Le Chatelier Principle And Volume Change Ap Chemistry Unit 7
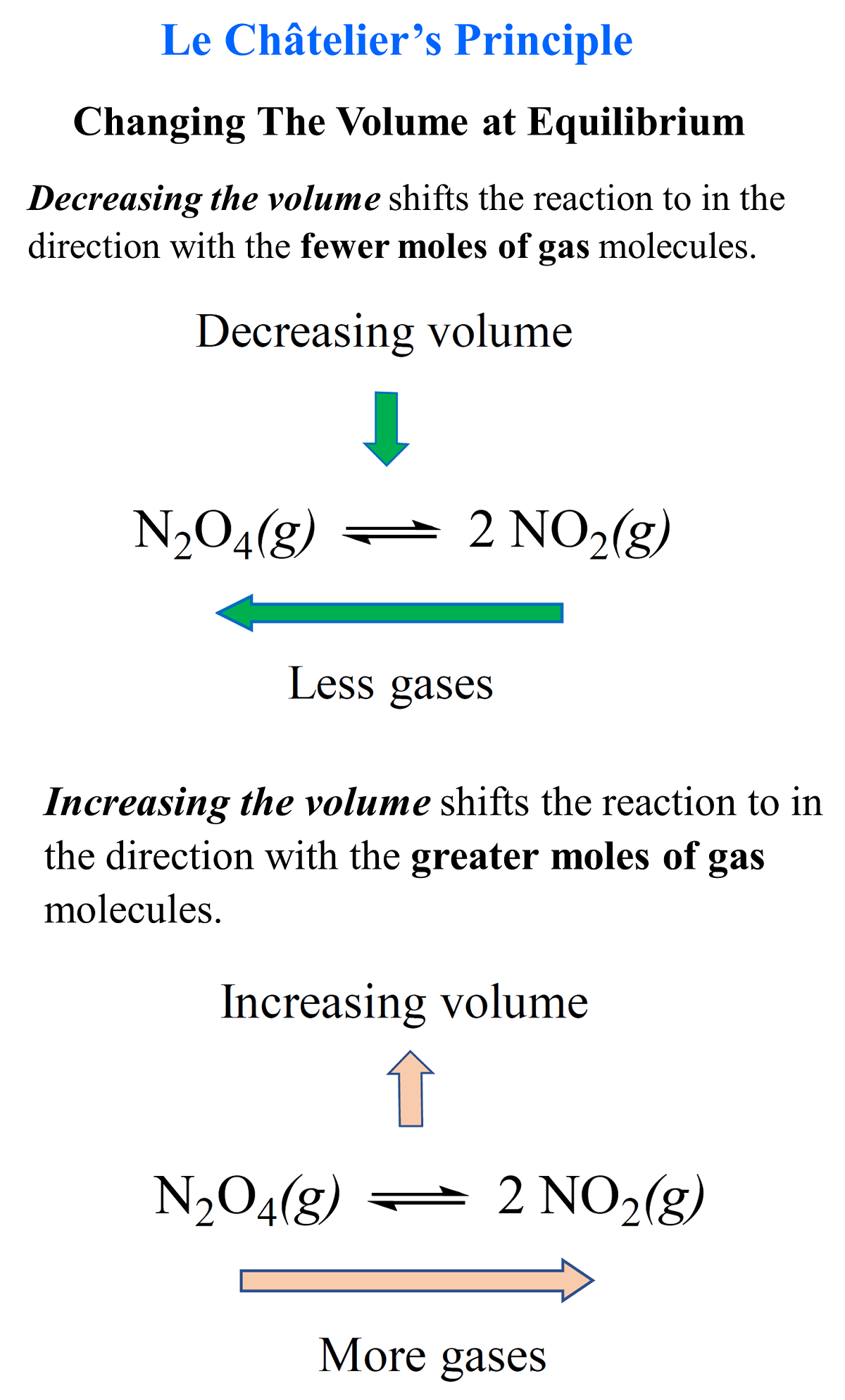
Le Chateliers Principle Chemistry Steps 🚀 access the best ap chemistry resources at apchemistrytutor 🎯 want to ace chemistry? access the best chemistry resource at conquerchemistry. Answer 1: when a reactant is added, the system shifts in the forward reaction direction to decrease the amount of reactants. in response to the stress, the amount of nh 3 (aq) decreases and the amount of cl (aq) increases. answer 2: when a product is removed, the system shifts in the forward reaction direction to increase the amount of products.

