Jerk Test For Shoulder Clinical Physio

Jerk Test For Shoulder Clinical Physio Youtube This tutorial takes you through this controversial test for the shoulder joint. it teaches you the methodology, and how to interpret your findings!⭐ website:. Evidence. a systematic review of the validity and accuracy of clinical tests used to detect labral pathology of the shoulder showed the lr of the jerk test to be lr 34.71 and the lr to be 0.27. [3] the reported diagnostic accuracy for the jerk test was a sensitivity of 73% and specificity of 98% [4].
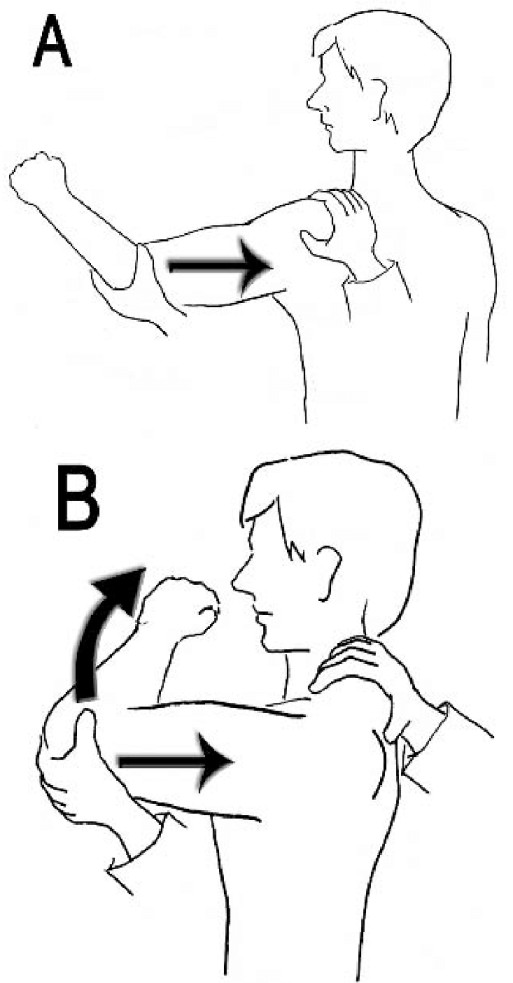
Jerk Test Of Shoulder Purpose How To Perform Mobile Physio The jerk test has moderate validity to confirm and good validity to rule out posteroinferior labral lesions. kim et al. (2004) have found a sensitivity of 90% and a sensitivity of 85%, while morey et al. (2018) found a sensitivity of 62.5% and a specificity of 96.4%. a painful jerk test is a predictor of failure of conservative treatment. 📌 free guide shoulder instability and labral pathology evidence based "cheat sheet" for clinicians: fitnesspainfree shoulder instability th. The content is intended as educational content for health care professionals and students. if you are a patient, seek care of a health care professional. the jerk test assesses for a posteroinferior labral tear of the shoulder. ??. Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive physiological movements, assessment of passive arthokinematic accessory joint mobility.

Jerk Test Posteroinferior Labral Tear Shoulder Assessment The content is intended as educational content for health care professionals and students. if you are a patient, seek care of a health care professional. the jerk test assesses for a posteroinferior labral tear of the shoulder. ??. Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive physiological movements, assessment of passive arthokinematic accessory joint mobility. The shoulder joint has a tremendous degree of mobility, which renders it prone to instability. while muscle forces control stability in mid ranges of motion, clinical instability presents itself at end range of motion (doukas et al. 2001). it is defined as abnormal motion of the humeral head on the glenoid, which presents as pain and or a sense. Shoulder orthopaedic test: jerk test. the jerk test is a physical examination maneuver used to detect posteroinferior instability of the glenohumeral joint. this test involves a sudden and forceful posteriorly directed force applied to the patient's arm while it is held in a position of abduction and external rotation.

Jerk Test Jerk Test Also Known As The Clunk Test Is Used To Check For The shoulder joint has a tremendous degree of mobility, which renders it prone to instability. while muscle forces control stability in mid ranges of motion, clinical instability presents itself at end range of motion (doukas et al. 2001). it is defined as abnormal motion of the humeral head on the glenoid, which presents as pain and or a sense. Shoulder orthopaedic test: jerk test. the jerk test is a physical examination maneuver used to detect posteroinferior instability of the glenohumeral joint. this test involves a sudden and forceful posteriorly directed force applied to the patient's arm while it is held in a position of abduction and external rotation.

Comments are closed.