Mandible And Maxilla Anatomy

Mandible Jaw Bone Anatomy Parts Function Mandible Dislocation The maxilla, also known as the upper jaw, is a vital viscerocranium structure of the skull. it is involved in the formation of the orbit, nose and palate, holds the upper teeth and plays an important role for mastication and communication. this bone consists of five major parts, one being the body and four being projections named processes. Mandibula. 1 2. synonyms: os mandibulare. the mandible is the largest bone of the facial skeleton (viscerocranium). besides the bones of the middle ear, the mandible is the only mobile bone in the skull. unlike other bones of the skull, the mandible doesn’t articulate with the surrounding bones via sutures, but rather via a synovial joint.

Mandible Anatomy Britannica Muscular attachments. the mandible serves as the attachment point for the various muscles, including the strong muscles of mastication. mandibular body: external (lateral) surface – mentalis, buccinator, platysma, depressor labii inferioris, depressor anguli oris. internal (medial) surface – genioglossus, geniohyoid, mylohyoid and digastric. The maxilla is the central, paired bone of the viscerocranium. the left and right maxilla fuse in the midline to form the upper jaw. between the two maxillae lies a cranial suture called the intermaxillary suture. the maxilla is made of several parts: the body; the zygomatic process (zygomatic arch) the frontal process. The maxilla is the most important bone of the midface. it has a central location and provides structural support to the viscerocranium. it has functional and aesthetic significance as it has a fundamental role in facial architecture, separates the nasal and oral cavities, forms the upper jaw, and contains the maxillary sinus (see image. maxillae).[1][2]. The mandible is the largest bone in the human skull, forming the lower jawline and shaping the contour of the inferior third of the face (see image. mandible anatomy).[1] articulation with the skull base at the bilateral temporomandibular joints allows a range of movements facilitated by associated muscles, including dental occlusion with the maxilla (see image. jaw anatomy, lateral view). the.
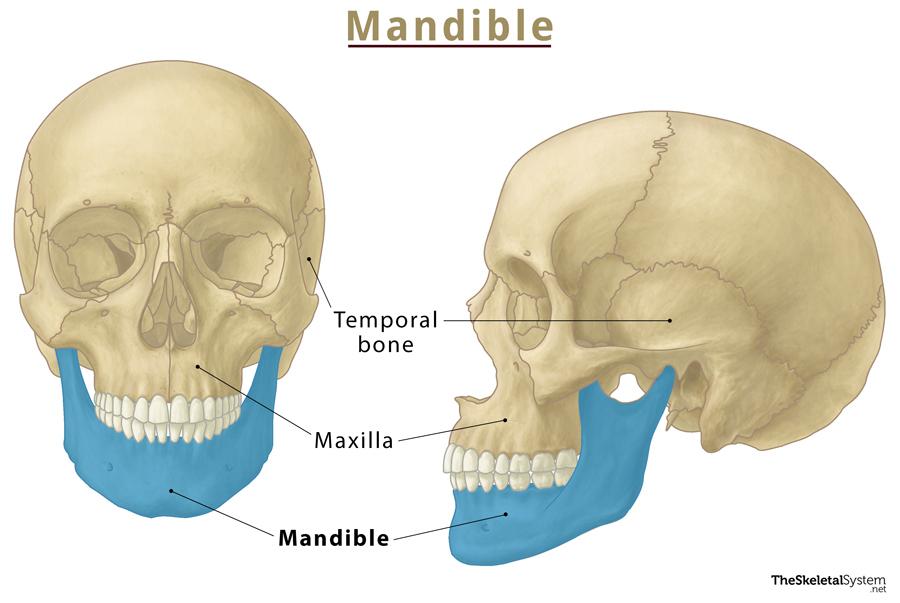
Mandible Lower Jaw Bone Location Functions Anatomy The maxilla is the most important bone of the midface. it has a central location and provides structural support to the viscerocranium. it has functional and aesthetic significance as it has a fundamental role in facial architecture, separates the nasal and oral cavities, forms the upper jaw, and contains the maxillary sinus (see image. maxillae).[1][2]. The mandible is the largest bone in the human skull, forming the lower jawline and shaping the contour of the inferior third of the face (see image. mandible anatomy).[1] articulation with the skull base at the bilateral temporomandibular joints allows a range of movements facilitated by associated muscles, including dental occlusion with the maxilla (see image. jaw anatomy, lateral view). the. Also known as the lower jawbone, the mandible is the largest and strongest bone of the face. it has a symmetrical, horseshoe shape. the mandible is not directly connected to other bones of the skull and is the only moving bone of the skull. the mandible and the maxilla form the lower and upper parts of the jaw, respectively. The maxilla is a bone which helps to make up the skull. it is specifically located in the mid face, forms the upper jaw, separates the nasal and oral cavities, and contains the maxillary sinuses (located on each side of the nose. one of the maxilla's most important functions is to make up the architecture of our faces and to support the rest of.

Maxilla And Mandible Diagram Quizlet Also known as the lower jawbone, the mandible is the largest and strongest bone of the face. it has a symmetrical, horseshoe shape. the mandible is not directly connected to other bones of the skull and is the only moving bone of the skull. the mandible and the maxilla form the lower and upper parts of the jaw, respectively. The maxilla is a bone which helps to make up the skull. it is specifically located in the mid face, forms the upper jaw, separates the nasal and oral cavities, and contains the maxillary sinuses (located on each side of the nose. one of the maxilla's most important functions is to make up the architecture of our faces and to support the rest of.

Mandible Jaw Bone Anatomy Parts Function Mandible Dislocation

Detailed Anatomy Of Maxilla And Mandible Diagram Quizlet

Comments are closed.