Kinds Of Elasticity Of Supply Inelastic And Elastic Supply

Kinds Of Elasticity Of Supply Inelastic And Elastic Supply Elasticities can be usefully divided into five broad categories: perfectly elastic, elastic, perfectly inelastic, inelastic, and unitary. an elastic demand or elastic supply is one in which the elasticity is greater than one, indicating a high responsiveness to changes in price. an inelastic demand or inelastic supply is one in which elasticity. 28 august 2019 by tejvan pettinger. price elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to a change in price. the price elasticity of supply (pes) is measured by % change in q.s divided by % change in price. if the price of a cappuccino increases by 10%, and the supply increases by 20%. we say the pes is 2.0.

The Elasticity Of Supply Meaning Types And Methods Tutor S Tips The price elasticity of supply measures the responsiveness of quantity supplied to changes in price. it is the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price. it is usually positive. supply is price inelastic if the price elasticity of supply is less than 1; it is unit price elastic if the price elasticity of. The five types are perfectly inelastic supply, relatively inelastic supply, unit elastic supply, relatively elastic supply, and perfectly elastic supply. these five types help to show how different products supply quantity changes when faced with changed in price. perfectly inelastic supply: this is when the e s formula equals to zero, meaning. As fig. 4.22 suggests nq < oq, the coefficient of elasticity of supply is less than one i.e., inelastic. if the nt straight line passes through the origin, the elasticity of supply becomes unity and if it passes through the price or vertical axis, the coefficient will be greater than one, i.e., elastic. determinants of elasticity of supply:. Understanding elasticity. 26 february 2017 by tejvan pettinger. elasticity is a concept which involves examining how responsive demand (or supply) is to a change in another variable such as price or income. price elasticity of demand (ped) – measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in price. price elasticity of supply (pes.
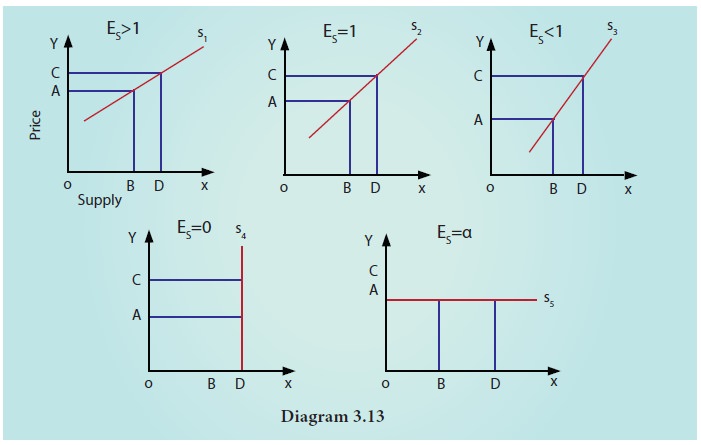
Types Of Elasticity Of Supply Economics As fig. 4.22 suggests nq < oq, the coefficient of elasticity of supply is less than one i.e., inelastic. if the nt straight line passes through the origin, the elasticity of supply becomes unity and if it passes through the price or vertical axis, the coefficient will be greater than one, i.e., elastic. determinants of elasticity of supply:. Understanding elasticity. 26 february 2017 by tejvan pettinger. elasticity is a concept which involves examining how responsive demand (or supply) is to a change in another variable such as price or income. price elasticity of demand (ped) – measures the responsiveness of demand to a change in price. price elasticity of supply (pes. Supply is price elastic if the price elasticity of supply is greater than 1, unit price elastic if it is equal to 1, and price inelastic if it is less than 1. a vertical supply curve, as shown in panel (a) of figure 5.11, is perfectly inelastic; its price elasticity of supply is zero. the supply of beatles’ songs is perfectly inelastic. The state of these factors for a particular good will determine if the price elasticity of supply is elastic or inelastic in regards to a change in price. the price elasticity of supply has a range of values: pes > 1: supply is elastic. pes < 1: supply is inelastic. pes = 0: the supply curve is vertical; there is no response of demand to prices.

Comments are closed.