to understand how a household will make its choices, economists look at what consumers can afford, as shown in a budget constraint (or budget line), and the total utility or satisfaction derived from those choices.

Ppt Principles Of Economics Powerpoint Presentation Free Download The theory of consumer choice assumes consumers wish to maximise their utility through the optimal combination of goods given their limited budget. to illustrate how consumers choose between different combinations of goods we can use equi marginal principle and indifference curves and budget lines. consumer equilibrium equimarginal. Marginal utility is the added satisfaction that a consumer gets from having one more unit of a good or service. the concept of marginal utility is used by economists to determine how much of an. Course: ap®︎ college microeconomics > unit 1. lesson 6: marginal analysis and consumer choice. marginal utility and total utility. visualizing marginal utility mu and total utility tu functions. total utility and marginal utility. utility maximization: equalizing marginal utility per dollar. marginal utility free response example. In almost all cases, consumer choices are driven by prices. as price goes up, the quantity that consumers demand goes down. this correlation between the price of goods and the willingness to make purchases is represented clearly by the generation of a demand curve (with price as the y axis and quantity as the x axis).
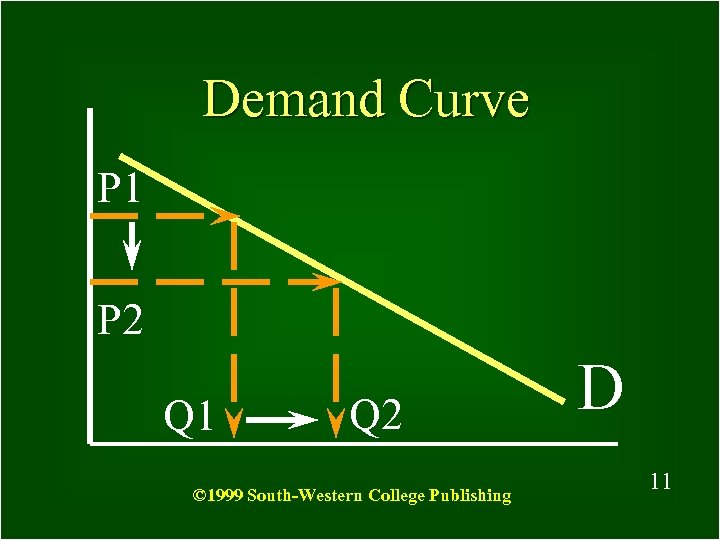
Chapter 5 Marginal Utility Consumer Choice 3 16 2018 Course: ap®︎ college microeconomics > unit 1. lesson 6: marginal analysis and consumer choice. marginal utility and total utility. visualizing marginal utility mu and total utility tu functions. total utility and marginal utility. utility maximization: equalizing marginal utility per dollar. marginal utility free response example. In almost all cases, consumer choices are driven by prices. as price goes up, the quantity that consumers demand goes down. this correlation between the price of goods and the willingness to make purchases is represented clearly by the generation of a demand curve (with price as the y axis and quantity as the x axis). Figure 1. a choice between consumption goods. josé has income of $56. movies cost $7 and t shirts cost $14. the points on the budget constraint line show the combinations of affordable movies and t shirts. utility is the term economists use to describe the satisfaction or happiness a person gets from consuming a good or service. When economists talk about consumer choice, what they are referring to is the combination of goods and services a consumer purchases. to understand how a household will make its choices, economists look at what consumers can afford, as shown in a budget constraint (or budget line), and the total utility or satisfaction derived from those choices.

Comments are closed.