Le Chatelier Principle And Volume Change Ap Chemistry Unit 7 Le chatelier's principle. states that when a system at equilibrium is subjected to a stress or change in conditions, the equilibrium will shift to counteract the stress and establish a new equilibrium; changing the concentration of a reactant or product will cause the equilibrium to shift in the direction that reduces the change. Exam questions. 3 mins 3 questions. download. all answers. 1 1 mark. 2hi (g) ⇌ h 2 (g) i 2 (g) kp = 83 at 723 k. a mixture of hi (g), h 2 (g), and i 2 (g) is placed in a sealed, rigid container at 723 k. after equilibrium is established, the pressure inside the container is halved while the temperature is held constant at 723 k. The reaction quotient or q is the value obtained by entering all of the required concentrations into the equilibrium expression and calculating the result. for a general equation: aa bb cc dd. q =. the equilibrium constant is the numerical value of kc when the reaction is at equilibrium. if the reaction is not at equilibrium, the numerical. As a consequence, le chatelier's principle leads us to predict that the concentration of fe (scn) 2 should decrease, increasing the concentration of scn − part way back to its original concentration, and increasing the concentration of fe 3 above its initial equilibrium concentration. figure 15.7.1: (a) the test tube contains 0.1 m fe 3 .
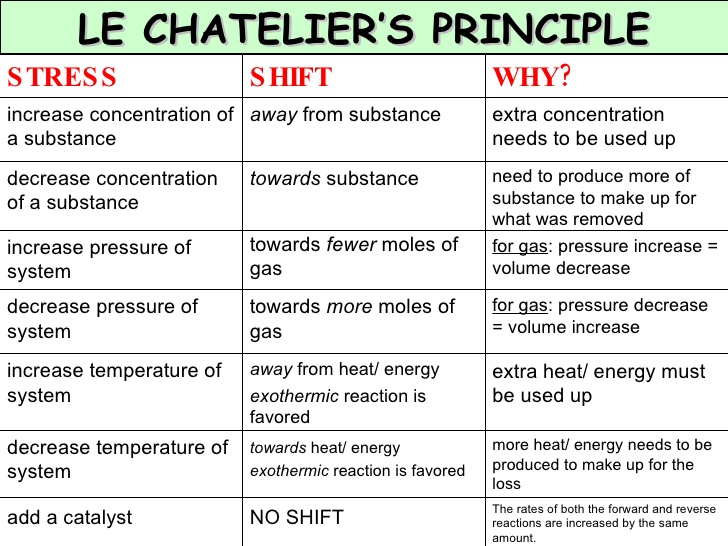
What Is Le Chatelier S Principle In Chemistry Socratic The reaction quotient or q is the value obtained by entering all of the required concentrations into the equilibrium expression and calculating the result. for a general equation: aa bb cc dd. q =. the equilibrium constant is the numerical value of kc when the reaction is at equilibrium. if the reaction is not at equilibrium, the numerical. As a consequence, le chatelier's principle leads us to predict that the concentration of fe (scn) 2 should decrease, increasing the concentration of scn − part way back to its original concentration, and increasing the concentration of fe 3 above its initial equilibrium concentration. figure 15.7.1: (a) the test tube contains 0.1 m fe 3 . Keep going! check out the next lesson and practice what you’re learning: khanacademy.org science ap chemistry beta x2eef969c74e0d802:equilibrium x. This phenomenon is summarized by le châtelier’s principle: if an equilibrium system is stressed, the system will experience a shift in response to the stress that re establishes equilibrium. reaction rates are affected primarily by concentrations, as described by the reaction’s rate law, and temperature, as described by the arrhenius equation.

Le Chatelier S Principle Keep going! check out the next lesson and practice what you’re learning: khanacademy.org science ap chemistry beta x2eef969c74e0d802:equilibrium x. This phenomenon is summarized by le châtelier’s principle: if an equilibrium system is stressed, the system will experience a shift in response to the stress that re establishes equilibrium. reaction rates are affected primarily by concentrations, as described by the reaction’s rate law, and temperature, as described by the arrhenius equation.
