Lumbar Puncture Neurology Medbullets Step 1

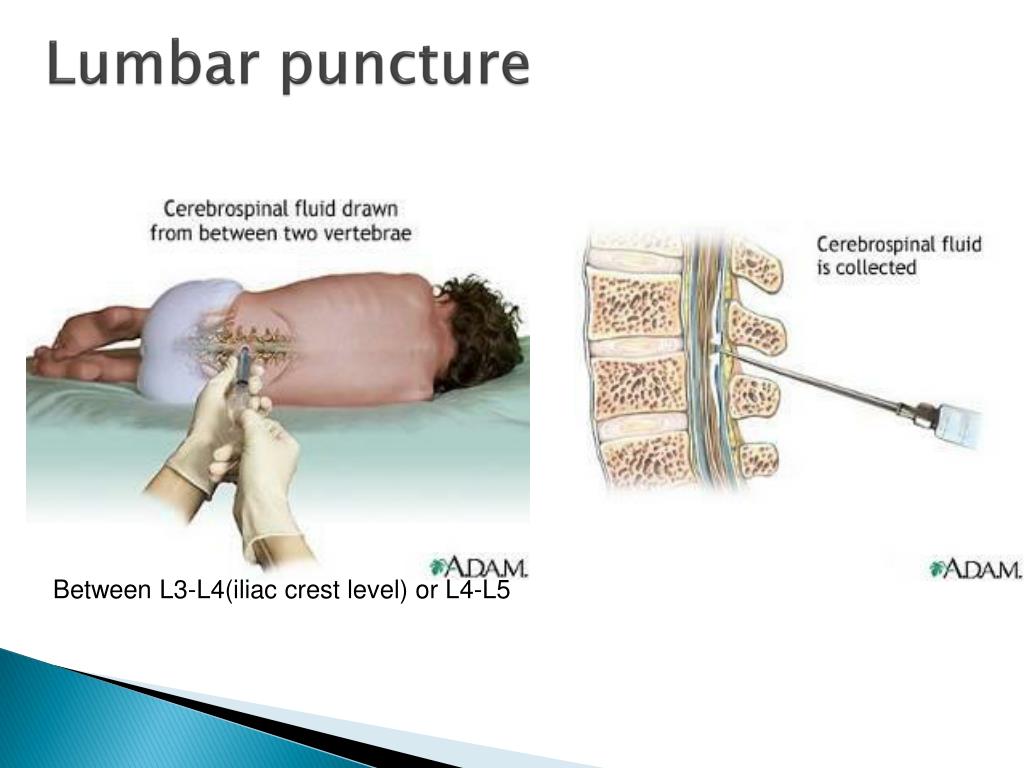
Lumbar Puncture Neurology Medbullets Step 1 Introduction. lumbar puncture (lp) is a procedure where a spinal needle is advanced into the subarachnoid space in order to collect cerebral spinal fluid (csf) the lp can allow the physician to determine. the etiology of meningitis. if the patient has a subarachnoid hemorrhage in the setting of a normal non contrast head ct. A lumbar puncture is performed, which demonstrates a cell count of 1 ul, protein is 135 mg dl, and glucose is 65 mg dl. he is admitted to the neurology floor for frequent negative inspiratory pressure and vital capacity measures and intravenous immunoglobulin.

Lumbar Puncture Procedure Position Lumbar Puncture Side Effects Meningitis. a 19 year old male is brought to the emergency department by his college roommate due to confusion and difficulty with arousing from sleep. the patient reports severe generalized headache, neck stiffness, and muscle aches. temperature is 102.2°f (39°c), blood pressure is 102 68 mmhg, pulse is 107 min, and respirations are 22 min. There are many differences in fluoroscopy guided lumbar puncture (fg lp) technique among radiologists. <6 cm h 2 o is indicative of low intracranial pressure; >25 cm h 2 o indicates idiopathic intracranial hypertension. in general, fg lp is a very safe procedure when good sterile technique is performed. the most common complication of fg lp is. Some studies have already assessed the risks of lp; and the procedure seems to be both “safe and acceptable” to do. in a multi site us study, 342 people underwent 428 lp. side effects such as pain, anxiety and the well known post lumbar puncture headaches (plphas) were quantified and compared to controls. F, the median percent change ([lumbar puncture – cisterna puncture] cisterna puncture × 100) is plotted for each biomarker with the interquartile range. nfl in csf taken from the cisterna magna area was significantly lower than of csf taken from the lumbar area (mann whitney u = 45.5, z = –2.779, p = .004). all other p’s > .05.

Anatomy For Lumbar Puncture Anatomy Reading Source Some studies have already assessed the risks of lp; and the procedure seems to be both “safe and acceptable” to do. in a multi site us study, 342 people underwent 428 lp. side effects such as pain, anxiety and the well known post lumbar puncture headaches (plphas) were quantified and compared to controls. F, the median percent change ([lumbar puncture – cisterna puncture] cisterna puncture × 100) is plotted for each biomarker with the interquartile range. nfl in csf taken from the cisterna magna area was significantly lower than of csf taken from the lumbar area (mann whitney u = 45.5, z = –2.779, p = .004). all other p’s > .05. Introduction. lumbar puncture (lp) is a procedure where a spinal needle is advanced into the subarachnoid space in order to collect cerebral spinal fluid (csf) the lp can allow the physician to determine. the etiology of meningitis. if the patient has a subarachnoid hemorrhage in the setting of a normal non contrast head ct. Meningitis. a 19 year old man presents to the emergency department with a headache. his headache was initially mild but then subsequently worsened over the course 2 days. his headaches are associated with fevers, chills, photophobia, and neck stiffness. his temperature is 101°f (38.3°c), blood pressure is 124 95 mmhg, pulse is 118 min, and.

How To Do Lumbar Puncture Neurologic Disorders Msd Manual Introduction. lumbar puncture (lp) is a procedure where a spinal needle is advanced into the subarachnoid space in order to collect cerebral spinal fluid (csf) the lp can allow the physician to determine. the etiology of meningitis. if the patient has a subarachnoid hemorrhage in the setting of a normal non contrast head ct. Meningitis. a 19 year old man presents to the emergency department with a headache. his headache was initially mild but then subsequently worsened over the course 2 days. his headaches are associated with fevers, chills, photophobia, and neck stiffness. his temperature is 101°f (38.3°c), blood pressure is 124 95 mmhg, pulse is 118 min, and.
Lumbar Puncture Landmarks

Comments are closed.