Lipid Nanoparticles In Treating Preeclampsia Medical Automation

Lipid Nanoparticles In Treating Preeclampsia Medical Automation Potential preeclampsia treatment uses lnps to deliver mrna to the placenta “the new study from swingle and her team [at the university of pennsylvania ] marks the first time scientists have successfully delivered mrna to the placenta using an lnp. 5.3.3 targeted lipid nanoparticles for treating obstetric disorders. chondroitin sulphate a (csa) is a protein present on the surface of the placental stb layer. targeted lipid nanoparticles composed of plga, soybean lecithin, and dspe peg, displaying a synthetic placental csa binding peptide on their surface also show efficient placental homing.

Lipid Nanoparticles Prorenata Biotech Ionizable lipid nanoparticles for in vivo mrna delivery to the placenta during pregnancy (a rat model) currently the only treatment for preeclampsia starts with delivery of the baby and the placenta. while this can be lifesaving for mother and infant, it is often accompanied by both short term and long term complications of prematurity. Nanoparticle technology has also been investigated for treatment of fetal growth restriction, often experienced concomitantly with preeclampsia and resulting from placental insufficiency. liposomal nanoparticles targeted to irgd, a peptide that binds selectively to the placenta, were loaded with insulin like growth factor 2 (igf 2) and injected. Oils and lipids help make water insoluble drugs soluble by dispersing them in an aqueous medium with the help of a surfactant and enabling their absorption across the gut barrier. the emergence of microemulsions (thermodynamically stable), nanoemulsions (kinetically stable), and self emulsifying drug delivery systems added unique characteristics that make them suitable for prolonged storage. Lipid nanoparticles (lnps) have emerged as leading non viral carriers for messenger rna (mrna) delivery in clinical applications. overcoming challenges in safe and effective mrna delivery to target tissues and cells, along with controlling release from the delivery vehicle, remains pivotal in mrna based therapies. this review elucidates the structure of lnps, the mechanism for mrna delivery.
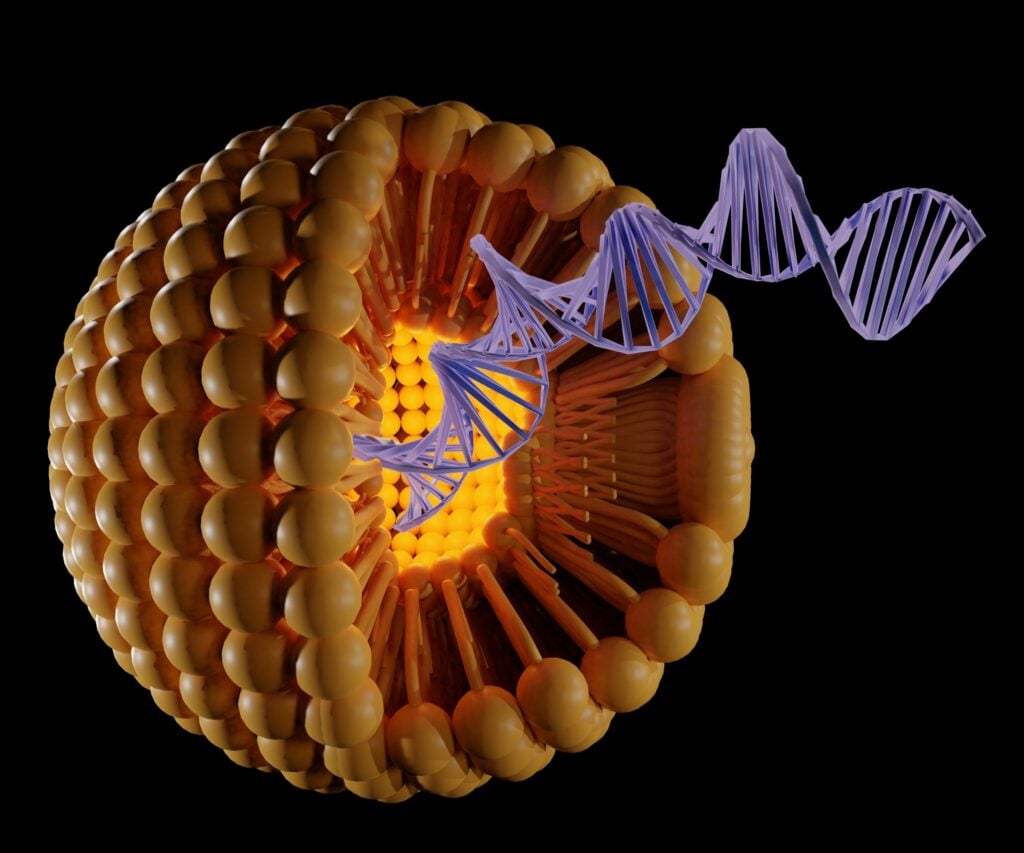
New Screening Platform For Uncovering Potent Lipid Nanoparticles To Oils and lipids help make water insoluble drugs soluble by dispersing them in an aqueous medium with the help of a surfactant and enabling their absorption across the gut barrier. the emergence of microemulsions (thermodynamically stable), nanoemulsions (kinetically stable), and self emulsifying drug delivery systems added unique characteristics that make them suitable for prolonged storage. Lipid nanoparticles (lnps) have emerged as leading non viral carriers for messenger rna (mrna) delivery in clinical applications. overcoming challenges in safe and effective mrna delivery to target tissues and cells, along with controlling release from the delivery vehicle, remains pivotal in mrna based therapies. this review elucidates the structure of lnps, the mechanism for mrna delivery. Lipid nanoparticles (lnps) are nanocarriers composed of four lipid components and can be used for gene therapy, protein replacement, and vaccine development. however, lnps also face several challenges, such as toxicity, immune activation, and low delivery efficiency. to overcome these challenges, artificial intelligence can be used to optimize. Over the past decade, the therapeutic potential of nanomaterials as novel drug delivery systems complementing conventional pharmacology has been widely acknowledged. among these nanomaterials, lipid based nanoparticles (lnps) have shown remarkable pharmacological performance and promising therapeutic outcomes, thus gaining substantial interest in preclinical and clinical research. in this.

Comments are closed.