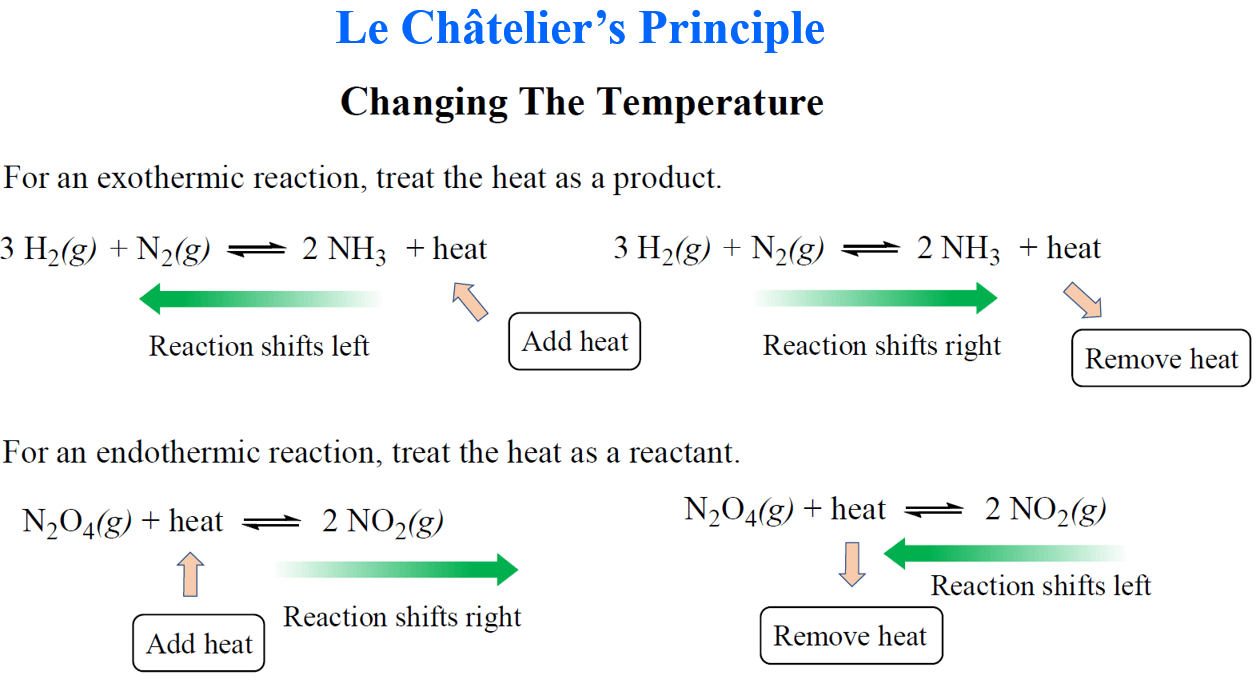
Le Chateliers Principle Chemistry Steps
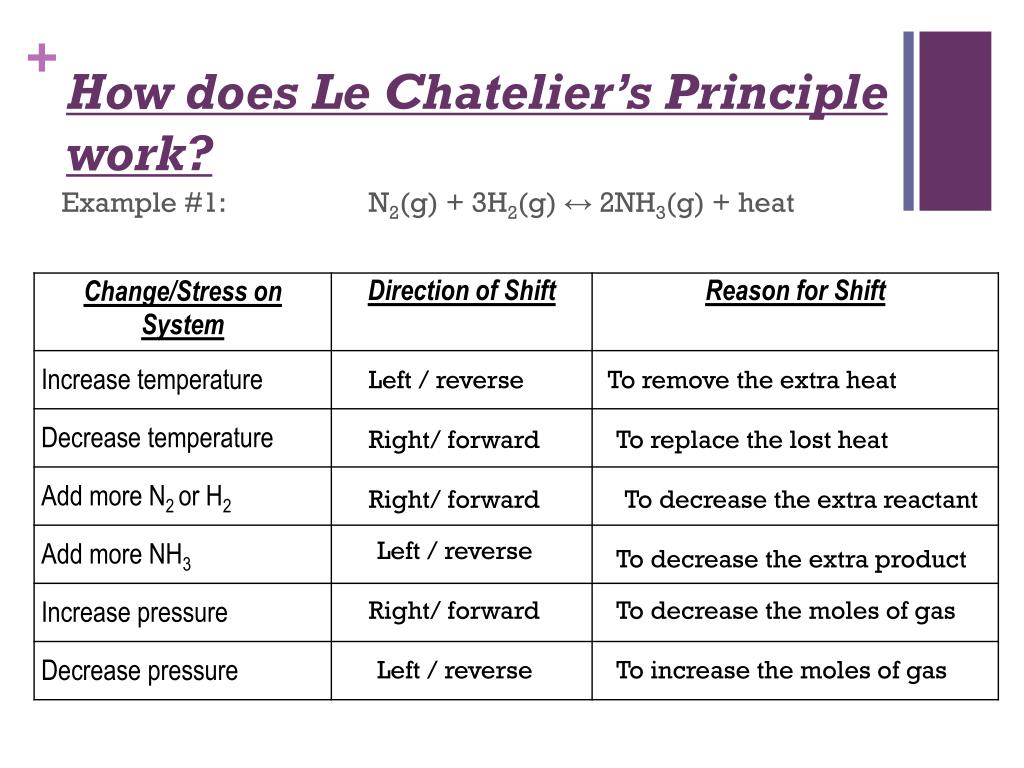
Le Chatelier S Principle Cheat Sheet

Comments are closed.