Lumbar Puncture Anesthesia Key
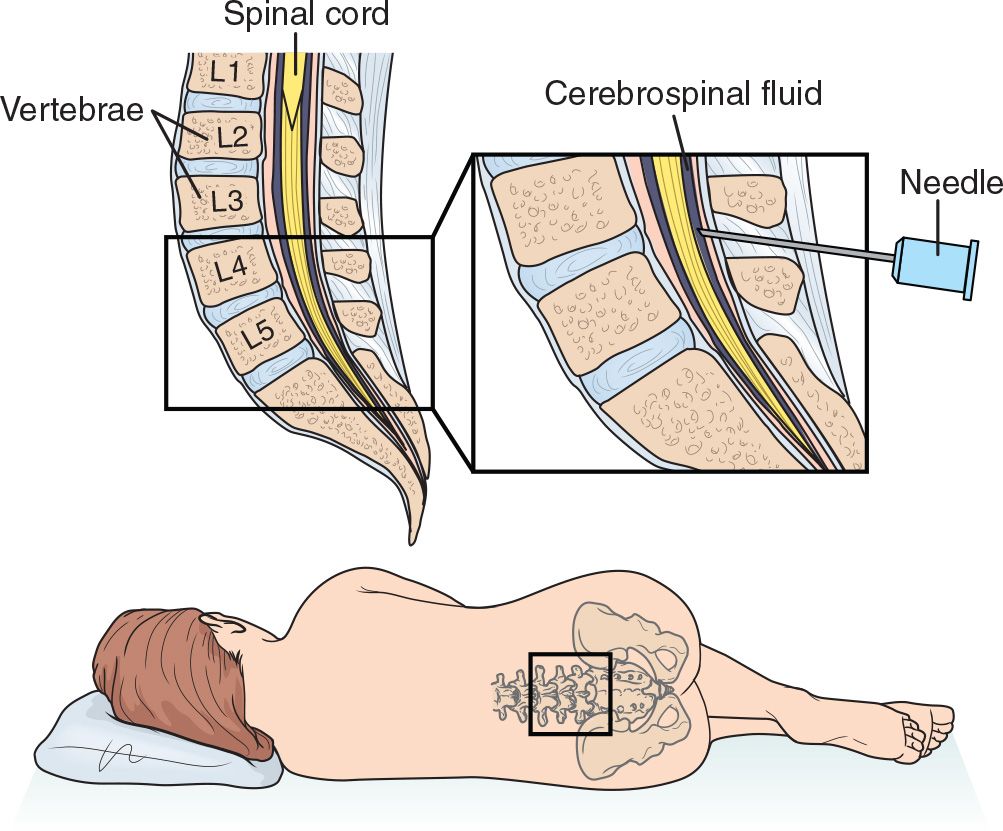
Lumbar Puncture Anesthesia Key Lumbar puncture (lp) is a time honoured method for obtaining cerebrospinal fluid (csf) for diagnostic evaluation of suspected central nervous system (cns) abnormalities. lp is an essential procedure in children with suspected meningitis, and represents the only simple method of obtaining fluid for rapid diagnosis and appropriate pathogen. Lumbar puncture (lp) with examination of cerebrospinal fluid (csf) is an important diagnostic tool for a variety of infectious and noninfectious neurologic conditions. the indications, contraindications, technique, and complications of lp in adults will be reviewed here. techniques of lp in children and of spinal and other types of neuraxial.

Lumbar Puncture Procedure Position Lumbar Puncture Side Effects Platelet count <20,000 mm 3 is an absolute contraindication; platelet counts >50,000 mm 3 are safe for lumbar puncture* international normalized ratio ≥1.5 * administration of unfiltered heparin or low molecular weight heparin in past 24 hours *. Lumbar puncture (lp), also referred to as “spinal tap,” is a commonly performed procedure that involves obtaining and sampling cerebrospinal fluid from the spinal cord. it was developed by heinrich quincke in the late 19th century.[1] it is the gold standard diagnostic procedure in the diagnosis of meningitis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and certain neurological disorders. it is also used in. Make sure the needle is directed toward the spinal canal, and not off to one side. if blood returns with a deep insertion, the needle may have entered the venous plexus on the ventral side of the cord. withdraw the needle in successive small (eg, 1 mm) steps, checking for csf return with each step. Introduction. cerebrospinal fluid collection by lumbar puncture (lp) is performed in the diagnostic workup of several neurological brain diseases. reluctance to perform the procedure is among others due to a lack of standards and guidelines to minimize the risk of complications, such as post lp headache or back pain.

Lumbar Puncture Lp Almostadoctor Make sure the needle is directed toward the spinal canal, and not off to one side. if blood returns with a deep insertion, the needle may have entered the venous plexus on the ventral side of the cord. withdraw the needle in successive small (eg, 1 mm) steps, checking for csf return with each step. Introduction. cerebrospinal fluid collection by lumbar puncture (lp) is performed in the diagnostic workup of several neurological brain diseases. reluctance to perform the procedure is among others due to a lack of standards and guidelines to minimize the risk of complications, such as post lp headache or back pain. Key points. lumbar puncture (lp) is essential for the diagnosis of two treatable but potentially fatal conditions, central nervous system (cns) infection and subarachnoid hemorrhage (sah) with a negative computed tomography (ct) scan. lp can also be helpful in the differential diagnosis of other conditions including cns malignancy, pseudotumor. ### what you need to know is the needle tip configuration important when performing a lumbar puncture for any indication? a systematic review published in the lancet in december 2017 suggests that it is. the review found that using atraumatic (pencil point) lumbar puncture needles instead of conventional lumbar puncture needles reduced the risk of post dural puncture headache and of return to.
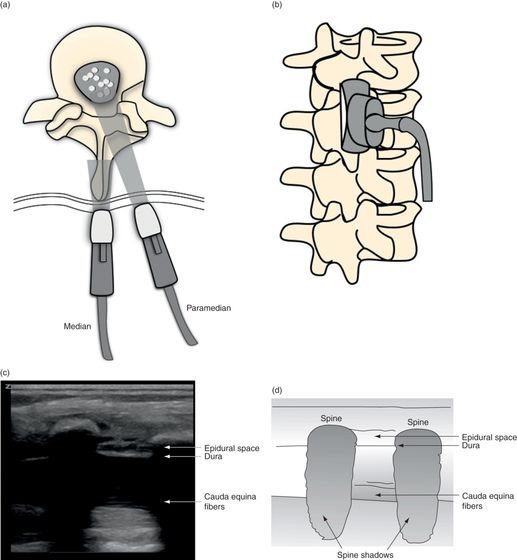
Ultrasound Guided Lumbar Puncture Anesthesia Key Key points. lumbar puncture (lp) is essential for the diagnosis of two treatable but potentially fatal conditions, central nervous system (cns) infection and subarachnoid hemorrhage (sah) with a negative computed tomography (ct) scan. lp can also be helpful in the differential diagnosis of other conditions including cns malignancy, pseudotumor. ### what you need to know is the needle tip configuration important when performing a lumbar puncture for any indication? a systematic review published in the lancet in december 2017 suggests that it is. the review found that using atraumatic (pencil point) lumbar puncture needles instead of conventional lumbar puncture needles reduced the risk of post dural puncture headache and of return to.

Comments are closed.