Iupac Naming With Other Functional Groups
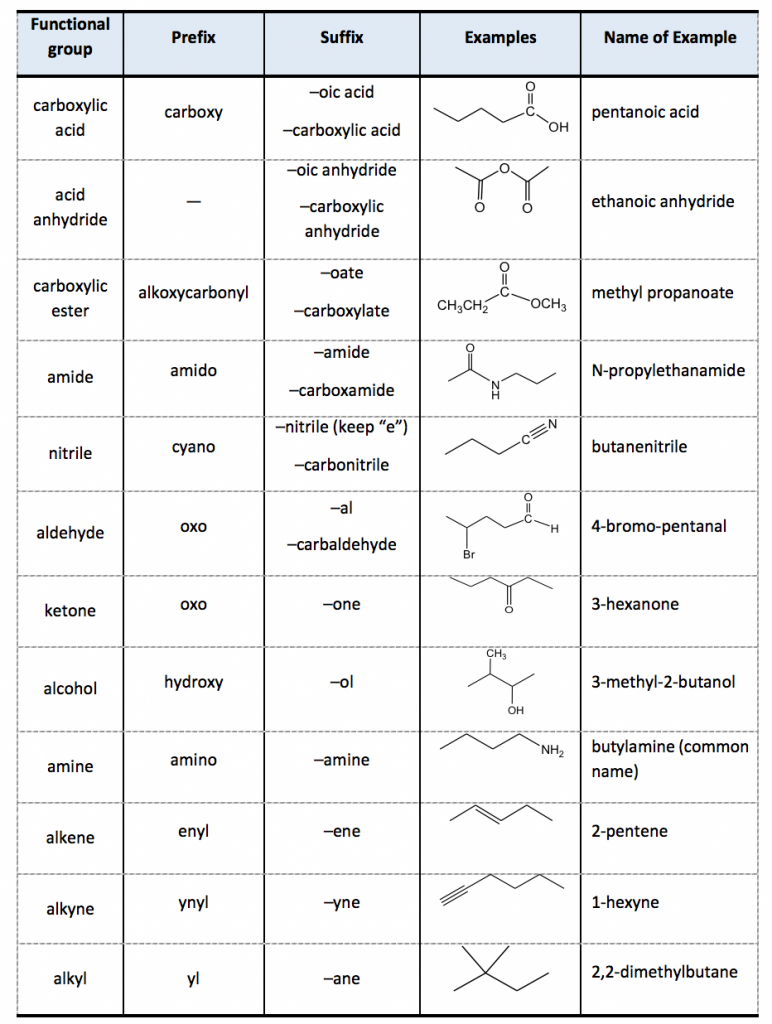
2 4 Iupac Naming Of Organic Compounds With Functional Groups The other groups are named as substituents by using the appropriate prefixes. assign stereochemistry, e z or r s, as necessary (details in chapter 5). for naming purposes, the functional groups are assigned with priorities (table 2.3). if the compound includes more than one functional groups, the one with the highest priority is the “parent. We need some kind of priority system for nomenclature. and so, iupac (think of the “ministry of magic”, but for chemists) has developed one. if you have a molecule with, say, a carboxylic acid and a ketone you consult the table. he functional group with the highest priority will be the one which gives its suffix to the name of the molecule.

Iupac Naming With Other Functional Groups Youtube Step 3. number the parent chain starting from the highest priority group and add the substituent (s) alphabetically: it is also noteworthy that if there is a functional group suffix and a substituent, the functional group suffix gets the lowest possible number. for example, alcohols have higher priority than amines and therefore, when naming a. 3. lowest sum rule. 4. alphabetical order rule (naming of substituents) 5. complex alkyl substituent rule. 6. multiple functional group rule. priority order of functional groups in iupac nomenclature. If other functional groups are present, the chain is numbered such that the aldehyde carbon is in the "1" position, unless functional groups of higher precedence are present. if a prefix form is required, "oxo " is used (as for ketones), with the position number indicating the end of a chain: choch 2 cooh is 3 oxopropanoic acid. Substitutive nomenclature is the main method for naming organic chemical compounds. it is used mainly for compounds of carbon and elements of groups 13–17. for naming purposes, a chemical compound is treated as a combination of a parent compound (section 5) and characteristic (functional) groups, one of which is.

Iupac Naming Of Organic Compounds With Functional Groups 57 Off If other functional groups are present, the chain is numbered such that the aldehyde carbon is in the "1" position, unless functional groups of higher precedence are present. if a prefix form is required, "oxo " is used (as for ketones), with the position number indicating the end of a chain: choch 2 cooh is 3 oxopropanoic acid. Substitutive nomenclature is the main method for naming organic chemical compounds. it is used mainly for compounds of carbon and elements of groups 13–17. for naming purposes, a chemical compound is treated as a combination of a parent compound (section 5) and characteristic (functional) groups, one of which is. All the structures can be manipulated using jmol. this priority order is important in nomenclature as the higher priority group is the principle functional group and it is typically numbered such that is has the lowest number (the locant). you need to learn to recognise these functional groups not just for nomenclature but in order to recognise. The iupac system of nomenclature is a universally recognized method for naming organic chemical compounds. the goal of the system is to provide each organic compound with a unique and unambiguous name based on its chemical formula and structure. the name of any organic compound consists of three essential parts: the root word, prefix, and.

Comments are closed.