Jaw Fracture Facial Trauma
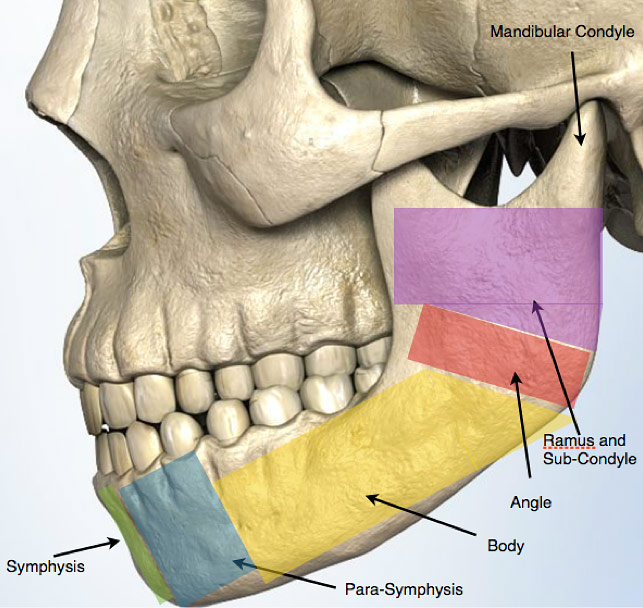
Jaw Fracture Facial Trauma Types of facial fractures. the most common facial fractures include: nasal fractures (broken nose). forehead fractures (broken frontal bone). orbital fractures (eye sockets). zygomatic fractures (cheekbones). tripod facial fracture (involving your eye socket, cheekbone and upper jaw). maxillary or mandibular fracture (broken jaw). The term jaw fracture often refers to a break of the lower jaw (mandible). fractures of the upper jaw (part of the bone called the maxilla) are sometimes called jaw fractures but are usually considered facial fractures. the mandible is most often broken as a result of blunt trauma, such as being punched or hit with a baseball bat or other object.
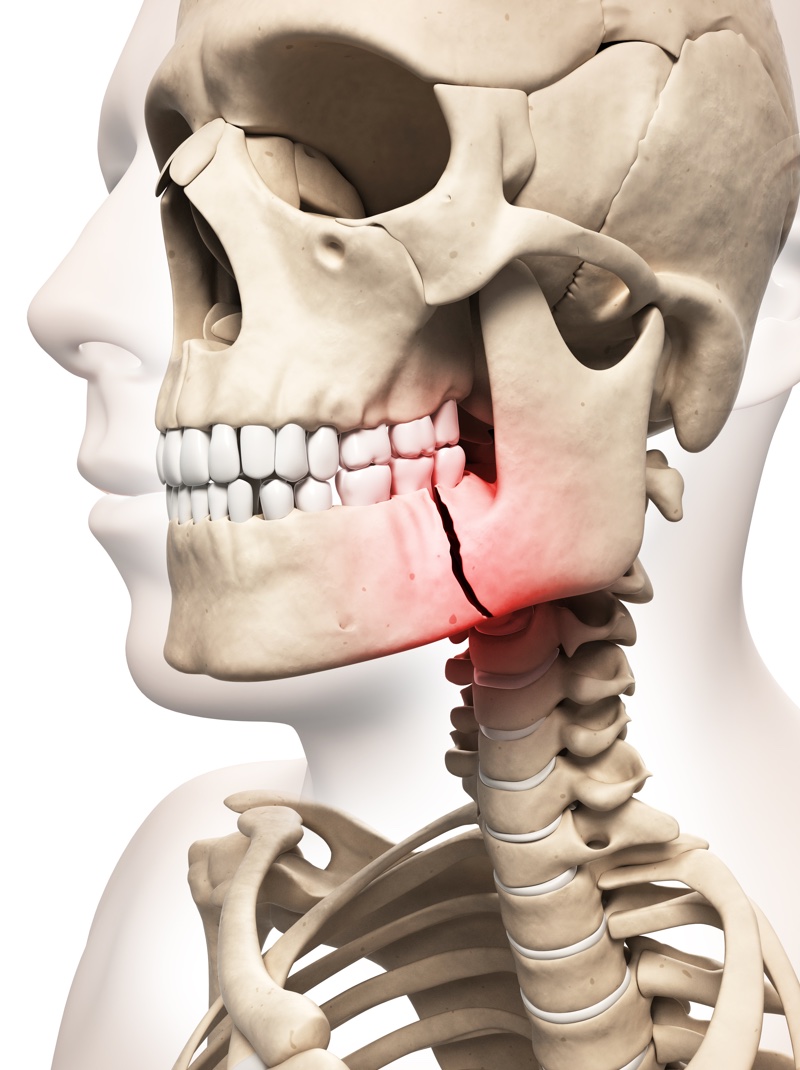
Facial Trauma Aspen Oral And Facial Surgery The basic anatomy, clinical manifestations, and acute management of facial trauma in adults will be reviewed here. eye injuries, pediatric facial trauma, and other aspects of facial trauma management are discussed separately. (see "open globe injuries: emergency evaluation and initial management" and "orbital fractures" and "retinal detachment. If you have a broken jaw, you also may notice that: your nose or mouth is bleeding. your jaw or cheek is bruised. your jaw or cheek is swollen. you have chipped or loose teeth or that teeth in your upper and lower jaws don’t match up when you close your mouth. you have trouble breathing. it hurts when you try to chew food or talk. Some fractures result in palpable instability. fractures of the mandibular condyle usually cause preauricular pain, swelling, and limited opening of the mouth (trismus). with a unilateral condylar fracture, the