Lateral Ventricles Anatomy And Function Kenhub
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/582/8VzbTRjFXVO6E9Z7jvdsg_ventricles-of-the-brain_english.jpg)
Lateral Ventricles Anatomy And Function Kenhub The lateral ventricles are the largest in the series of four interconnecting fluid filled cavities within the brain. these cavities and their interconnecting channels, constitute the cerebral ventricular system. the other two cavities of this system are the third and fourth ventricles, while the cerebral aqueduct of sylvius is one of the. It is a narrow slit that is bordered laterally by the medial nuclei of each thalamus, the hypothalamus and interrupted anteriorly by the interthalamic adhesion. the roof of the cavity is formed anteriorly by the fornix and posteriorly by the splenium of the corpus callosum. third ventricle. ventriculus tertius. 1 5.
/images/vimeo_thumbnails/258821481/9nDgpAc5CeUL7D42CGrw_overlay.jpg)
Lateral Ventricles Anatomy And Function Kenhub The hippocampus is a paired structure present in each temporal lobe of the brain. it takes its name from the greek word for the seahorse, because it resembles this small upright swimming fish. the hippocampus is part of a larger structure of the temporal lobe called the hippocampal formation. the hippocampal formation extends from the amygdala. From their intricate anatomy to their vital functions in csf production and circulation, the lateral ventricles are true marvels of nature’s engineering. they protect our brains, help maintain the delicate balance of intracranial pressure, and even play a role in clearing waste from our most important organ. The cerebral ventricles have been studied since the fourth century bc and were originally thought to harbor the soul and higher executive functions. during the infancy of neuroradiology, alterations to the ventricular shape and position on pneumoencephalography and ventriculography were signs of mass effect or volume loss. however, in the current era of high resolution cross sectional imaging. The lateral ventricles communicate with the third ventricle through the interventricular foramina of monro. 5 each lateral ventricle has an estimated capacity of 7–10 ml. 6. the frontal horn (fig 1) extends anteriorly from the foramina of monro and communicates with the body of the lateral ventricles posteriorly.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/temporal-horn-of-the-lateral-ventricle/luhF1fp8UtmONEos3xToA_inferior_horn_of_the_lateral_ventricle_.png)
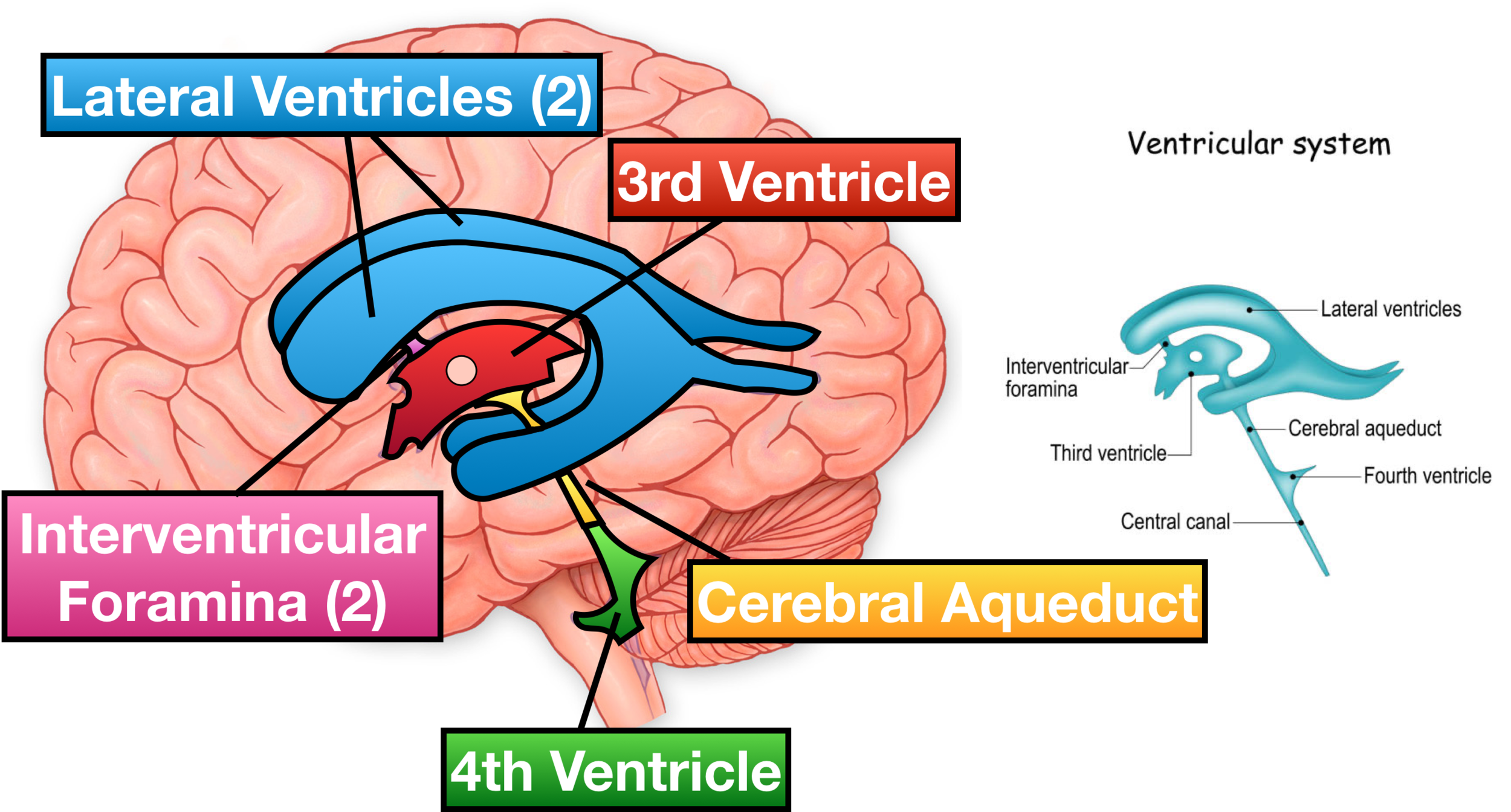
