Lumbar Puncture Neudrawlogy Simplifying Neurology

Lumbar Puncture Neudrawlogy Simplifying Neurology Vascular neurology neuromuscular index about open menu close menu. folder: other authors. back. casey albin lumbar puncture. download jpeg read tweetorial. Chloride in neurology. decompressive hemicraniectomy in ischemic stroke. lumbar puncture and opening pressure. leptomeningeal versus pachymeningeal enhancement.

How To Do Lumbar Puncture Neurologic Disorders Msd Manual Introduction. lumbar puncture (lp) is commonly used in neurology practice for diagnostic and therapeutic indications. in the context of an ageing population, increasing numbers of patients are prescribed regular antiplatelet or anticoagulant medication (collectively known as antithrombotics), and or have comorbid coagulopathies including thrombocytopenia, platelet dysfunction and coagulation. Introduction. cerebrospinal fluid collection by lumbar puncture (lp) is performed in the diagnostic workup of several neurological brain diseases. reluctance to perform the procedure is among others due to a lack of standards and guidelines to minimize the risk of complications, such as post lp headache or back pain. Lumbar puncture (lp) with examination of cerebrospinal fluid (csf) is an important diagnostic tool for a variety of infectious and noninfectious neurologic conditions. the indications, contraindications, technique, and complications of lp in adults will be reviewed here. techniques of lp in children and of spinal and other types of neuraxial. A lumbar puncture (lp) is performed to obtain cerebrospinal fluid. it is implemented in the clinic on a routine basis to aid the diagnosis of neurologic diseases. this paper accompanies an informative lumbar puncture video that shows the lumbar puncture procedure as routinely performed in the vumc alzheimer center based on the consensus.
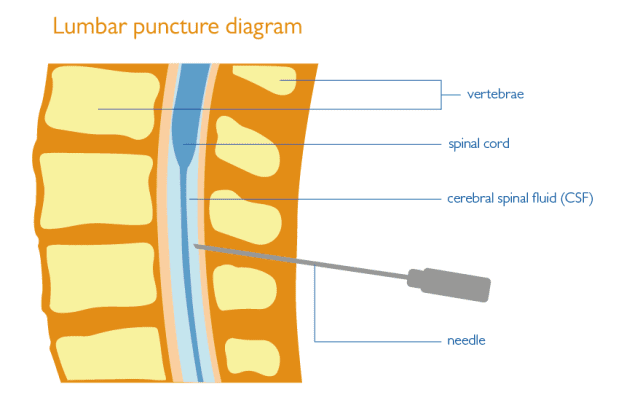
Lumbar Puncture Fact Sheet Health Information Brain Spine Lumbar puncture (lp) with examination of cerebrospinal fluid (csf) is an important diagnostic tool for a variety of infectious and noninfectious neurologic conditions. the indications, contraindications, technique, and complications of lp in adults will be reviewed here. techniques of lp in children and of spinal and other types of neuraxial. A lumbar puncture (lp) is performed to obtain cerebrospinal fluid. it is implemented in the clinic on a routine basis to aid the diagnosis of neurologic diseases. this paper accompanies an informative lumbar puncture video that shows the lumbar puncture procedure as routinely performed in the vumc alzheimer center based on the consensus. Make sure the needle is directed toward the spinal canal, and not off to one side. if blood returns with a deep insertion, the needle may have entered the venous plexus on the ventral side of the cord. withdraw the needle in successive small (eg, 1 mm) steps, checking for csf return with each step. A lumbar puncture needle with stylet is inserted into the l3 to l4 or l4 to l5 interspace (the l4 spinous process is typically on a line between the posterior superior iliac crests); the needle is aimed rostrally toward the patient’s umbilicus and, if the patient is supine, always kept parallel to the floor. entrance into the subarachnoid.

Comments are closed.