Light Diagram Reflection At Catherine Brubaker Blog

Light Diagram Reflection At Catherine Brubaker Blog Reflection and the ray model of light. lesson 1 reflection and its importance; the role of light to sight; the line of sight; the law of reflection; specular vs. diffuse reflection; lesson 2 image formation in plane mirrors; why is an image formed? image characteristics in plane mirrors; ray diagrams for plane mirrors. See answer. a ray of light drawn from the sun's position at 7 pm to the distant window reflects off the window and travel to the observer's eye. on the other hand, a ray of light drawn from the 1 pm sun position to the window will reflect and travel to the ground, never making it to the distant observer's eye. 4.

Light Diagram Reflection At Catherine Brubaker Blog Step by step guide to drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors. step 1: draw the mirror and the object. step 2: identify and mark the object distance. step 3: draw reflected rays to the image. step 4: use law of reflection to work out incident rays. properties of image formed in plane mirror. worked examples. Incident ray: the ray of light that is incident on the interface. reflected ray: the ray of light that is reflected from the interface. normal: the perpendicular to the interface. angle of incidence: the angle that the incident ray makes with the normal. angle of reflection: the angle that the reflected ray makes with the normal. A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. this is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. there are a few important things to note: light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can change direction upon entering a different medium). Reflection of light. reflection is when light bounces off an object. if the surface is smooth and shiny, like glass, water or polished metal, the light will reflect at the same angle as it hit the surface. this is called specular reflection. diffuse reflection is when light hits an object and reflects in lots of different directions.
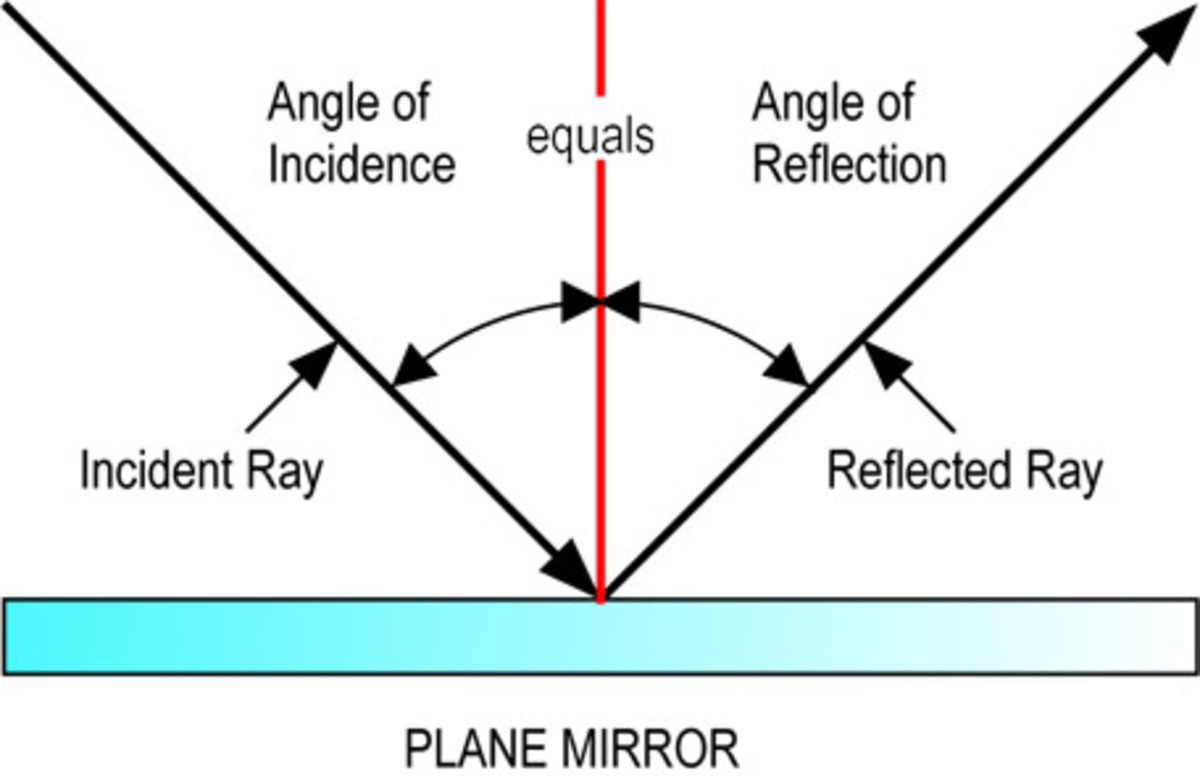
Light Diagram Reflection At Catherine Brubaker Blog A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. this is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. there are a few important things to note: light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can change direction upon entering a different medium). Reflection of light. reflection is when light bounces off an object. if the surface is smooth and shiny, like glass, water or polished metal, the light will reflect at the same angle as it hit the surface. this is called specular reflection. diffuse reflection is when light hits an object and reflects in lots of different directions. Up class 12 physics. course: up class 12 physics > unit 2. lesson 1: reflection of light by spherical mirrors. reflection laws & ray diagrams. reflection of light and ray diagrams for spherical mirrors. mirror formula, magnification formula, sign convention. sign convention. mix questions on mirror formula and magnification. A ray of light is light from a single point source (normally represented by a long and straight arrow on diagrams. incident ray is a ray of light striking a surface. reflected ray is a ray of light reflected from a surface. normal is an imaginary line perpendicular () to a surface where the reflection occurs. angle of incidence () is the angle.

Light Diagram Reflection At Catherine Brubaker Blog Up class 12 physics. course: up class 12 physics > unit 2. lesson 1: reflection of light by spherical mirrors. reflection laws & ray diagrams. reflection of light and ray diagrams for spherical mirrors. mirror formula, magnification formula, sign convention. sign convention. mix questions on mirror formula and magnification. A ray of light is light from a single point source (normally represented by a long and straight arrow on diagrams. incident ray is a ray of light striking a surface. reflected ray is a ray of light reflected from a surface. normal is an imaginary line perpendicular () to a surface where the reflection occurs. angle of incidence () is the angle.

Comments are closed.