Lateral Ventricles Anatomy And Function Kenhub The cerebral ventricles have been studied since the fourth century bc and were originally thought to harbor the soul and higher executive functions. during the infancy of neuroradiology, alterations to the ventricular shape and position on pneumoencephalography and ventriculography were signs of mass effect or volume loss. however, in the current era of high resolution cross sectional imaging. The lateral ventricles communicate with the third ventricle through the interventricular foramina of monro. 5 each lateral ventricle has an estimated capacity of 7–10 ml. 6. the frontal horn (fig 1) extends anteriorly from the foramina of monro and communicates with the body of the lateral ventricles posteriorly. Function. the ventricular system produces, transports, and excretes csf, which coats the central nervous system. each ventricle contains choroid plexus, which makes the circulating csf. the csf moves from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle and finally to the fourth ventricle, where it exits and bathes the brain and spinal cord. The ventricular system is the interconnecting network of fluid filled cavities within the brain, comprising two lateral ventricles, the third ventricle and the fourth ventricle. the ventricles contain cerebrospinal fluid (csf), which is produced by the choroid plexus within the ventricles. 1. the ventricular system helps protect the brain by.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/en/lateral-ventricles/4xttYsXUGKFnwMyidStmaQ_SictAdvCU4S8NFlwLuAPDw_Ventriculus_lateralis_sinister_01.png)
Lateral Ventricles Anatomy And Function Kenhub Function. the ventricular system produces, transports, and excretes csf, which coats the central nervous system. each ventricle contains choroid plexus, which makes the circulating csf. the csf moves from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle and finally to the fourth ventricle, where it exits and bathes the brain and spinal cord. The ventricular system is the interconnecting network of fluid filled cavities within the brain, comprising two lateral ventricles, the third ventricle and the fourth ventricle. the ventricles contain cerebrospinal fluid (csf), which is produced by the choroid plexus within the ventricles. 1. the ventricular system helps protect the brain by.
Ventricles Of The Brain Labeled Anatomy Function Csf Flow
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/posterior-horn-of-the-lateral-ventricle-2/0j3BgQFXcbeYVBiPXpp8Q_Occipital_horn_of_lateral_ventricle_01.png)
Occipital Horn Of Lateral Ventricle

Comments are closed.