Jean Piagets Theory Of Cognitive Development
Psychological Theories Jean Piaget S Theory Of Cognitive Development Jean piaget's theory of cognitive development suggests that children move through four different stages of learning. his theory focuses not only on understanding how children acquire knowledge, but also on understanding the nature of intelligence. piaget's stages are: sensorimotor stage: birth to 2 years. preoperational stage: ages 2 to 7. Piaget divided children’s cognitive development into four stages; each of the stages represents a new way of thinking and understanding the world. he called them (1) sensorimotor intelligence, (2) preoperational thinking, (3) concrete operational thinking, and (4) formal operational thinking. each stage is correlated with an age period of.

Piaget Operant Conditioning Cognitive Development Child Development On this staircase, piaget labeled four stages of cognitive growth that occurred at an approximate age in children. sensorimotor intelligence, from birth to age 2. preoperational thinking, from ages 2 to 7. concrete operational thinking, from ages 7 to 11. formal operational thinking, from age 11 on. Piaget's stages of development is a theory about how children learn and gain skills as they grow up, from birth to adulthood. jean piaget was a renowned psychologist and cognitive theorist in. The late swiss psychologist jean piaget was a major figure in the study of cognitive development theory in children. he believed that it occurs in four stages—sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. this article discusses piaget’s stages of cognitive development, including important concepts and principles. Jean piaget in ann arbor. piaget's theory of cognitive development, or his genetic epistemology, is a comprehensive theory about the nature and development of human intelligence. it was originated by the swiss developmental psychologist jean piaget (1896–1980). the theory deals with the nature of knowledge itself and how humans gradually come.

What Is Piaget S Theory Of Cognitive Development Jean Piaget Child The late swiss psychologist jean piaget was a major figure in the study of cognitive development theory in children. he believed that it occurs in four stages—sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. this article discusses piaget’s stages of cognitive development, including important concepts and principles. Jean piaget in ann arbor. piaget's theory of cognitive development, or his genetic epistemology, is a comprehensive theory about the nature and development of human intelligence. it was originated by the swiss developmental psychologist jean piaget (1896–1980). the theory deals with the nature of knowledge itself and how humans gradually come. 17 minute read. jean piaget, a swiss psychologist, is known for his theory of children’s cognitive development. his theory identified 4 stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. piaget’s work emphasized that children actively construct knowledge through interacting with their environment. Preoperational. concrete operational. formal operational. the goals of each stage are understanding: object permanence. symbolic thought. operational thought. grasping abstract concepts. piaget.

The Jean Piaget Stages Of Cognitive Development The Psychology Notes 17 minute read. jean piaget, a swiss psychologist, is known for his theory of children’s cognitive development. his theory identified 4 stages: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. piaget’s work emphasized that children actively construct knowledge through interacting with their environment. Preoperational. concrete operational. formal operational. the goals of each stage are understanding: object permanence. symbolic thought. operational thought. grasping abstract concepts. piaget.
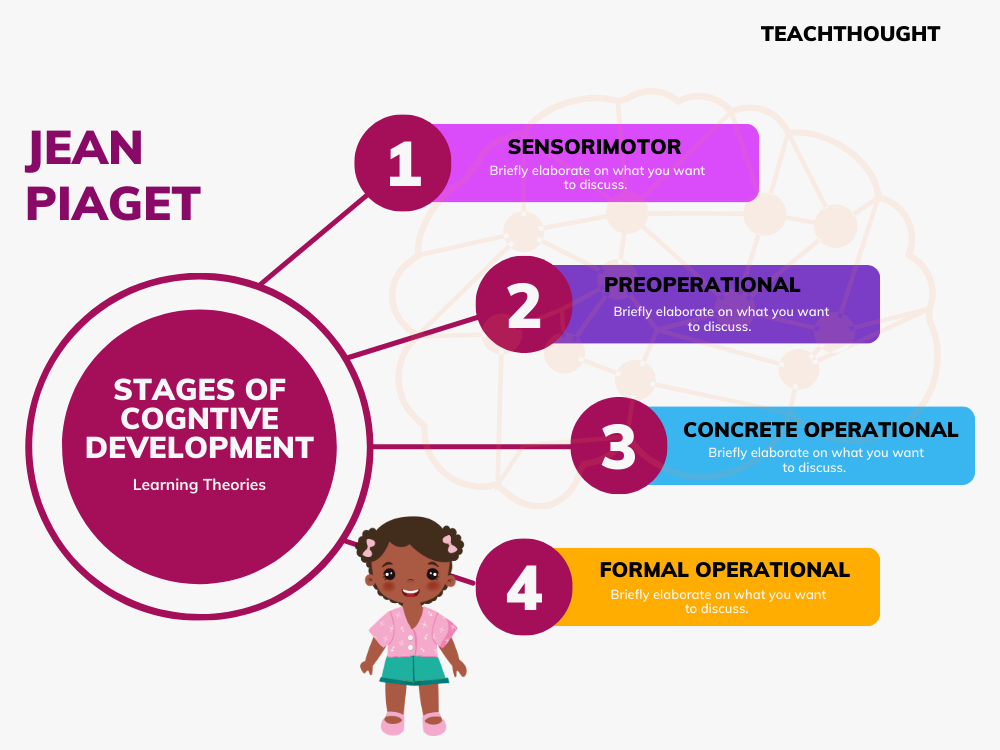
Piaget Learning Theory Stages Of Cognitive Development Reportwire

Comments are closed.