jaw deviates to the affected side when the mouth is opened. fractures of the midface, which includes the area from the superior orbital. Facial trauma is bone or soft tissue damage to the face caused by motor vehicle accidents, assaults (including gunshots), sports injuries, falls, chemical exposures, thermal burns or animal bites. because the human face is an intricate area containing many bones, blood vessels, nerves, muscles and sensory organs, if untreated, facial trauma may.
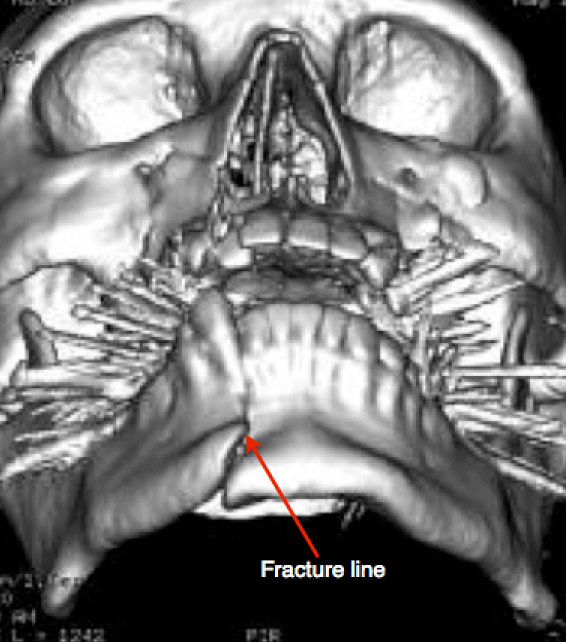
Jaw Fracture Facial Trauma Some fractures result in palpable instability. fractures of the mandibular condyle usually cause preauricular pain, swelling, and limited opening of the mouth (trismus). with a unilateral condylar fracture, the jaw deviates to the affected side when the mouth is opened. fractures of the midface, which includes the area from the superior orbital. Facial trauma is bone or soft tissue damage to the face caused by motor vehicle accidents, assaults (including gunshots), sports injuries, falls, chemical exposures, thermal burns or animal bites. because the human face is an intricate area containing many bones, blood vessels, nerves, muscles and sensory organs, if untreated, facial trauma may. Numbness in the forehead, eyelids, cheek, or upper lip teeth. swelling of the cheek or forehead. broken jaw. pain. bruising, swelling, or tenderness along the jaw or below the ear. inability to. A broken jaw (or mandible fracture) is a common facial injury. only the nose is broken more frequently. a broken jaw is the 10th most common fractured bone in the human body. fractures (breaks in the bone) are generally the result of a direct force or trauma to the jawbone (mandible).

Comments are closed.